Chipboard is a popular material in construction, building decoration and furniture making. When choosing, take into account the characteristics of the products that are important for the safe use of the boards.
Description and production of chipboard
It is more correct to call the products Chipboard, but in the conventional sense the abbreviation Chipboard has taken root.
The name "chipboard" is more applicable to wood-laminated plastics made in accordance with GOST 13913-78, "Laminated wood plastics (chipboard)". But these products have a special purpose - they are rarely used in construction and everyday life.
Structure

The main ingredient in the production of particle board is technological chips and shavingsobtained in the process of woodworking raw materials of deciduous and coniferous species. The use of wastes from sawmills, matches, plywood and other industries can reduce the cost of production.
Chips are used for low quality products, shavings are used to form the outer layer of three-layer boards.
Chips and shavings must pass cleaning from impurities, they are passed through an electromagnetic separator to remove metal impurities.
An indispensable component used for gluing chips, imparting the necessary properties are chemical substances:
- urea-formaldehyde resins, the least environmentally harmful;
- phenolic-formaldehyde resins, toxic with a pungent odor, are more often used in chipboard made of hardwood;
- water-repellent (hydrophobic) additives and substances that increase the strength of products.
It is undesirable to use particle board based on phenol-formaldehyde in places of permanent residence of people.
Production stages
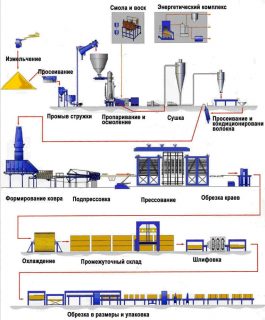
Production technology standardized and includes several stages:
- Preparation of raw materials, which consists in mixing components of different quality and origin.
- Shredding components to the required fraction while bringing the mass to a homogeneous state.
- Drying base plates to the required moisture content.
- Mixing organic raw materials with chemicals until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
- Chipboard formation on a moving belt by hot pressing.
- Slicing slabs required size.
The final surface treatment can consist in grinding, as well as pasting with veneer (veneered chipboard) or polymer film (laminated chipboard).
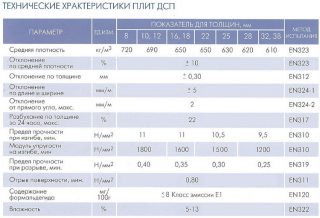
Specifications
Products of any manufacturer must comply with the characteristics:
- GOST 10632-2014. "Chipboards", for products without an external finishing layer.
- GOST 32289-2013 "Particle boards, lined with films based on thermosetting polymers", or as it is commonly called laminated chipboard.
- deviation from straightness and perpendicularity of edges no more than 2 mm / r.m .;
- tensile strength for bending from 5.5 to 11.5 MPa - the dependence is inverse: the thicker the plate, the worse it resists fracture;
- warpedness - no more than 2 mm;
- hydrothermal resistance: measured for sheets intended for the manufacture of furniture that are resistant to water vapor, for example, for kitchen furniture;
- abrasion resistance and staining;
- limit formaldehyde norms.
Separate paragraphs of GOST provide slab tolerances:
- dents;
- foreign inclusions;
- scratches;
- distortions or non-printing of the picture;
- gloss of the surface.

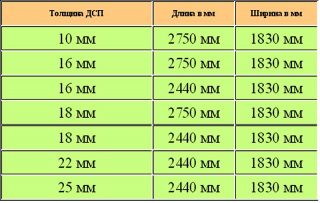
Dimensions (edit)
Standard sizes a sheet of ordinary chipboard without coating can be within:
- in length from 1800 mm with a step of 10 mm;
- in width from 1200 mm with a graduation of 10 mm;
- in thickness from 10 mm.
Laminated chipboard has a wider range of sizes:
- length - from 1830 to 5680 mm;
- width - 1220–2500 mm;
- the thickness is not limited.
Before purchasing and making calculations, it is necessary to check with the seller the actual dimensions of the available products.
The assortment found in retail sale is often limited. standard dimensions 2800x1830 - it is convenient for delivery and cutting.
Varieties of material
Appointment
Chipboard boards used for production:
- consumer goods;
- furniture;
- structural finishing materials, in mechanical engineering and instrument making.
Any chipboard, even moisture resistant, is not intended for permanent use in rooms with high humidity.
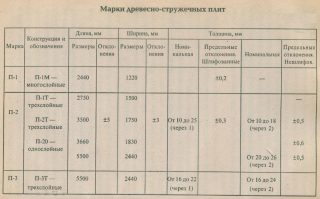
Brand
- Р1 - general purpose, for use in dry conditions;
- P2, for indoor use in dry rooms, including for the production of furniture.
Laminated boards classified by characteristics:
- Appearance layers (flat surfaces) for I and II grade.
- Surface type: ordinary (O) and fine-structured (M).
- Processing degree surfaces: sanded (W) and unpolished (NSh).
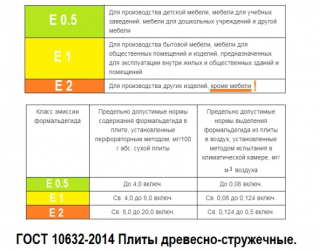
- Formaldehyde emission into the environment: E0.5, E1, E2.
Example of a symbol chipboard boards without a laminated surface: "P2, I, O, W, E0.5, 3500x1830x16, GOST 10632-2014 ". Explanation of designation:
- plate type P2, for dry rooms;
- grade 1;
- the surface is ordinary, polished;
- formaldehyde emission class E0.5;
- dimensions: 3500x1830x16 mm;
- characteristics and parameters correspond to GOST 10632-2014.
- Physical and mechanical properties suggest the allocation of three quality groups A, B, U (improved).
- Gloss levels: G (glossy), M (matte).
- By type of printing coating: one-color (Ots) or with a printed pattern (Pr).
- By surface texture: smooth (Gl) or embossed (P).

