Different types of chipboard are used for a wide variety of jobs. The characteristics of plates and sheets are very different. One of them - fiberboard - is a lightweight, thin material, intended mainly for finishing work.
Material description
Heavy-duty fiberboard with a thickness of 16-25 mm is also produced.
Production
Base material for fiberboard - chips, the manufacturing process begins with its processing:
- the chips are washed and all impurities are removed;
- dry the material and separate with a magnet to remove metal impurities;
- in a fiber grinding machine, chips are crushed in 2 stages;
- the ground raw material is fed to the defibrillator, where resins, paraffins, and modifiers are added to it.
Distinguish 2 production methods: wet and dry.
- Divide the mass prepared chips and part of it are transferred to the hopper. Here the raw materials are impregnated with water-repellent agents.
- The "carpet" is being cast. The mass supply is regulated by dispensers. It is important that the crop feed is constant and even.
- "Carpet" is served in the press. The press platen is heated with hot water. A sheet is formed in a press under a pressure of 3-5 MPa, depending on the thickness of the fiberboard and at a temperature of 210-230 ° C. Pressing takes 11 minutes.
Dry the method is simpler and is performed without heat treatment. Chips are prepared in a slightly different way: they are not moistened, but dried.
- Dried mass laid on the netto remove air.
- Then add to the resin mixture and other ingredients.
- Ready "Carpet" is served on the press, squeeze. Material cut by size.
- Blanks a second time put under the press and compressed again under slight pressure.
The dry method is much cheaper, however, the fiberboard obtained in this way has lower physical and mechanical characteristics, and does not differ in strength.
Application area
- Fiberboard sheathing - the fastest and cheapest way of finishing floors, walls and ceilings for painting, wallpapering, sheathing with fabric materials. The slabs form a flat smooth surface, due to their lightness, they do not create stress on the walls.
- Fiberboard is used for manufacture of back walls of cabinets, wardrobes, dressers, bottom of drawers and sofas and other similar elements. No high bearing capacity is required here. Its task is to limit the cavity.
- Hardboard - the version with the top decorative layer, painted or laminated, is used as finish replacing wood... Hardboard is stronger than ordinary fiberboard and copes with the role of wall panels, sheathing of partitions. It is also used in the manufacture of furniture.
- The sheet dampens sound well, so they apply in the construction of soundproof partitions.
- He also serves thermal insulation material for ventilation systems and boxes in cinemas, television studios, theaters.
- Used as cladding material in vehicles: buses, trams, trolleybuses, trains.
At home, a variety of fiberboard is made templates for cutting, sewing... It is allowed to use formwork material.
Difference from chipboard and MDF
Different characteristics lead to different uses of the materialso it's hard to compare.
- MDF - the most eco-friendly material... In its manufacture, sawdust is literally ground into flour, and then glued together with lignin and paraffin. In the manufacture of chipboard, and often fiberboard, formaldehyde resins are used. Therefore, when buying such sheets, you need to pay attention to the class of the product. Do not use material below class E2 in the living area.
- Strength and density MDF boards are the largest. In load-bearing structures such as an interior partition. MDF can serve as a filler, not just a finish. Chipboard is inferior to MDF, but it is quite suitable for wall decoration, door production, flooring. Fiberboard, in addition to special heavy-duty options, is used only as a cladding material.
- Water resistance MDF is also the highest. Furniture made of it can be used in the bathroom and in the kitchen. Furniture is also made from chipboard, but it falls into disrepair 2 times faster. Fiberboard is more resistant to moisture than particleboard. Therefore, for example, finishing the balcony with chipboard is not recommended, but fiberboards can be safely used.
- MDF and chipboard lend themselves well machining: cut, sawn, milled, glued. Fiberboard has fewer possibilities, but it is also easy to cut sheets.
- Decorative possibilities MDF is much higher than fiberboard or particleboard. MDF is covered with foil, trimmed with veneer, as well as chipboard. However, MDF can be bent. This is how curved facades are obtained. Fiberboard serves as a rough flooring or cladding, so it is rarely beautiful. The only exception is hardboard, but its aesthetic characteristics are small.
- All materials are combustible. Thicker sheets burn less willingly, so MDF is considered the safest.
The technology for the manufacture of fiberboard does not allow for the most part to make thick sheets. This severely limits its use.
