Wood materials - boards, beams, panels, beams - are used everywhere. The basic material for construction is timber. This type of lumber has a high bearing capacity, is strong, durable and easy to cut.
- Definition and varieties of timber
- Normal construction
- Profiled
- Glued
- LVL
- How to determine the quality of lumber
- Sizes and thickness of the timber
- How to choose a size based on the purpose of the building
- Home construction
- Outbuildings
- Roof
- Floor ceiling
- Calculation of the amount of timber for building a house
- Timber connection
- With the remainder
- No residue
Definition and varieties of timber
Wooden beams are used for the construction of load-bearing structures... The strength and reliability of each beam and post depends on the type of wood and thickness. The cross section ranges from 40 to 500 mm... It makes no sense to make thicker beams. In terms of bearing capacity, they are inferior to metal pipes, and weigh significantly.
The types of timber depend on the production method, processing method, and the nature of the wood.
Normal construction
The standard way to obtain timber is sawing the trunk lengthwise. The material cut from the core of the tree is more durable, less susceptible to fungi and mold, therefore it is valued higher. Since the shape of the lumber does not fit well with the round shape of the trunk, there is more waste when sawing into bars. All surfaces of the timber, including the end surfaces, are leveled.
According to the degree of humidity there are 2 types of timber.
- Natural moisture - contains from 20 to 40% moisture. Such material gives a strong shrinkage during drying, therefore it is impossible to take it for the supporting frame of the building. At the same time, it is readily used for the construction of temporary structures, fences.
- Dry - humidity less than 20%. The wood is dried naturally in open sheds or in a drying chamber. The specialists have not yet decided which option is preferable. Naturally dried material swells and cracks less. Kiln-dried timber can contain up to 12% moisture and gives minimal shrinkage. However, in damp areas, it absorbs moisture more.
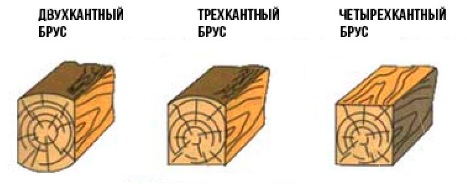
Solid material of any moisture content is divided into profiled and non-profiled... The second option is a standard square or rectangular bar with straight sides. Distinguish two-piece - processed only on 2 sides, three-cante - with 3 sides, and four-cant - curved from all sides.
During construction, it is necessary to take into account the degree of humidity. One side, dry wood fits tighter... And even if the material swells at high humidity, the joint will remain at the same level. But at the same time, deformation and warping of the tree is possible due to too rigid fasteners. The strength of the frame in such a house is determined by the quantity and quality of the dowels. If you overdo it with the mount, the beam will begin to lead.
With the material of natural moisture, the picture is the opposite.... It dries up already in the "composition" of the building, being fixed in a certain position. Dry timber often cracks, twists, elements in the wall move away from each other. Such a house cannot be finished or equipped with windows and doors throughout the year. And later, you will have to periodically repeat the caulking or perform other measures in order to close up the gaps between the bars.
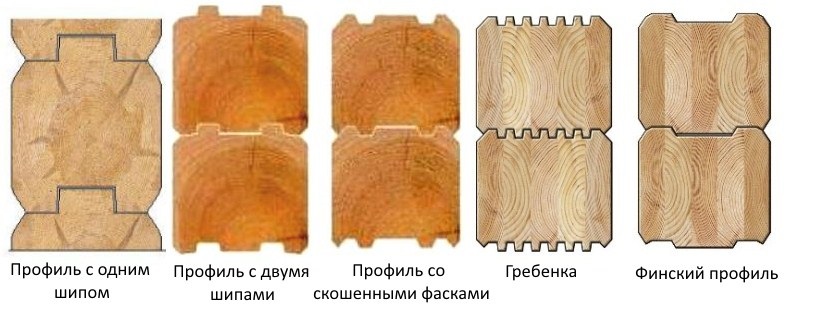
Profiled
For such a property to be useful, the material must have exact geometrical dimensions... Therefore, profiled timber is made only from dry wood. Its dimensions are precisely indicated in GOST and TU, and this is a verification parameter. Due to the accuracy of the form and the presence of a docking mechanism, laying the wall beam takes less time.
If the profiled timber is made of damp wood, it shrinks. You cannot live in such a building for a year.
Generally the characteristics of the profiled bar are higher... However, this leads to a higher cost of the material compared to non-profiled - from 30 to 50%. If you buy this option, you should choose a dry one: it guarantees greater strength and heat saving.
