Increased attention is always paid to the issues of thermal insulation of residential buildings. The industry has mastered the production of various samples of protective materials that meet the requirements of current standards. Among them, a special place is occupied by modern compositions called "liquid thermal insulation", with the features of the application of which it is desirable to familiarize yourself in more detail.
Varieties of liquid thermal insulation

On the domestic market, there are several varieties of liquid heaters that have a different basis and differ in application technology. This category includes the following materials:
- liquid ceramic insulation;
- expanded polystyrene or penoizol;
- sprayed ecowool.
Each of the listed liquid heat insulators is suitable for specific conditions of work and has its own specifics.
When choosing this category of insulation for a residential building, it is important to understand that they are united by the possibility of mechanized application to protected surfaces.
The first of these varieties is presented on the market by a number of well-known positions, which include "Akterm", "Corundum" and "Bronya". The second type includes Teploizol, which has already gained popularity, and a special composition, Teplo Plus. When using these means, it is possible to close large areas at high speed.
Rapid spray capability is one of the merits of this category of liquid thermal insulation. However, it should be remembered that to carry out such work, you will have to invite professionals with special equipment, which significantly increases operating costs.
Sprayed ecowool for outdoor and indoor use is made on the basis of:
- printing waste that remains unused in the production of magazines and books;
- corrugated or ordinary cardboard packaging waste;
- secondary raw materials (waste paper), which include newspapers, magazines, old books and the like.
Liquid heaters have clear advantages over sheet protective materials.
Pros and cons
- the ability to apply on surfaces with complex relief;
- resistance to climatic factors;
- high processing speed of protected surfaces;
- obtaining a monolithic coating that does not have unwanted joints.
The possibility of application without changing the configuration of the facade of buildings eliminates the need to coordinate this procedure with the relevant supervisory authorities. The good adhesion properties of liquid insulators make it possible to do without careful preparation of the surface for their spraying.
Among the shortcomings, the following technical difficulties stand out:
- at the slightest violation of the rules for storing and transporting the liquid mixture, a premature loss of the declared qualities of the insulation is possible;
- relatively short service life in comparison with traditional insulation materials;
- the high cost of foam heat insulators, which cannot be applied without the involvement of builders and special equipment or mechanisms.
It is possible to minimize costs if a preliminary survey of the treated areas is carried out and the optimal application method is selected.
Scope of use
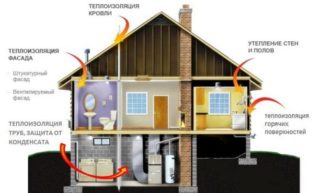
The liquid state allows the use of heaters of this type when carrying out the following special work:
- thermal insulation of walls and floors;
- insulation of ceilings and roofing elements;
- protective treatment of highways and individual pipelines of various profiles, as well as steam pipelines and air ducts in air conditioning systems;
- thermal insulation of window and door openings in the apartment;
- protection of freezing systems (here they are used to insulate refrigerators, thermo boxes and trailers).
One of the most common applications for liquid coatings is the insulation of existing cold water supply lines. After processing with these materials, the likelihood of corrosion on metal pipes is sharply reduced.
Thermal insulation for the floor
The choice of a particular brand of thermal insulation is determined by the type of flooring and its current state.
For walls and ceilings
Liquid insulation for walls is presented on the market in the following positions:
- polyurethane foam;
- penoizol;
- liquid mixture in compact cylinders.
For spraying liquid thermal insulation to cover walls from the inside and outside, special equipment is used, which mixes the components of the polyurethane composition, and then delivers it to the surfaces to be treated. Suitable materials and method of applying insulation for the ceiling are the same.
How to choose a liquid insulation

Before choosing a certain type of coating thermal insulation, it is first of all important to determine the nature of the insulated surface. If it is required to insulate the internal elements of the structure, a specially designed liquid material is selected ("Astratek Universal" or "Actorm Standard"). For the treatment of surfaces located outside the building, special mixtures of the "Facade" type are traditionally used. Regardless of the place of application, it is advisable to consult with a specialist before purchasing and carefully study the instructions for using the insulation. It is also recommended to check its quality by external signs: consistency, color and absence of impurities. The Magniterma mixture, for example, must meet the following requirements:
- a high-quality product looks like a homogeneous mass, there are no clots and foreign fragments in it;
- the color of the overwhelming majority of classic liquid heaters is milky white;
- the density is not very high, which can be checked by the weight of the container with the mixture (it is usually lighter than water).
If there are noticeable deviations in at least one of these signs, it is better to refuse this offer and look for another option.
Application features

Most types of liquid thermal insulation do not require special skills or expensive equipment to apply. The exception is liquid foam and penoizol. For work, it is necessary to prepare a roller, which can be replaced with a brush or spray. When using a rolling tool, you will need to prepare a container that allows you to evenly distribute the mixture over its working surface.
The process of applying insulation itself is reduced to the following sequence of actions:
- The surface to be treated is cleaned of dirt and excess solution, after which it is swept with a brush and washed with clean water.
- The purchased composition is diluted to the desired consistency (according to the instructions) and poured into a container of a suitable volume.
- The roller is dipped into a container with the working mixture and rolled out on a special platform until the coating is completely saturated.
- Next, you should carefully roll the absorbed composition over the surface, without trying to press hard on it.
The first layer of insulation is applied from the bottom up. All subsequent ones are rolled after its complete "solidification" (polymerization), which occurs in about 24 hours.













