Correct design of a heating system is to take into account all possible factors influencing its efficiency efficiency. In addition to the correct selection of the main components, boiler, radiators, safety groups, the cross-section of the lines should be correctly calculated. To do this, you need to know the optimal diameter of the heating pipes: how to choose the right one and calculate it yourself?
- Difficulties in choosing the diameter of heating pipes
- The procedure for calculating the cross-section of heat supply lines
- Determination of the heat output of the system
- Water velocity in pipes
- Calculation of the heating manifold and mounting sleeves
- Additional data for calculating the diameter of heating pipes
- Heating pipe material
Difficulties in choosing the diameter of heating pipes
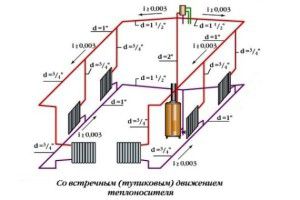
It would seem that the choice of the diameter of pipes for heating a private house is not a difficult task. They must only ensure the delivery of the coolant from the source of its heating to the heating devices - radiators, batteries.
But in practice, an incorrectly selected diameter of the heating collector or supply pipe can lead to a significant deterioration in the operation of the entire system. This is due to the processes that occur during the movement of water along the highways. To do this, you need to know the basics of physics and hydrodynamics. In order not to go into the jungle of accurate calculations, you can determine the main characteristics of heating, which directly depend on the cross-section of the pipelines:
- Coolant movement speed... It affects not only the increase in noise during the operation of heat supply, but is also needed for optimal heat distribution among heating devices. Simply, the water should not have time to cool down to the minimum level when it reaches the last radiator in the system;
- Coolant volume... So, the diameter of pipes with natural circulation of heating should be large in order to reduce losses during friction of the liquid against the inner surface of the line. However, along with this, the volume of the coolant increases, which entails an increase in the cost of heating it;
- Hydraulic losses... If different diameters of plastic pipes for heating are used in the system, then a pressure difference at their junction will inevitably arise, which will lead to an increase in hydraulic losses.
How to choose the diameter of the pipe for heating, so that after installation you do not have to redo the entire heating system due to extremely low efficiency? First of all, you should perform the correct calculation of the cross-section of the highways. To do this, it is recommended to use special programs and, if desired, manually check the result yourself.
At the junction, the diameters of polypropylene pipes for heating are reduced due to overlap. Reducing the cross-section depends on the degree of heating during soldering and compliance with the installation technology.
The procedure for calculating the cross-section of heat supply lines
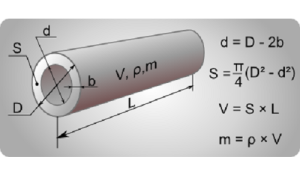
Before calculating the diameter of the heating pipe, it is necessary to determine their basic geometric parameters. To do this, you need to know the main characteristics of the highways. These include not only performance, but also dimensions.
Each manufacturer indicates the value of the pipe section - diameter. But in fact, it depends on the wall thickness and the material of manufacture. Before purchasing a certain model of pipelines, you need to know the following features of the designation of geometric dimensions:
- The calculation of the diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating is done taking into account the fact that manufacturers indicate the external dimensions.To calculate the useful section, it is necessary to subtract two wall thicknesses;
- Internal dimensions are given for steel and copper pipes.
Knowing these features, you can calculate the diameter of the heating collector, pipes and other components for installation.
When choosing polymer heating pipes, it is imperative to clarify the presence of a reinforcing layer in the structure. Without it, when exposed to hot water, the line will not have the proper rigidity.
Determination of the heat output of the system
How to choose the right pipe diameter for heating and should it be done without calculated data? For a small heating system, complex calculations can be dispensed with. It is only important to know the following rules:
- The optimum diameter of pipes with natural circulation of heating should be from 30 to 40 mm;
- For a closed system with forced movement of the coolant, smaller pipes should be used to create optimal pressure and water flow rate.
