The dimensions of the GVL sheet allow for construction quickly, with minimal labor costs. Drywall and gypsum plasterboard are similar in appearance and have approximately the same characteristics. When making the final choice of building material, it is necessary to figure out what is the difference between GVL and GKL.
Material description
The manufacturer determines the exact proportions based on the technology and local conditions, while the technical characteristics of the GVL must comply with the requirements of GOST.
The crushed and moistened material is pressed into thin sheets, which are cut to the required size. The slabs do not have an outer shell. To give strength to shock loads and prevent fractures during transportation and installation, the panels are reinforced with fiberglass mesh.
One or both sides are sanded until a smooth surface is obtained.
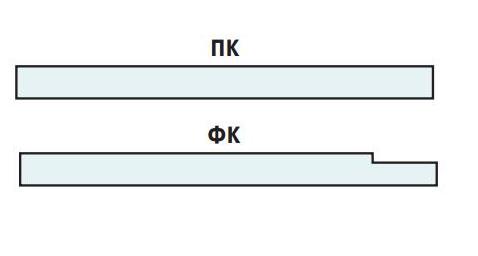
The difference between drywall and gypsum plasterboard consists in the composition of raw materials and structure. In drywall, a homogeneous layer of gypsum (core) is located between the cardboard casings. GKL reinforcement is provided only for flexible sheets with a thickness of 8 mm. The actual dimensions of GKL and GVL coincide with a length of 2500 to 3000 mm, the width is up to 1200 mm.
Use in construction
Main areas of application gypsum fiber sheets are defined by the guiding document:
- arrangement of interior partitions;
- filing of false ceilings;
- cladding of internal walls in residential, utility rooms and industrial facilities;
- installation of the base for the final floor covering;
- cladding of building structures, providing an increase in fire resistance.
The use of GVL for the construction of internal surfaces of ventilation shafts is not provided, since odors and harmful substances are actively absorbed by gypsum, and moisture destroys the material.

GVL tolerates moisture better, therefore it finds greater application (than gypsum board) when arranging the walls of bathrooms.
Mandatory characteristics defined by GOST
Release two types of products:
- common with GVL marking;
- moisture resistant GVLV, decoding of designation - moisture resistant gypsum fiber sheet.
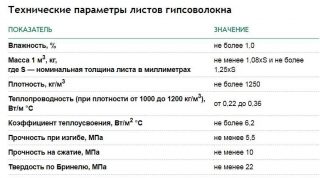
Water absorption of GVLV sheets should not exceed 1.0 kg / m² of surface.
Longitudinal the edges of the sheets are straight or folded. Plates with folded edges are used for walls and ceilings. Folds make it easier to close up joints when preparing surfaces for painting or wallpapering. In other cases, choose GVL with straight edges. Since the rebate is made up to 32 mm wide, this eliminates waste, which can be a lot in large objects.
Provided by GOST geometric dimensions are presented in the table.
| Characteristic | Value, mm |
| Length | 1500, 2000, 2500, 2700, 3000 |
| Width | 500, 1000, 1200 |
| Thickness | 10, 12,5, 15, 18, 20 |
Bigger deviations are not allowed by the requirements. Sheets can be less than 3-5 mm in length and width. The declared thickness cannot differ from the actual one by no more than 0.3 mm. The difference in the length of the diagonals for one sheet cannot exceed 4 mm.
Products are marked in the same way by all manufacturers... Examples:
- GVL-PK-2500x1200x10 GOST R 51829-2001: gypsum fiber sheet with straight edges, size 2500x1200 mm, thickness GVL 10 mm, manufactured in accordance with GOST 51829-2001.
- GVLV-FK-2700x100x12.5 GOST R 51829-2001. Moisture-resistant gypsum fiber sheet with folded edge, 2700 mm long, 1000 mm wide, 12.5 mm thick.
If the products are manufactured according to their own specifications, this should be reflected in the labeling.
Appearance
Oil stains are not allowed on the front surface of the gypsum fiber. GOST excludes scuffing and sticking of gypsum, damage to corners and edges. Traces of the impact of pushers and stackers are permissible.
Other characteristics
- flexural strength - from 4.3 to 6 MPa, depending on the thickness, and the dependence is inverse: the thicker the sheet, the worse it resists lateral load;
- hardness of the face - 20 MPa;
- activity of natural radionuclides no more than 370 Bq / kg, which corresponds to the natural background.
