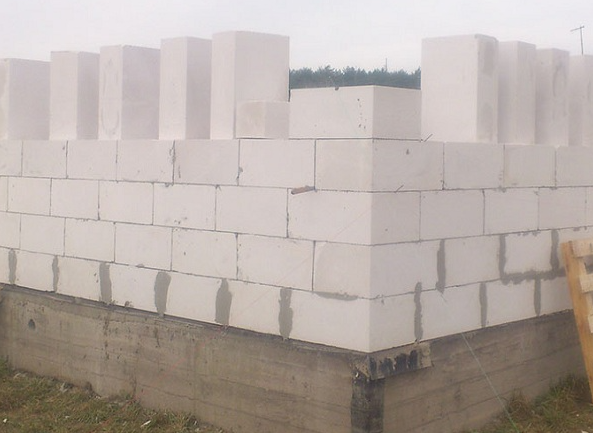
Aerated concrete is a type of aerated concrete. Its structure is determined by the manufacturing method. A blowing agent is added to the initial mixture, it interacts with the components of the mixture, as a result of which hydrogen is released. Gas cannot escape from the thickness of the material and forms many small bubbles throughout the volume.
Such a structure gives concrete properties uncharacteristic for it and is of great interest to the builder.
- Using aerated concrete blocks for building a house
- Strength and thermal conductivity of aerated concrete
- Calculation of the amount of material at home
- Reinforcement for reinforcing aerated concrete masonry
- Aerated concrete blocks
- Construction features
- Masonry technology for the first and subsequent rows
- Overlapping systems
- Options for finishing the facade of a house made of aerated concrete
Using aerated concrete blocks for building a house

The properties of aerated concrete depend not only on the materials used, but also on manufacturing method... The difference is significant, before building a house, it is necessary to decide which gas block will be used.
Non-autoclave - the initial mixture, after swelling, is poured into molds, where it cools down and hardens naturally... This requires 5-6 days... The disadvantages of this kind of aerated concrete are related to the nature of drying. In this case, the bubbles are not completely distributed evenly, their sizes are larger, the material does not gain high density... There is also an undoubted plus: they remove from the form closed cell finished stone, since bubbles do not come out to the surface. Non-autoclaved aerated concrete less water absorption.
Autoclave is processed in a special unit. The mass solidified after swelling is cut into blocks, and then placed in an autoclave and steamed at a temperature of 200ºC and a pressure of 10-12 atm... Such blocks are much stronger, harder, have the exact size and shape. The production cycle itself takes 5-6 hours.
The disadvantage is obvious: the pores of the stone are open, it easily absorbs moisture - up to 16%. Autoclaved aerated block houses need cladding or plastering.
Aerated concrete is produced different densities and sizes... The material is selected taking into account the size of the house, weather conditions, and relief features.
- High strength is especially characteristic of autoclaved aerated concrete. Grades are produced that can withstand up to 5–5.5 MPa.
- Due to its high porosity, the material is much lighter than conventional material. A gas block house weighs much less. Therefore, it is not necessary to build a massive monolithic foundation under it. This significantly reduces construction costs.
- Porosity provides another useful property - lower thermal conductivity. Aerated concrete retains heat better, especially heat-insulating, so the wall from it can be made less thick. This also saves you money.
- The material can be sawn, cut, holes can be made in it.
- Gas blocks can be put not on a regular solution, but on glue. The seam is only 1-3 mm. This eliminates the appearance of cold bridges.
- The porosity also provides high sound insulation properties.
- Average frost resistance - produce materials with indicators from F35 to F150.
- Gas blocks have where big sizesthan ordinary brick. This speeds up and simplifies laying.
- The stone is at least 80 years old.
Disadvantages of aerated concrete for building a house are as follows.
- Autoclaved aerated concrete is capable of absorbing up to 16% of water from the air, and in contact with water - up to 50%.The walls of the building must be plastered and this procedure must be repeated. Compensates for this minus vapor permeability. Aerated concrete easily absorbs water. But it also gives away easily.
- The material is used for the construction of houses no higher than 5 floors. In difficult conditions, it is necessary to construct the frame of the building from reinforced concrete, and fill the wall with aerated blocks.
- To hold ordinary shelves, the self-tapping screw into the wall must deepen at least 10 cm.
- Foundation under the building can be light and shallow, however must be tough... Otherwise, shrinkage cracks form inside the blocks, and the building begins to deform.
Aerated concrete is readily used for construction residential and public buildings in the southern and middle latitudes... The use of the material in the northern regions is very limited, since its frost resistance is insufficient.
Strength and thermal conductivity of aerated concrete
- Structural - D600 and higher. Its porosity is relatively low, its strength is maximum - up to 5.5 MPa. The material is used for the construction of load-bearing and self-supporting walls in buildings up to 5 storeys high. The thermal conductivity of the gas block is, of course, higher than that of ordinary concrete - 0.183 W / m * C, however, it is insufficient for middle latitudes. Such a house should be insulated.