Glued
Splices the fragments with glue... The composition is chosen as safe as possible, but resistant to water. Fragments are stacked in size, but without respecting the direction of wood fibers... This technology determines 2 most important material properties.
In solid wood, the fibers are oriented approximately in one direction. This allows the wood to absorb and wick moisture away in one direction. If the room becomes too humid, the wood absorbs the excess and takes it outside. If the house is too dry, moisture is absorbed from the outside and into the room. Thus, wood regulates the microclimate. But at the same time, the tree grows and shrinks in size.
Glued laminated timber is not of such quality. Hence:
- material much less moisture removal and less vapor permeablethan a solid bar;
- where is he less responsive to changes in humidity, temperature, therefore, does not dry out, does not warp and does not shrink.
Problems with vapor permeability usually arise when using too bulky timber and poor ventilation of the building itself.
Strength of glued material comparable to the strength of solid wood and is almost one and a half times higher. Low thermal conductivity completely preserved. He is less afraid of frost, since it practically does not absorb moisture.
Another plus: glued laminated timber has very precise dimensions, configuration and smooth surfaces. The house from it does not need finishing.
Glued laminated timber costs almost 2.5 times more. This is the main drawback of the material.
LVL
This feature provides the bar high bearing capacitybut in one direction. Its resistance to bending load is noticeably lower.... LVL is produced in the form of bars, beams and slabs. The latter serve as an excellent material for the wall.
LVL is superior in strength to ordinary wood. In terms of moisture resistance, it is better than glued. The material is extremely homogeneous, easy to cut, sawn, holds fasteners perfectly. Sizes vary widely.

How to determine the quality of lumber
The quality of the timber is determined taking into account the following parameters:
- grade;
- humidity;
- configuration.
- Extra - selected material, in which there are no defects: pockets, chips, knots, etc. The wood is as clean and smooth as possible. In terms of strength characteristics, the "Extra" grade does not exceed 1, but in terms of aesthetics it does not know any equal.
- 1st grade - depending on the type of wood, small blind cracks from the ends, captive knots, 2 per 1 running meter, are allowed. Stains, chips, stripes are excluded. The beam is mainly used for the construction of frame buildings and other structures where a high bearing capacity is required from the beam.
- 2nd grade - may have deep blind cracks, resinous pockets and knots in a little more. Spots and stripes are allowed - not blue. The material is used for the construction of the lathing of the substrate, ceiling structures, fences.
- Grade 3 - there are pockets, intergrown and captive knots, chips, through cracks, if they are small. The bearing capacity of such a bar is low, so it is used in auxiliary construction work.
- Grade 4 - in addition to the above, may include blue spots and stripes, deep cracks - to the center of the bar. The material is taken for the construction of light outbuildings, fences.
Natural humidity cannot exceed the norm. But when choosing a dry tree, the parameter must be evaluated. Humidity is usually specified in the batch specifications. If the indicator is more than 20%, you should not take it.

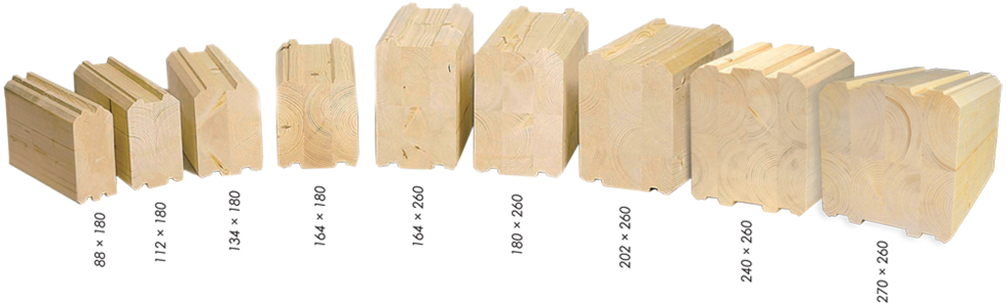
Sizes and thickness of the timber
Dimensions of non-profiled timber:
- width - 50,60, 75, 100, 130, 150, 180, 200, 230, 250 mm;
- thickness - 130, 150, 180, 200, 220, 250 mm.
Typical length of sawn timber is 6 m. By special order, bars with other dimensions can be produced.
Profiled timber dimensions are evaluated to obtain an average width. In this case, the protrusions and grooves do not affect the indicator.
