Wooden boards are a very popular material. Edged, unedged, planed grooved boards are in demand in a wide variety of construction work. A product of a strictly defined thickness - 25.5 mm - is called an inch.
Material description
Another important parameter is degree of material processing and dimensions... The purpose determines the thickness, while the length and width vary quite widely. The inch board got its name for its thickness of 25.5 mm, which is almost equal to an inch - 25.4 mm.
The inch is made of any breed. In this case, with the same thickness, the material has different properties and cost. This affects the scope of application. The dimensions of the inch board are regulated by the TK. In construction, a 150 mm wide option is more often used..
Scope of application
Thumbovka belongs to the category of massive. This expands the scope of the material.
- Most often it is used for flooring and wall cladding... It is better not to take it for the ceiling - it is too heavy.
- Good material for the construction of small load-bearing structures - verandas, gazebos, awning over the terrace.
- Very often the inch is used for the construction of baths... Convenient thickness allows you to lighten the building as much as possible, but at the same time not lose strength.
- Off-grade and unedged boards with such a thickness are taken for any auxiliary work: construction of scaffolding, erection of formwork of any type and complexity, construction of lathing, as a filing for the floor.
- The board goes on construction of fences, as well as temporary structures.
- Will do quite well for the construction of stairs.

Varieties of inch boards
The parameters for evaluating an inch are the same as for other boards: grade, processing method, moisture level and many other factors.
One of the most important factors - grade of wood... This indicator describes what defects and in what quantity a material can have and how this affects its properties.
- Extra - or selected. Such an inch with a length of 6 m does not contain cracks, knots, spots. The wood is very clean.
- 1st grade - blind cracks, pockets and captive knots are allowed, in an amount of no more than 2 per 1 running meter of the board. 1 grade is practically not inferior to the perfect one, but at the same time it is much cheaper.
- 2nd grade - such lumber includes deep, but not through cracks, 2 resinous pockets each and a knot falling out by 1 rm, stains and stripes are allowed - not blue. Loose bitches can also occur.
- Grade 3 - 1 running meter has pockets, knots, including fallen out spots. Chips and separate through cracks are allowed.The material is used for packaging, pallets, in the construction of formwork. It cannot be used for loaded structures - low bearing capacity.
- Grade 4 - spots of rot, colored stripes, intergrown and fallen knots, deep through cracks, wane are permissible. Such material is used for the construction of sheds, outbuildings.
The cost of varietal material depends on the cleanliness of the board and the nature of the wood itself.
Wood species
The characteristics of wood, such as resistance to moisture, strength, durability in certain conditions, determine not the dimensions, but the characteristics of the wood. A pine or oak thumbnail has different qualities.
The material is cut from coniferous and leafy wood. The most popular conifers:
- Pine - the most demanded material due to its cheapness and availability. The rock is relatively soft, but strong; it is used in building structures without restrictions. It contains a large amount of resins, which protects it from the direct action of moisture and increases its resistance to dampness. However, this resistance is not so high as to leave the tree unprotected.
- Larch - with a lower resin content, it is exceptionally resistant to water and moisture. Moreover, under the influence of moisture, it only becomes stronger. Wood is used for the manufacture of window frames, doors, decking, gazebos and other external structures. It is better not to take larch for roofing: the material conducts heat well.
- Spruce - timber that is not inferior to pine in resistance to moisture and fungus, but less resinous. It is most often offered in the form of boards, since it shrinks strongly during drying.
- Cedar - expensive, solid, durable wood, very beautiful and fragrant. Cedar can withstand heavy loads, is durable, therefore it is more often used in the construction of critical units, as well as for cladding living quarters and saunas.
Hardwoods are found:
- Linden - the wood is soft, silky, beautiful and emitting a wonderful aroma. Its main difference is low heat conductivity: even at temperatures of 100 ° C, it does not heat up. Linden boards are used primarily for finishing saunas and baths.
