Bitumen is a multifunctional material used in a wide variety of jobs. Materials impregnated with this substance are absolutely insensitive to the action of water, steam and moisture. This property is the most popular among the characteristics of bitumen.
The history of the origin of bitumen
In a more civilized era in Mesopotamia bitumen was used as a glue in mosaics. Areology believe that at the same time the material began to be used for waterproofing... Mesopotamia exported it to other countries.
Natural and artificial bitumen is widely used today. It part of asphalt and was used in the construction of all existing roads. Compositions of different types are used for any waterproofing work: when building foundations, erecting walls, roofing. Hard material modifications are used in the electrical and foundry industries.
Bitumen is extracted from bituminous rocks. Its production is up to 115 million tons per year. No less volume is created by an artificial version obtained by processing oil, shale, and coal.
Main properties and characteristics
This varied blend of carbohydrates provides a wide variety of physical and chemical properties of the mixture... The most interesting from the user's point of view are the following.
- Density bitumen - ranges from 0.95 to 1.50 g / cm³ depending on the origin and type.
- Thermal conductivity typical for amorphous substances - 0.5-0.6 W / m * K. The heat capacity is 1.8–1.97 kJ / kg • ° С. It cannot be used as a heat-insulating material, however, it helps to retain heat as part of a building structure.
- One of the main properties of the composition - amorphousness... Being solid, it exhibits the properties of a liquid. When heated, it becomes liquid, it can be wetted and impregnated with solid surfaces. When cooled, it solidifies. The process is accompanied by polymerization, so objects moistened with it stick together very firmly.
- Melting temperature bitumen depends on the composition, ranges from +160 to + 200 ° C. The process takes place gradually.
- The material is dielectric and can be used in the arrangement of insulation.
- Bitumen does not interact with water and does not dissolve in it... When cured, it forms an impermeable, non-porous layer.
- Resistant to most acids, alkalis and saline solutions, but not resistant to organic solvents like gasoline, acetone, benzene. Bitumen impregnation makes concrete, steel pipes, reinforced concrete structures resistant to a chemically aggressive environment.
- Bitumen is characterized by such a phenomenon as aging... Under the influence of sunlight and oxygen from the air, the material gradually changes its composition.The content of resins and oils decreases, hydrophobicity and elasticity decrease.
Physical and chemical properties of bitumen largely depend on its composition. It is important to pay attention to the brand of the substance and take into account its characteristics when choosing.
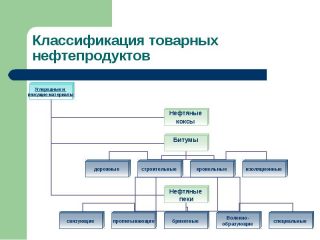
Classification
- building - BN, used for waterproofing, mastic, as a raw material for the manufacture of other materials;
- roofing - BNK, used for the production of soft roofing materials, like ondulin, shingles;
- road - BND, used in the laying and production of asphalt concrete.
The main classification is related to the origin of the material. There are 2 large groups.
- clean bitumen - with a share of mineral impurities not exceeding 10%;
- asphalt rocks - dolomites, limestones containing the substance;
- asphaltites - high-melting bitumen;
- asphalt - a mixture of asphalt material and minerals.
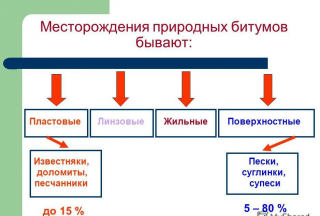
- reservoir - included in the composition of the rock and developed by the mine or open-pit method;
- superficial - bitumen exit to the surface, most often these are not very pure mixtures;
- vein - pure mixtures with a small amount of impurities.
The latter materials practically do not need cleaning and processing, others - asphaltites, asphalt rocks - require processing.
- oil fuel oils - liquid residues of oil sublimation;
- oil tar - the result of distillation of fuel oil from oil components;
- acid oil sludge - they are obtained by purifying lubricating oils with sulfuric acid;
- petroleum bitumen - are formed as a fraction during the distillation of petroleum products.
Unlike natural bitumen, the properties of artificial bitumen vary more widely. Depending on the production technology, a composition with strictly specified properties can be obtained.
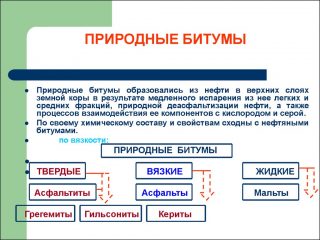
Natural bitumen
Natural material is included in the composition of fossil fuels... Most often it has to be cleaned and recycled. Compared to artificial ones, it does not have any more valuable qualities. However, it is more difficult to modify natural material by adding certain substances.
Structure
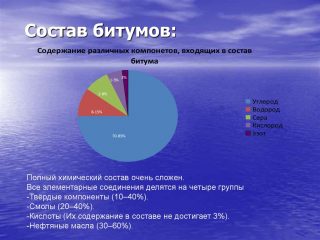
The composition of bitumen in fractions of elements looks like this: 70–87% carbon, 8–12% hydrogen, 0.5–7% sulfur... However, that doesn't tell the consumer much. A more informative enumeration of the components of the mixture is:
- petroleum oils - from 30 to 60%, they impart viscosity and plasticity to the composition under the influence of temperature;
- resins - from 20 to 40%, determine the adhesive properties;
- carbides, carbenes, asphalt-tenes - their content reaches 40%, provide hardness and refractoriness;
- asphaltenic acids - 3%, act as surfactants.
Mixtures can include other substances, most often mineral additives.