Varieties of fiberboard sheets
Fiberboard sheets are obtained in a wide variety of densities. The main classification of the material is associated with this indicator.
Soft
Distinguish 3 types of material: M1, M2, M3... The higher the number, the greater the density of the sheet. You can distinguish them by their appearance: the softer the material, the more wood fibers stick out from the edge.
The material is used as an analogue of drywall: for cladding frames and walls, soundproofing partitions, interfloor ceilings.
Semi-solid
The water absorption of the material is 40%, so fiberboard is not taken in damp rooms for finishing.
Solid
Solid fiberboard has a decorative surface: smooth, matte, imitating aged wood.
Super hard
Density up to 1200 kg / m³. Maximum hardness: bending strength is 47 MPa. Water absorption is low - only 12%. These qualities are due to the inclusion of Petkol in the initial mixture. Doors, interior arches are made of material, walls and partitions are sheathed. It can be used as a floor covering, the slabs can withstand a very noticeable load.
Superhard fiberboard is an excellent electrical insulator and is often used in the installation of electrical panels.
Laminated
Several options are produced: tiled - for finishing the floor, walls, under the lining and sheet. The second option has spikes and grooves on the end, which facilitates the assembly of the trim. Sheets are offered in standard sizes.
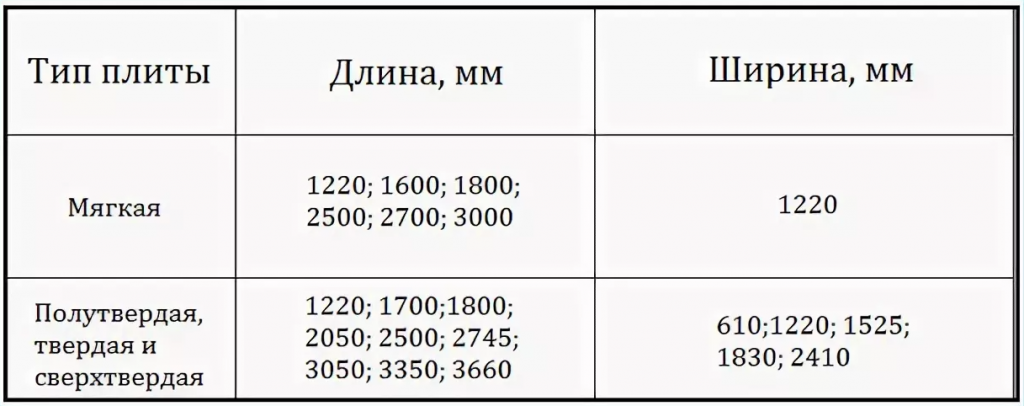
Sheet sizes
Standard the width of the sheet is from 1220 to 2140 mm, and the length is from 1220 to 3600 mm. In fact, the sizes can be different, depending on the demand in the market.
Material thickness determined by density:
- HDL of low or medium density can be 8, 12, 16.5 mm thick;
- semi-solid varieties are produced with a thickness of 6, 8, 12 mm;
- superhard and hard sheets reach 2.5, 3.2, 4.5 and 6 mm.
The weight of the product depends on the density.
How to choose
Soft fiberboard is used mainly as a soundproofing material, so the thickest sheet is preferable for finishing an office or studio. The dimensions of the stove depend on convenience. It is more convenient to cover a large area with large ones.
For the manufacture of the back walls of furniture, it is better to take semi-solid with a minimum thickness: they are lighter, but still strong. Solid slabs, up to 6 mm thick, are used to decorate a room, frame sheathing and partitions. Thin solid material - 2.5 mm is also suitable for the back wall in high-quality furniture.
The dimensions of the decorative laminated fiberboard are selected according to the intended purpose. For cladding the ceiling or walls in a small room, tiles with different textures or lining are more suitable. For the decoration of large halls - sheets.
Decoding of marking
The marking includes the abbreviation of fiberboard and several additional letters indicating the density of the material:
- T - solid with a normal surface;
- TP - solid sheet, the top layer of which is painted;
- TS - the outer layer of the sheet consists of finely dispersed wood pulp;
- TSP - a plate in which such a surface is painted;
- ST - a superhard sheet with a normal surface;
- STS - superhard boards with a laminated top layer.
Plates of category "T", "TS", "TP", "TSP" are divided into types "A" and "B".