For an accurate calculation, it is recommended to use a program for calculating the diameter of heating pipes. If they are not there, you can use approximate calculations. First you need to find the thermal capacity of the system. To do this, you need to use the following formula:
Q = (V * Δt * K) 860
Where Q - calculated thermal power of heating, kW / h,V - the volume of the room (house), m³,Δt - the difference between temperatures outside and indoors, ° С,TO - the estimated coefficient of heat loss at home,860 - the value for converting the obtained values into an acceptable kW / h format.
The greatest difficulties in the preliminary calculation of the diameter of plastic pipes for heating are caused by the correction factor K. It depends on the thermal insulation of the house. It is best taken from the data in the table.
| Coefficient K | The degree of thermal insulation of the building |
| 3-4 | Minimum thermal insulation |
| 2-2,9 | The minimum insulation of the facade is brick cladding. |
| 1-1,9 | Average level of thermal insulation |
| 0,6-0,9 | High-quality insulation of the house, modern windows and doors are installed |
As an example of calculating the diameters of polypropylene pipes for heating, you can calculate the required heat output of a room with a total volume of 47 m³. At the same time, the temperature outside will be -23 ° С, and indoors - + 20 ° С. Accordingly, the difference Δt will be 43 ° C. We take the correction factor equal to 1.1. Then the required thermal power is.
Q = (47 * 43 * 1.1) /860=2.585 kWh
The next step in choosing the diameter of the pipe for heating is to determine the optimal speed of movement of the coolant.
The presented calculations do not take into account the correction for the roughness of the inner surface of the highways.
Water velocity in pipes
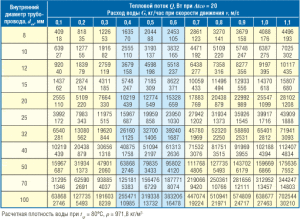
The optimal pressure of the coolant in the mains is necessary for the uniform distribution of heat energy over the radiators and batteries. For the correct selection of the diameters of heating pipes, the optimal values of the speed of water advance in the pipelines should be taken.
It is worth remembering that when the intensity of movement of the coolant is exceeded, extraneous noise may occur in the system. Therefore, this value should be between 0.36 and 0.7 m / s. If the parameter is less, additional heat losses will inevitably occur. If it is exceeded, construction noises will appear in pipelines and radiators.
For the final calculation of the diameter of the heating pipe, use the data from the table below.
Substituting into the formula for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe into the previously obtained values, you can determine that the optimal pipe diameter for a particular room will be 12 mm. This is just a rough estimate. In practice, experts recommend adding 10-15% to the obtained values. This is because the formula for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe may change due to the addition of new components to the system.
For an accurate calculation, you will need a special program to calculate the diameter of heating pipes.Such software packages can be downloaded in a demo version with limited calculation capabilities.
Calculation of the heating manifold and mounting sleeves

The above calculation technology can be applied to all types of heat supply - one-pipe, two-pipe and collector. However, for the latter, it is necessary to make the correct calculation of the diameter of the heating collector.
This heating element is necessary to distribute the coolant over several circuits. In this case, the calculation of the correct diameter of the heating collector is inextricably linked with the calculation of the optimal cross-section of the pipeline. This is the next stage in the design of a heat supply system.
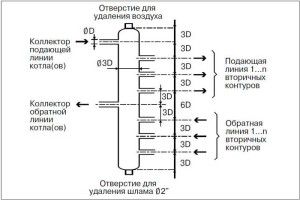
To calculate the diameter of the heating manifold, you must first calculate the cross-section of the pipes according to the above scheme. Then you can use a fairly simple formula:
M0 = M1 + M2 + M3 + M4
Where M0 - the required collector diameter,M1, M2, M3, М4 - diameters of connected pipelines.
When determining the height and the optimal distance between the nozzles, the principle of "three diameters" is applied. According to him, the distance of pipes on the structure should be 6 radii each. The total diameter of the heating manifold is also equal to this value.