- Ash - a breed of medium density, excellent thread holding. The wood is light, beautiful, beautifully dyed and processed with stains or paints. The board is very uniform, which makes ash a stable element. Thumbnail is taken for flooring, staircase construction.
- Oak - wood of medium density, rather heavy in processing, very beautiful. The material is completely insensitive to moisture, it only becomes harder from direct contact with water. Due to the high content of tannins, oak can last for centuries.
Other types of wood are also used, but mostly dense or medium density.
Edged and unedged
Unedged the board is obtained by sawing the trunk. Wherein the ends are not processed and the bark is not removed... The appearance is not presentable, but the cost is lower. Distinguish 2 subspecies:
- fence - made of low quality sawn timber, with knots and cracks, - not intended for loads;
- carpentry - made of 1–2 grade wood and used in construction.
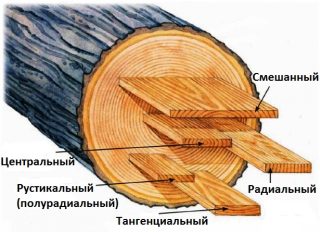
- board radial cut - cut out from the middle of the trunk, practically does not shrink and dries well;
- semi-radial - obtained by cutting a log at 45 degrees and a slightly lower grade;
- tangential inch - cut out in areas that are distant from the center, gives noticeable shrinkage and has a pronounced texture.
Tangential cutting allows you to get the largest possible number of boards.
Sizes of lumber
The dimensions of the edged board of 25 mm are regulated by GOST. Different standards apply for sawn softwood and hardwood: for conifers - GOST 24454-80, for deciduous - 2695-83.
The standards are set for wood with a moisture content of 20%.
Conifers GOST
| Thickness | Width | ||||||||
| 16 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 19 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | — | — | — | — |
| 22 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | — | — |
| 25 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 32 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 40 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 44 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 60 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 75 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 100 | — | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 |
| 125 | — | — | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | — |
| 150 | — | — | — | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | — |
| 175 | — | — | — | — | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | — |
| 200 | — | — | — | — | — | 200 | 225 | 250 | — |
| 250 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 250 | — |
Deciduous GOST
Dimensions (edit) by lenght defined as follows:
- from hard hardwood - from 50 cm to 6.5 m in 10 cm steps;
- from soft varieties and birch - from 0.5 to 2 m with a step of 10 cm;
- from 2 to 6.5 m in 24 cm steps;
- thickness ranges from 19 to 100 mm including 25 mm;
Width depends on the type of board:
- edged - from 60 to 110 cm in 10 cm increments and from 130 to 200 in 20-30 cm increments;
- unedged or cut on one side - from 50 or more in 1 cm increments.
Cubature and weight
Thumbovka is offered in linear meters and or in cubes. In order not to make calculations manually, they use ready-made tables.
| Dimensions, mm | The volume of the boards, m³ | The number of boards in 1 cube, pcs | Number of boards in m² |
| 25x100x6000 | 0,015 | 67 | 40 |
| 25x120x6000 | 0,018 | 55 | 40 |
| 25x150x6000 | 0,0225 | 44 | 40 |
| 25x180x6000 | 0,027 | 37 | 40 |
| 25x200x6000 | 0,03 | 33 | 40 |
| 25x250x6000 | 0,0375 | 26 | 40 |
Selection recommendations

Buying an inch, take into account the following tips.
- If the boards are used outdoorschoose lumber without deep cracks. Better even without knots, since the latter reduce the mechanical strength.
- When a board that can withstand heavy loads is required, pay attention to the growth rings. If they are parallel to each other and do not taper, this means that the board is cut from the hardest part of the trunk.
- For construction work like lathing or formwork structures no need to buy first-class raw materials.
- If the boards are intended for stairs, flooring, wall cladding, you need to select material with even cuts, without chips. If there are places with traces of insects on the inch, you should refuse to purchase.