One of the interesting and practical types of building material is aerated concrete. Includes tiny air-filled pores. This option has less weight and low thermal conductivity compared to dense concrete and stone.
What is autoclaved concrete and how does it differ from non-autoclaved
An initial mixture is prepared and a blowing agent is added to it. The latter reacts with the components of the mixture and fills the mass with bubbles of the evolved gas. The bubble size and distribution depends on the nature of the gas. The smaller the pores and the more uniform, the higher and more uniform the quality of the material.
The base is Portland cement, lime and quartz sand... For gas silicates, they take aluminum powder or paste... When interacting with lime, hydrogen is released. The latter forms many bubbles. The volume reaches 80% from the volume of the material, so that the autoclave foam block is distinguished by lightness and low thermal conductivity. Air is the best heat-saving agent.
With the general method of obtaining a porous material, the manufacturing technology affects its characteristics. Distinguish non-autoclave and autoclave method production. In the first case, the mass is loaded into molds and dried. In the second the material is processed with steam under pressure in a special unit - an autoclave... Then he gets where high density and hardness compared to non-autoclaved concrete.
Non-autoclave produce according to a simplified scheme: the original mixture is kneaded, poured into molds, dried and taken out.
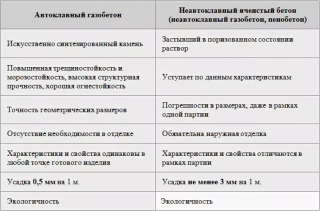
- Steam treated material does not shrink... For AB blocks, it is 10 times less than that of NB. So gas silicate buildings can be finished immediately after construction.
- Under the influence of pressure and temperature, more chemical reactions occur in the thickness, therefore AB stronger.
- The solidified mass is cut into blocks after complete drying. This allows you to get a brick perfectly accurate dimensions and shape, which greatly simplifies the laying. The dimensions and configuration of the NB are provided by the shape, so they are not as accurate.
- When autoclaving bubbles hydrogen in the mass are distributed more evenly... The block turns out to be homogeneous in properties.
- A disadvantage due to the same feature is open pores. With high hardness and strength, the gas block strongly absorbs water. However, this does not significantly affect the durability of the material, since it easily gives off moisture. HA block hardens in forms, therefore the pores in it are closed. The hygroscopicity of non-autoclave blocks is noticeably lower.
The high cost is also a consequence of the difference in the method of obtaining. Non-autoclaved concrete is cheaper, but takes longer to manufacture.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
- The use of a gas block facilitates construction. You can build a house yourself.
- Large dimensions significantly simplify laying and increase construction speed.
- The porous material retains heat much better. The thermal conductivity of gas silicate is 0.1–0.28 W / sq. m, which is lower than that of a clay brick or even a hollow brick. Foam concrete walls are much warmer. However, this characteristic depends on the density of the stone. The higher the density, the fewer pores in the block and the worse it retains heat.
- Aerated concrete copes with the task of removing excess moisture from the room and is slightly inferior to a wooden beam.
- The material does not burn and does not support combustion.
- Gas silicate can be placed on a very thin layer of glue rather than on a mortar. At the same time, the docking is so tight that the appearance of cold bridges is excluded.
Disadvantages associated with porosity blocks:
- The compressive strength of the material is 2-3 times lower than that of bricks, so the material is suitable for the construction of 3-, maximum 5-storey buildings.
- With high thermal conductivity, frost resistance is very average - a maximum of 35 freezing cycles. Despite the thermal insulation qualities, the material is not used in the north.
- When forming aerated concrete, the mass forms a single block with a closed surface. But then this mass is cut into separate bricks, opening the pores. And open pores absorb moisture - up to 47%. The material is capable of giving off moisture and quite quickly. However, the walls still need to be protected with plaster.
- The material does not hold the fasteners well. To hang shelves or a TV on the wall, you have to use very long screws and dowels.

Types and scope of application
Autoclaved aerated concrete blocks are used for the most part in private construction... This is due to the relatively small bearing capacity.
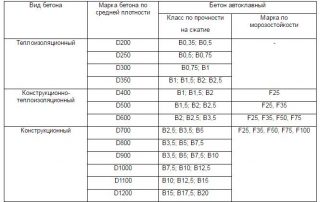
The use of aerated concrete depends on its density. This parameter is distinguished 3 types.
- Structural - with a density of up to 1200 kg / cu. m. The material is used for the construction of load-bearing structures: building walls, capital partitions.
- Structural and thermal insulation - with a density of 500 to 100 kg / cu. m. Combines medium strength and higher heat capacity. They are used for the construction of partitions.
- Heat insulating - 300-500 kg / cubic meter m. Quite fragile due to low density, therefore they are used for the construction of only one-story buildings, usually non-residential. In large buildings, the material is used for wall insulation.

Autoclaved aerated concrete production
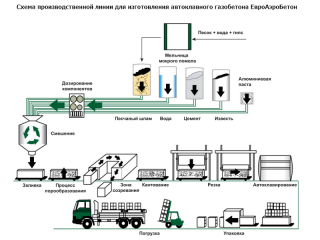
- Preparation of raw materials - sand is sieved, quicklime is divided into fractions, finely crushed. It is not uncommon for sand and lime to be homogenized together in a ball mill.
- Preparation of the mixture - Portland cement, sand sludge, lime, cuttings sludge and aluminum powder in the form of a suspension are dosed and mixed. In mixers, the composition is brought to a homogeneous state.
- Shaping arrays - the mixture is loaded into a mold, where swelling occurs. The process is considered complete when the swelling reaches its maximum height and vigorous gas evolution stops.