But in addition to this component of the system, it is often necessary to use additional ones. How to find out the diameter of the heating pipe sleeve? Only after performing a preliminary calculation of the cross-section of the highways. In addition, you need to take into account the thickness of the walls and the material of their manufacture. The design of the sleeve and the degree of its thermal insulation will depend on this.
The value of the diameter of the sleeve for heating pipes is affected by the material of manufacture of the wall, as well as the pipe. It is important to consider the possible degree of expansion when the surface is heated. If the diameters of the plastic heat supply pipes are 20 mm, then the same parameter for the sleeve must be at least 24 mm.
The installation of the liner must be done on cement mortar or a similar non-combustible material.
Additional data for calculating the diameter of heating pipes
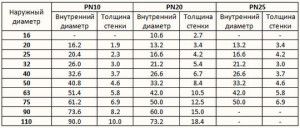
After choosing the diameter of pipes for heating a private house, you need to choose the right material for their manufacture, and also take into account the features of the heating system. This parameter is influenced by the layout of the highways, as well as the number of shut-off and control valves.
In addition to knowing the diameter of pipes in heating with natural circulation, it is necessary to take into account the height of the booster riser and correctly select the size of its section. It should be at a minimum height of 1.5 relative to other heating elements. To increase the speed of movement of the coolant, the diameter of the polypropylene pipes used in the construction of the boost manifold must be one size larger than that of the main line.
It is also important to consider the wall thickness of the pipelines. It depends on the material of manufacture and can vary from 0.5 mm (steel) to 5 mm (plastic). The choice of the diameter of pipes for the heating system of a private house is influenced by the material of manufacture. So, plastic lines are recommended to be installed for systems with forced circulation. Their inner diameter can vary from 10 to 30 mm. More information about the wall thickness of polymer pipes for heating can be found in the data in the table.
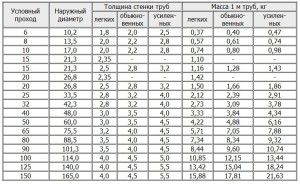
For steel models, it is necessary to take into account not only their geometric dimensions, but also their mass. It directly depends on the wall thickness. In programs for calculating the diameter of heating pipes, there must be a function for calculating the specific gravity of 1 lm. steel line.
Knowing these additional characteristics, you can make the most accurate calculation of the parameters of the heating system, including the correct selection of heating pipe diameters.
If there is a need to calculate only the cross-section of heat-conducting lines, you can use free demo versions of professional programs.
Heating pipe material

In addition to the correct choice of pipe diameters for heat supply, you need to know the characteristics of their material of manufacture. This will affect the heat loss of the system, as well as the laboriousness of the installation.
It should be remembered that the calculation of the diameters of heating pipes is carried out only after the choice of the material for their manufacture. Currently, several types of pipelines are used to complete heat supply systems:
- Polymer... They are made from PP or XLPE. The difference lies in the additional components added during the production process. After calculating the diameter of polypropylene pipes for heat supply, you need to correctly select the thickness of their wall. It varies from 1.8 to 3 mm, depending on the parameters of the maximum pressure in the lines;
- Steel... Until recently, this was the most common option for arranging heating. Despite their more than good strength characteristics, steel pipes have a number of significant disadvantages - complex installation, gradual surface rusting and increased roughness. Alternatively, stainless steel pipes can be used. One of their cost is an order of magnitude higher than "black" ones;
- Copper... In terms of technical and operational characteristics, copper pipelines are the best option. They are characterized by sufficient elongation, i.e. if water freezes in them, the pipe will expand for some time without loss of tightness. The disadvantage is the high cost.
In addition to the correctly selected and calculated pipe diameter, you need to decide on the method of their connection. It also depends on the material of manufacture. For polymer, a sleeve connection is used by welding or on an adhesive basis (very rarely). Steel pipelines are installed using arc welding (best quality connections) or threaded method.
In the video, you can see an example of calculating the diameter of pipes depending on the optimal flow rate of the coolant:








