When choosing reliable in operation and easy-to-use radiators, the main attention is paid to their efficiency. Among the proposed designs stand out the currently popular vertical radiators, which are noticeably different from the horizontally placed models. Before purchasing heat engineering products of this class, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with their design.
Design features

The main difference between vertical batteries and horizontal products is their non-standard dimensions, according to which the width of the radiator is less than its height.
If conventional batteries are traditionally installed in a niche under windows, then their vertical counterparts can be placed on the walls in any convenient place in the apartment. They are allowed to be mounted in free niches, openings of rooms or in rooms where there are no windows at all. In terms of basic parameters, wall-mounted radiators do not differ significantly from horizontal models, since they are made of the same materials. These are traditional cast iron, as well as the following common metals:
- steel;
- rolled aluminum;
- combination of steel and aluminum.
In addition, they are the same in their design and can be sectional, panel, and tubular. By the way they are connected to the central heating system, they are divided into diagonal, side and bottom connection products.
The difference between vertical radiators and conventional models is the original design, which combines a wide variety of colors and shapes. This advantage allows them to be installed even in the front corners of a modern apartment.
In what cases are applied

Taking into account the peculiarities of vertical type heating devices, it is preferable to use them in the following cases:
- it is required to save on the occupied space in small rooms (including loggias combined with the room);
- it is necessary to heat areas with panoramic glazing that occupies the wall from floor to ceiling;
- in rooms completely devoid of windows: in bathrooms, hallways or in small dressing rooms.
In addition, they can be used as a decorative element of the interior when arranging a living space.
It is important to take into account situations when a wall-mounted vertical radiator is not suitable for installation and operation in specific conditions:
- the owners plan to mount radiators on the walls (interior partitions) of plasterboard blanks without additional reinforcement;
- with insufficiently insulated external walls;
- in low rooms, the small volume of which makes it difficult for air convection.
In most situations, vertical radiators are purchased with the aim of creating a unique design in the house, despite the significant costs of purchasing them.
Advantages and disadvantages

Among the advantages of high heating batteries are the following:
- saving living space in the room, which is explained by the small dimensions of the heating device;
- increased heat transfer associated with a significant area of the heat-emitting surface;
- the possibility of using not only for its intended purpose: as a basis for drying towels, for example, a hanger or an original frame for a mirror;
- the admissibility of operating the battery while decorating the surrounding spaces;
- the ability to do without decorative grilles.
The undoubted advantage of relatively high radiators is their ease of installation, as well as the subsequent maintenance.

The disadvantages of vertical radiators are:
- relatively low heat transfer due to uneven heating of the upper and lower parts of the device;
- the need to prepare a reliable base for fastening - this is due to the significant weight of the heating structure;
- the need for insulation of the outer wall on which the radiator itself is installed;
- difficulties with installing batteries with lateral (diagonal) connections.
The latter inconvenience is explained by the need for covert laying of pipes, which otherwise noticeably spoil the appearance of the heated premises.
The disadvantages of heating systems of this type also include some difficulties with the control of the air bleed valve and the relatively high cost.
Material selection
The main feature that allows you to classify vertical radiators is the source material from which each of the products under consideration is made. In accordance with this criterion, they are:
- cast iron or steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic;
- based on copper and plastic (extremely rare).
Cast iron batteries

Cast iron heating batteries belong to the classic models, widespread in past centuries. They are still in demand among the consumer, which is explained by their following advantages:
- product strength;
- relatively low price;
- durability.
On the other hand, this material has a number of significant drawbacks that forced manufacturers to master the production of modern samples based on more "advanced" materials:
- the difficulty of installation due to the significant weight of the mounted systems;
- fragility of cast iron material, inability to withstand shock loads;
- low thermal conductivity, forcing artificially to raise the temperature of the coolant.
If you need to heat cast-iron batteries to 45 degrees, the water temperature in them will have to be raised to 70 degrees. As a result, there is an overexpenditure of energy resources, which is especially noticeable during the heating season in private suburban buildings. Therefore, for a private consumer, the problem of saving is decisive when choosing a material for a heating device.
Aluminum products

A vertical tubular radiator based on aluminum looks much more attractive than cast iron samples of the same class. In addition, the thermal conductivity of such heating elements is much higher.
Before buying aluminum batteries for a private house, you should take into account that they are sensitive to the quality of the coolant water. If the supplied fluid is heavily contaminated, and there are no filters at the inlet of the system, it is undesirable to use them in private houses. Without special cleaning of the carrier, aluminum radiators will quickly fail. On the other hand, the installation of filter elements will require additional costs. Their disadvantages also include the inability to operate at elevated water pressure.
Steel radiators

Steel radiators are a typical example of "advanced" heating systems, which have two different designs: tubular and panel. The last option is positioned as a budget one and is somewhat inferior to tubular products in terms of heat transfer.On the other hand, such radiators are unpretentious in operation and are in demand in private houses where additional filtration of the coolant is not provided.
Unlike panel samples, tubular steel batteries are classified as elite models with the following advantages:
- high level of heat transfer;
- profitability;
- attractive design;
- durability (the service life declared by the manufacturer is about 25 years).
Due to their attractiveness, tubular radiators are often used as an element of decorative decoration for living quarters.
Among the models of this class, steam heating batteries made of stainless steel stand out.
Steel batteries in comparison with products made from other materials have an undoubted advantage, since their heat transfer is much higher.
Bimetallic radiators

Bimetallic radiators stand out in a separate group, which are a worthy choice for any living space. They are made from two metals. They use steel pipes as a supporting base, on which aluminum fins are attached on top.
Combined radiators have a number of advantages:
- Long service life - according to the manufacturer's statement, they reach 30 years.
- A high-carbon steel core that gives the bimetallic radiator the required strength.
- High level of heat transfer - up to 190 W per section.
- A wide selection of items that differ in their designs and colors.
The standard set includes a temperature controller that allows you to change the heat transfer over a wide range.
Disadvantages of combined products:
- direct contact of two metals with different coefficients of expansion leads to the appearance of extraneous sounds during the operation of a bimetallic radiator;
- small sizes of the inlet and outlet pipes often cause blockages, especially if there is a large amount of foreign particles in the coolant.
- the need to install a filter element at the inlet.
The relative disadvantages of these radiators include their high cost.
Features of individual connection types
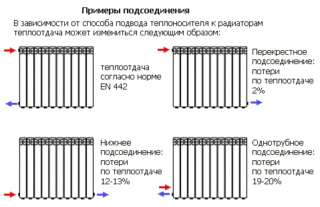
With a side connection, the number of connection methods, especially in the case of two-pipe distribution, increases. The following options appear:
- diagonal connection;
- one-way connection;
- saddle switching.
The first of these methods is considered the most suitable in terms of the efficiency of the heating system. All other connection options do not guarantee the desired level of heat transfer.