For individual customers, the manufacturer has the right to change various characteristics, but such products must not be released to retail.
Product selection basics

When starting the choice of GVL, the operating conditions and scope of application are assessed.
To prepare the foundation under the screed it is recommended to choose small-sized sheets. This will facilitate the delivery, unloading and lifting of products to the place of work. Smaller sheets are easier to fit in the room to reduce waste.
For wall cladding and partitions, on the contrary, choose GVLs that coincide in length with the height of the premises. If the wall is sewn up with small sheets, you will have to spend money and time on finishing and hiding the joints.
Pay attention when buying for release dates products and storage conditions in a warehouse. Warehousing is allowed in closed rooms with normal humidity conditions without access to sunlight. GVL panels are used in dry rooms and in buildings with normal humidity conditions.
GVLV can be used in humid conditions. At the same time, GOST prescribes the installation of forced exhaust ventilation.
Installation features
The technology for installing GVL on the floor, walls and ceiling differs, this is due to the tasks being solved and the characteristics of the material.
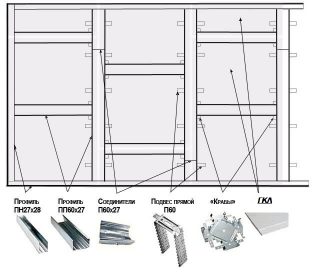
Sheathing of walls and partitions
Frame they are built for arranging partitions or on walls with large surface flaws. The advantage of the method lies in the possibility of laying additional heat and sound insulation between the racks. Racks and logs can be steel or wood. In brick buildings, preference is given to metal in wooden houses - timber.
Algorithm for the construction of the frame:
- Walls cleaned from dirt, slugs of masonry mortar. Wooden surfaces are freed from rot. The surfaces are impregnated with deep penetration primers with antiseptic additives.
- Markup, focusing on the sizes of sheets available for purchase. For standard GVL with a width of 1200 mm, the racks are located at distances of 600 mm. The same size is suitable for laying insulation with minimal gaps.
- With brackets fix the racks to the wall surface... The vertical profiles of the partitions are mounted to the mounting profiles pre-fixed on the floor and ceiling.
- Horizontal lintels fixed at distances of 50–55 cm, depending on the height of the sheet.
For structural strength, the guide profiles are fastened with dowels, and the racks and jumpers are connected with self-tapping screws with press washers. It is permissible to use blind rivets.
- Adjust the screwdriver so that the fuse ratchet is triggered when the screw head is fully recessed, but does not destroy the blade.
- They start to work from the places of interface with the wall or from doorways. The order depends on the sizes of the sheets available. Achieve a layout in which there will be the least number of cuts and the minimum amount of waste.
- Sheathe one side of the frame, leaving gaps up to the wall 3–4 mm, to the floor and ceiling about 5 mm. For fastening, self-tapping screws are used for metal or wood, depending on the material of the frame. Fixing step 15–20 cm.
- Lay down communications, insulation, wiring in a corrugation, excluding combustion.
- Close the second side partitions or frame mounted on the wall.
Finishing consists in sealing the seams and filling the surface. The method depends on the chosen option of the topcoat.
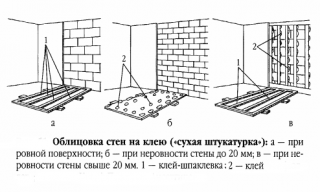
Fastening without crate
Installation of GVL on self-tapping screws or glue allow you to level the wall much faster than equipping the lathing. This method is cheaper, since material costs are excluded.
The disadvantage should be considered the difficulty of frameless cladding, if the roughness of the wall surface exceeds 4–5 cm.
- Prepare the base. Stone (brick, block) walls are freed from the influx of masonry mortar, treated with a deep penetration primer with an antiseptic. Derevyanthe walls are additionally treated with a fire retardant.
- Carry out markings, install beacons... The easiest way is to pull 3-4 horizontal cords, along which the vertical alignment of the plate will then be carried out.
- Old walls from any material free from the decorative layer - paints and plasters that impair adhesion. The work is labor intensive, so the gluing method is rarely used in old buildings.
- The side of the sheet to which the adhesive will be applied impregnated with a primer.
- A continuous layer of glue is applied along the perimeter of the slab and 2-3 strips of the composition are placed on the surface within the perimeter.
- Glue the gypsum fiber board to the wall, leaving a margin of 5 mm to the floor and ceiling.