How to choose a size based on the purpose of the building
To perform different work, you will need material with different dimensions. It should be selected in size, bearing capacity and method of laying - horizontally vertically. It is not worth buying a large section of wood for the construction of a simple frame for a barn. For beams of the ceiling structure, for the lower strapping of the house, a thick beam will be required.
Home construction
- The dimensions of the house itself, the higher and larger it is, the more solid the material will be required.
- Weather - in this case, the choice is determined taking into account the thermal resistance of the wall and roof being constructed. For a house with the same area in the southern area, you can take a bar with a section in 150 * 150mm... In the middle lane, a value of at least 200 * 200mm, although the load bearing requirements are not increased. In the northern latitudes, they build from a bar with a cross section 250 * 250mmto ensure sufficient heat storage.

Outbuildings
When it comes to sauna, steam bath or animal enclosure, use wood in 100 * 150mm... Such buildings must be warm enough, they are usually operated all year round.
Roof
Floor ceiling
For floors, ceilings, additional structures inside the house, a bar with a cross section of 40 * 40mm... It is usually laid horizontally, therefore, it is not the bearing load that is more important here, but the resistance to bending.
For the lathing, a bar is used 40 * 40mm... A thinner one is chosen for the counter-lattice.
Calculation of the amount of timber for building a house

The calculation of lumber for a building depends on its type. If the material is used as a carrier, the amount of wood is determined as follows:
- Calculate perimeter of the house and multiply it by box height... The roof is calculated separately. For example, with a width of 5 m and a length of 10 m, you get 50 m. Multiply by the height - 3 m, and you get 90 m².
- Multiply the resulting value by the thickness of the used timber... For example, if its cross section is 150 mm, the volume will be equal to 13.5 m³.
- The resulting cubic capacity does not take into account window and door openings, but since the amount of material is increased by 20% during construction, this difference is not important in general.
Often required calculation of timber in pieces or cubic meters, depending on how it is offered. This is not difficult to do: multiply the width, height and length of the bar, and then divide the result obtained above by this value.
In the same way, the amount is calculated by a cubic meter: divide 1 m³ by the volume of the bar.
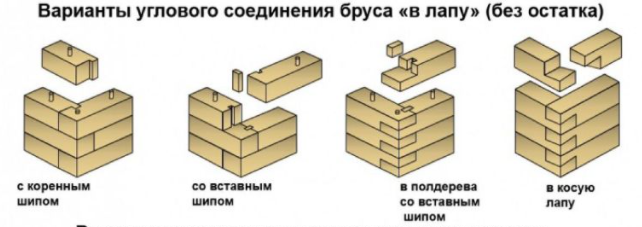
Timber connection
When erecting walls, constructing a frame or rafter system, you have to join a tree... It is unreasonable to fasten it with metal corners or self-tapping screws: the characteristics of the materials are too different. So they use methods without fasteners or using dowels.
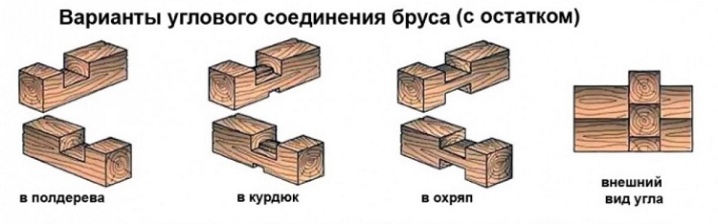
With the remainder
Allocate several ways.
- Unilateral - a groove is made on one of the bars, equal in size to the cross-section of the second bar, but less deep. When laying, one element enters the second and serves as a receiving element for the next.
- Bilateral - the groove is made in both bars. They fit groove into groove, immediately form a tight connection between themselves.
- Four-way - stepping back from the edge, make cuts from all 4 sides. The next element is placed with a groove in the groove, but it rises above the connection plane.
The more complicated the method, the better heat preservation it provides.
No residue
- "Half a tree" - at the ends of the elements, cuts are cut with a depth of half the thickness. When docked, the tree enters the groove and is firmly held. You can additionally reinforce the connection with a key.
- Root thorn - a groove is cut out in one bar, in the other - a spike of the same shape. When joining, the spike is inserted into the groove.
- "Dovetail" - cuts are made on both bars, but give them a trapezoidal shape. This mount is stronger, but more difficult.
- "Into the paw" - at the joint, a part of the wood is cut off to form an undercut. Here slopes are cut out at an angle.