Under the universal name "laminated waterproof plywood" sellers and buyers can mean products that are different in their consumer properties and technical characteristics. To avoid mistakes when choosing a product, it is better to familiarize yourself with the product range in advance.
General description of the material
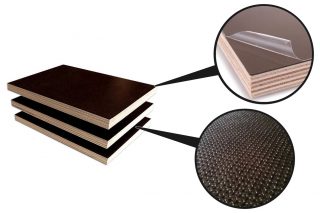
The products are made of waterproof birch plywood faced with thermosetting polymer film.
The outer layers of the leaf are always made of birch, for interior use hardwood veneer:
- alder;
- beech;
- aspen;
- poplar;
- linden;
- maple.

Conifers are used:
- pine;
- spruce;
- fir;
- cedar;
- larch.
Symmetrical veneer layers must be of the same wood species and the same thickness.
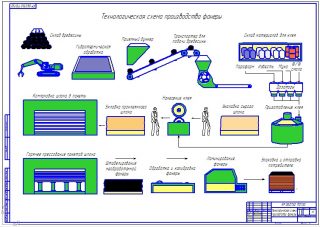
Production of laminated moisture-resistant plywood
- Calibrate and trim logs to the required length.
- Thermal steaming in baths with hot water.
- Debarking - removal of knots and remnants of bark, depending on the workpieces, the cleaning stage can be carried out before steaming.
- Peeling - production of veneer of a given thickness. The process is similar to sharpening a pencil in a sharpener.
- Pruning blanks to the required size. Waste is sent to fiberboard and particleboard production lines.
- Impregnation veneer with adhesive to full thickness.
- Forming stacks veneer from the required number of sheets.
- Preliminary pressing.
- Cooling down blanks and drying to moisture content, provided by the technological map.
- Pruning plywood to the desired size.
- Grinding surface.
- Sealing of defects: fallen out knots, cracks, cavities, special adhesives. The glued film should lie on a flat surface, excluding air chambers under the outer layer.
- Finish grinding.
- Pasting plywood with thermal protective polymer film.
- Processing or painting ends with moisture-resistant compounds based on alkyd or polyester components. The ends can be protected with a film, but this material is expensive.
Protection against moisture is achieved by films and veneer impregnation - plywood is protected from moisture throughout its entire thickness.
Varieties of plywood
GOST classifies products:
- by brands depending on the type of coating;
- by grade, depending on the quality of the outer layer.
Plywood grades lined birch (FOB):
- F / F - covered with a smooth film on both sides;
- F / W - one side is smooth, the other is mesh non-slip;
- F / SP - smooth surface on both sides, one of which (SP) is intended for painting;
- SP / SP - smooth film, glued on both surfaces, can be painted;
- F / U - the product is faced only on one side.

Plywood, uncoated on one side, is not intended for use in wet conditions.
Products with the W index are often used as film faced plywood for floors.
Varieties

Upon receipt of products, one of the following is assigned three grades: I, II or III... The parameter depends on external defects, which are described in GOST 15.
So first grade prohibits:
- any places where there is no film;
- dots and spots;
- swelling of the film;
- press prints;
- roughness, through scratches of the surface layer.
Allowed in minimum quantities:
- film overlays no more than 5 mm;
- visible traces of veneer roughness no more than one per 1 m2;
- blind scratches and risks;
- cutting defects up to 5 mm long;
- paint smudges up to 12 mm long.
Plywood of grades 2 and 3 may have various defects that did not allow the product to be assigned to grade 1.

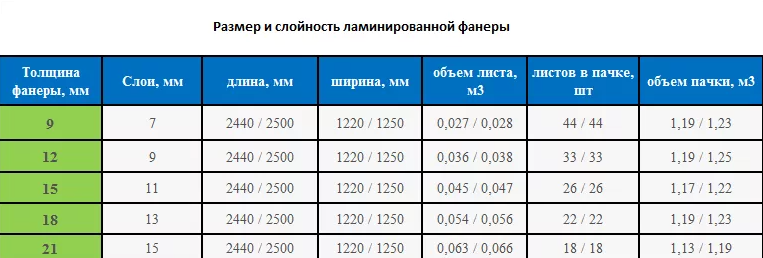
Dimensions and thickness
The dimensions of the sheets are chosen by the manufacturer, but if the direct customer does not put forward the exact parameters, factories adhere to the line of a certain GOST:
- with a length or width of 1200, 1220 and 1250, a deviation of 2 mm is allowed;
- sheets of 1500, 1525, 2400, 2440 and 2500 mm may have an error of 3 mm;
- product dimensions 3000 and 3050 mm may differ by 4 mm.
The thickness of the sheets ranges from 6.5 to 30 mm, with an error of 0.4 to 1.3 mm.
Application area
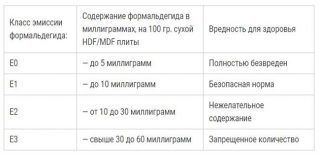
- E 0.5 allowed for widespread use, including childcare facilities;
- E 1 it is permissible to use in all rooms, except for children's rooms;
- E 2 - material not intended for the manufacture of furniture and decoration of living rooms.
Batches may vary even from the same manufacturer, so before buying study the safety certificate.
Most of the products of all factories meet the E1 emission class.

The main directions of use:
- production of removable formwork for reusable use;
- construction of internal and external walls of buildings and structures, construction of terraces, interior partitions;
- production of facades and interior furnishings;
- flooring in office premises, in transport, including water transport;
- manufacturing of shipping containers and packaging for devices;
- construction of vehicle bodies;
- installation of hard floors, decking and seats in boats and boats.