- Material cut into blocks using a cutting machine.
- Zloaded into autoclave... Here the mass is treated with superheated steam at a temperature of 190 ° C and a pressure of up to 12 atm.Products are gaining strength.
- Pallets with ready-made blocks cool naturally... Then the material is cleaned, packaged and labeled on an automatic line.
Material is stored in a warehouse on pallets. It is transported by regular freight transport, in which it is possible to secure the packages.
Features of autoclaved aerated concrete masonry
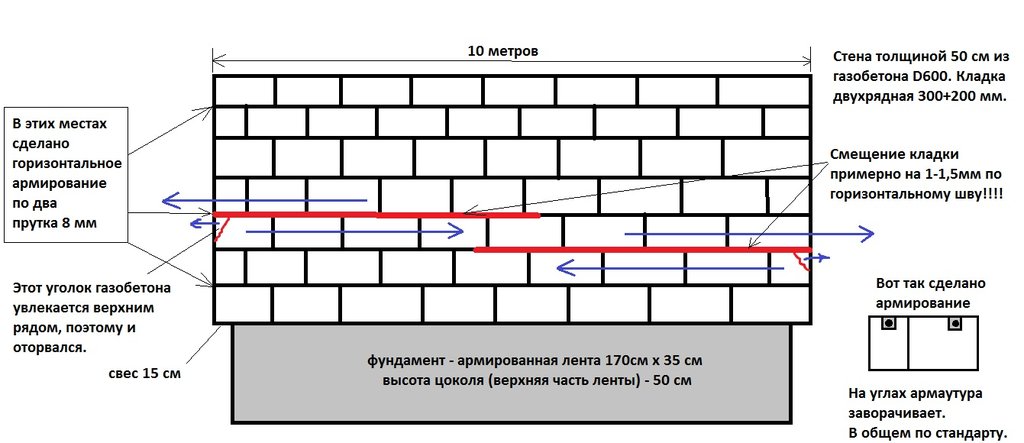
The high accuracy of dimensions and configuration leads to some construction features from this material.
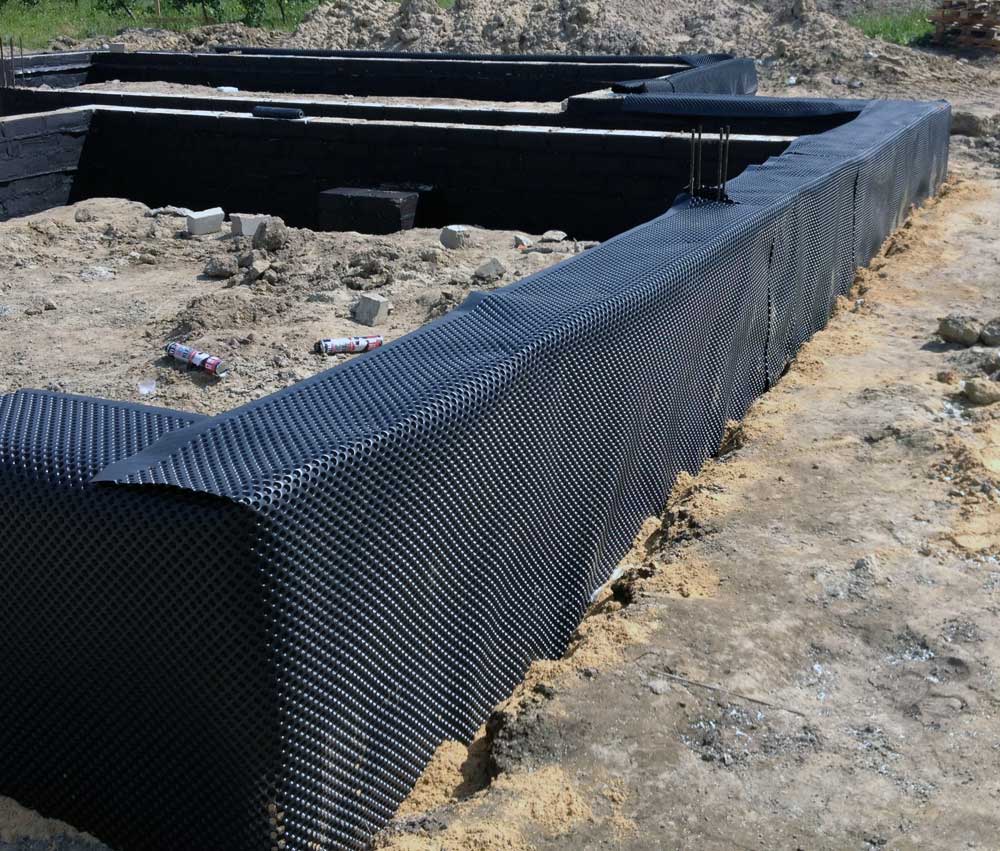
- Foundation under masonry it is necessary thoroughly waterproof... Aerated concrete easily absorbs water and, with insufficient insulation, will draw moisture from the basement floor.
- First row laid on a cement mortar.
- Aerated concrete blocks are large in size. Evenness and correctness of the masonry check very carefully: mandatory in corners and optionally in a row. After laying, the entire row is adjusted.
- Put blocks on glue... This allows the joint thickness to be reduced to a minimum - up to 0.5–3 mm. Such a wall does not let the cold through.
- Each 4th row produces reinforcement... For the rods, grooves are made in the stone.
- Before overlap or roof, be sure to equip reinforced belt.