Example of a symbol chipboards coated with films:"Plate I / II-M-Ots-Gl-A-E1, 3500x1500x22 GOST 32289-2013".Decoding:
- foil lined plate;
- covering of class I on one side and class II on the back;
- type of coating matt, one-color, glossy;
- size 3500x1500x22 mm;
- corresponds to GOST 32289-2013.
Designations are subject to change for products manufactured to specifications.
Grade
The grade of particle board is determined surface appearance... The indicator does not say anything about other important technical characteristics.
For example, products of the highest grade 1 may be banned for use in permanently occupied areas based on the formaldehyde emission rate.
Surface treatment method

Surface finishing affects mainly the consumer properties of products.
Slabs polymer coated perfectly resist swelling in humid conditions, if the end surfaces of the chipboard are properly processed. Otherwise, moisture will quickly penetrate into the body of the slab and the process of destruction will begin.
Laminated boards must withstand exposure to various liquids for 24 hours without forming stains on the surface. The exception is acetone, the test for resistance to which in the laboratory is checked in just 15 minutes.
Grinding the surface of uncoated slabs, the required degree of roughness is achieved, the indicator of which is fixed by documents.
How to choose

Before buying chipboard it is necessary to consider the issues:
- Where will be used finished product, the amount of time spent indoors.
- Operating conditions - temperature and humidity in the room - at high temperatures, harmful substances are released more intensively, and at high humidity, particleboard swells and rapidly disintegrate.
- Appearance requirements... Grade 2, which allows dents on the surface of up to 2 mm, is quite suitable for the manufacture of invisible pieces of furniture or for partitions that will be covered with a finish.
Important when choosing is slab thickness.
- Products thick 8-10 mm used for cladding walls and partitions, making doors for sliding wardrobes.
- Particleboard 16 and 18 mm received the greatest distribution for the production of facades and internal parts of cabinet furniture.
- Chipboard from 18 to 32 mm used for sheathing floors, making countertops and window sills.

External examination pay attention to the following features:
- Density of the slab. The larger the chips and shavings, the larger the voids will be, this can affect the reliability of holding fasteners (self-tapping screws, screws, tongue-and-groove), it is difficult to tongue loose slabs.
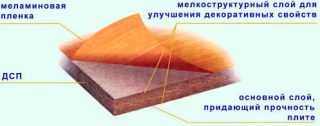
- The presence of layers that can be seen from the end of the slab... High-quality products consist of an inner, relatively loose and two outer, dense, made of fine shavings.
- Lack of dustiness... If you hold it with effort over the surface, then there should be no particles of shavings on the hand.
Pay attention to uniformity of size and uniformity of color, it can also be appreciated by examining the stack of chipboard.
Application area

GOST permits the use of particle board in various fields, subject to safety conditions.
In addition to furniture production, chipboard used for making:
- fences for construction sites;
- garden houses and outbuildings;
- wall cladding and dividing partitions of residential and public premises;
- decorations;
- sheathing of floors and ceilings;
- removable formwork for pouring foundations;
- walls of ice rinks;
- buildings of equipment;
- transport packaging;
- interior doors.
Chipboard is a versatile material that is durable when used correctly.
Is chipboard harmful to health
Depending on the category of products for the release of formaldehydes, GOST directly indicates scope of application:
- E 0.5 - for furniture, including those intended for children's and school institutions;
- E 1 - for any furniture, except for those intended for rooms with the stay of children;
- E 2 - for various products, except for any furniture.
The best environmental friendliness is inherent in the E0.5 category; the use of products with the E2 index in everyday life should be abandoned despite the low price.
Chipboard manufacturers
There are about 80 large enterprises in Russia, of which about 40 produce over 100 thousand cubic meters of products per year.
The products of large factories are more popular, since they have a competitive price due to the volume of production.
Famous manufacturers:
- Cherepovets FMK CJSC;
- OJSC "Dyatkovo TOZ";
- LLC "Kronospan";
- OJSC "Ufa FPK";
- OJSC MK Shatura;
- CJSC "Murom";
- Volgodonskiy KDP OJSC.