How is it mined
- extraction of rock;
- separation of raw materials into organic and mineral parts;
- transportation of the product;
- bitumen processing.
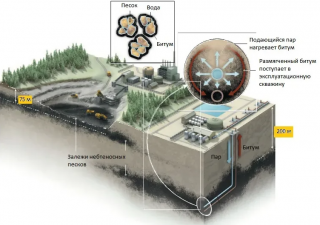
- Quarry or mine treatment plant - the rock is taken up, the bitumen mixture is extracted with a solvent or by boiling to obtain an emulsion. The mining method is used to extract rock containing at least 10% of the material and occurring no deeper than 90 m.
- Mine drainage - bitumen goes upward through the system of ascending drainage channels by gravity. This option is used in the production of liquid mixtures with a depth of more than 100 m.
- Downhole in-situ - the rocks are affected thermally or otherwise through wells drilled from above. The recovery factor is no more than 30%, so this method is rarely used.
Natural bitumen is not a commercial product like gas or oil. It needs processing.
Where is used
The areas of use of natural bitumen are due to its properties. It is used:
- for insulation during the construction of buildings, roads, other structures, as well as for laying pipelines of various types;
- in the production of asphalt concrete;
- in the manufacture of battery mastics;
- in the cable and paint and varnish industry;
- upon receipt of roofing materials.
Bitumen is used in other areas such as horticulture.
Chemical bitumen
Such material is not mined, but produced. The raw material for it is the residues obtained after the distillation of oil., which significantly reduces the cost of the product. In this case, it becomes possible to modify the mixture, since its properties depend on the composition and method of preparation.
Production technology
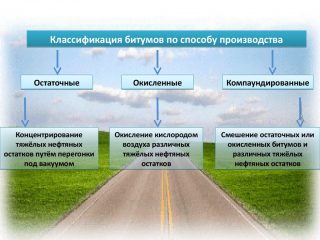
- Residual - produced by deep vacuum stripping on special devices. The feedstock is fuel and lubricant fractions from oil with a high resin content. The product is obtained as a solid, slightly viscous.
- Oxidized - is obtained by blowing with oxygen of tar oil residues. At the same time, the viscosity increases in the mixture, it is oxidized and compacted. This modification is more elastic and heat-resistant than natural.
- Cracking - produced by the decomposition of crude oil oil in the production of gasoline. The residues are oxidized. The product is highly fragile and not popular.
- Compounded - it is obtained by mixing the residues of the distillation of oil. The technology involves the addition of tar, light oil, oils, and other fractions to obtain bitumen with specified properties. This method is universal.
Also, liquid bitumens are isolated, obtained by liquefying solid ones. Fuel oil and highly resinous oil are added to the mixture. Liquid substances are more often used for impregnation.
Elementary and component composition
Component composition is also close. However, the ability to vary the content of different constituents in artificial bitumen makes some constituents more significant.
- Oils - the lightest fraction. The greater the proportion of oil, the more elastic and viscous bitumen is obtained and the lower its softening point. At the same time, oil - mono-, bi-, polycyclic - affects the quality of the mixture in different ways.
- Paraffin-naphthenic hydrocarbons - the main plasticizer. The properties are most influenced by hard paraffins, they should be no more than 3–6% in the mixture. With an increase in the proportion, the structural and mechanical characteristics decrease.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons - there are usually few of them, so they do not affect the properties.
- Resins - the main structural element. They often contain up to 10% sulfur and up to 25% nitrogen.
- Asphaltic acids - when the material melts, they decompose, but do not turn into a liquid state. Under the influence of sunlight, they become insoluble. This ensures the aging of bituminous coatings.
Compound bitumen is most interesting from the point of view of composition, since when it is obtained, it is possible to add a modifier, changing its characteristics.
Artificial bitumen is used in the same works as natural.
Marking and decoding of material
- 2 or 3 letters at the beginning indicate the application of the material. BN - petroleum bitumen, indicates a building modification. BNK - roofing, BND - road.
- The numbers following the abbreviation and written with a forward slash indicate penetration... This is the depth of penetration of the needle of the material by 0.1 mm at + 25 ° C and at 0 ° C. The indicator demonstrates how the hardness and elasticity of the material changes under the influence of temperature.
Sometimes additional letters appear in the marking. They indicate additives that affect the properties of bitumen.
Application technology
- Concrete surface before coating you need clear, free from cavities with bubbles, remove sharp protrusions and dents in the joints of the formwork. For this, fine-grained cement compositions or dry construction mixtures are used.
- Dry the surface. Moisture content not exceeding 4% is allowed.
- Recommended treat the surface with a bituminous primer (grades BN70 / 30, BN 90/10). Apply a primer in 1 layer. In areas where cement-sand mortar adjoins, in 2 layers.
- Bituminous the mastic is placed on the moisturizing side... It is applied in strips - with a spatula, roller, in bulk. The layer should be uniform in thickness and continuous.
- Apply mastic down up. It is important.
- Next layer bitumen is applied after complete hardening and drying of the previous one.
A layer is considered dry if there are no traces left on the cotton swab when you apply it.
Transport and storage
Store bituminous mixtures in cylindrical vessels... The latter can be located vertically and horizontally. If the product is stored for a long time, containers are heating systems... Preference is given to horizontal options, since here the evaporation of moisture leads to the appearance of a crust on the surface of the mass, which prevents further evaporation.
If the bituminous mixture is stored motionless, its properties do not change. When circulating during delivery to the pipeline, the qualities change due to oxidation.
They transport bitumen in special automobile and railway tanks... The material is flammable, so the containers must exactly meet the requirements of GOST.