- Structural and heat-insulating - with a density of 400 to 600 kg / sq. m. The bearing capacity of the stone is less, so it is usually taken for the construction of two-story cottages. Thermal conductivity is higher - from 0.117 W / m * C to 0.147 W / m * C. Such a building does not need insulation.
- Heat insulating - grade D300 and below, withstands a load of no more than 1.5–2 MPa, which is not enough for the construction of load-bearing walls. Although one-story outbuildings are still being built from it. Thermal conductivity - 0.83 W / m * C and below. The material is used for insulation: the load-bearing wall is constructed from the wall of the D600 brand, and the inner row of the wall is laid out from heat-insulating blocks.
When choosing a material, its weight is also taken into account. The higher the density, the more the gas block weighs and the greater the load on the foundation.
Calculation of the amount of material at home
Before starting construction, it is necessary to calculate the volume of materials. You need to do this taking into account the peculiarities of masonry in different weather - in winter or summer, in different areas - lowland, steep slope, and other factors.
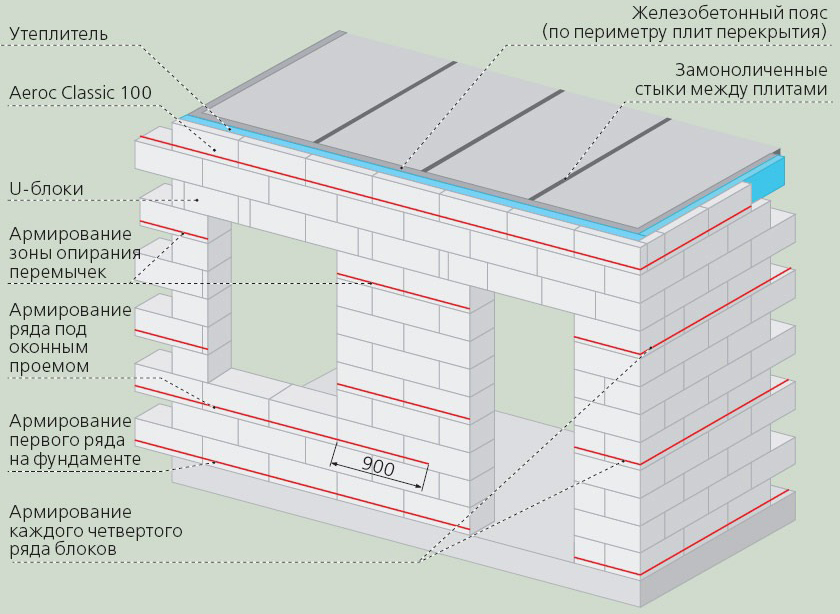
Reinforcement for reinforcing aerated concrete masonry

Aerated concrete blocks are laid with reinforcement. The only exception is a simple one-story building with a wall length of less than 5 m.Distinguish between horizontal and vertical reinforcement.
Aerated concrete, although it has sufficient bearing capacity and does not give strong shrinkage, is not resistant to bending load. Therefore, when the soil or base moves, cracks appear in the thickness of the material. Subsequently, they come to the surface, and the wall collapses. To avoid this, apply horizontal reinforcement: grooves (grooves) are cut out in the surface of the block and steel rods - reinforcement are laid in them. The diameter of the latter is 0.02% of the brick thickness.
Number of fittings calculated based on the height of the building and other parameters:
- the first row and the last one before the overlap must be reinforced;
- every 4th row in the wall is strengthened, the length of which reaches 6 m and more;
- the window sill and the doorway are reinforced.
When calculating, take into account and number of strobes... If the block is placed on the narrow side, it is a light construction, the strobe is made 1. If the wall is thick, 2 grooves are made and 2 rods are laid.
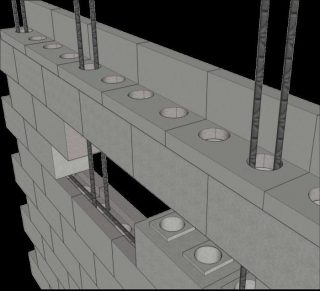
Vertical reinforcement connects the foundation to the floor. The need for it arises if the house is being built in a seismically active area, located on a slope, storms and hurricanes are frequent in the region.
According to the rules, reinforcement is performed not as masonry, but after the wall is built... Grooves are cut out under the reinforcement in the surface, rods are laid and tied to the upper and lower chord. Anchors are placed under the vertical elements in the foundation. The corners must be reinforced. Additional architectural elements are also subject to reinforcement.
Aerated concrete blocks
The easiest way to calculate a gas block for laying is using a special calculator on the site. The calculations are not difficult, you can do them manually. Taken into account:
- wall thickness - it determines the masonry method: in 1 row, in 2 rows, with a poke, on the bed;
the dimensions of the gas block - they differ from different manufacturers, and the blocks for the wall and partitions have different dimensions; - wall area minus window and door openings;
- dimensions of architectural elements - columns, ledges;
- the height of the building.
The calculation of aerated concrete is completed, increasing the total by 10-15% - for battle and masonry mistakes... Then the number of blocks is recalculated into cubes - this is more convenient.
Gas blocks are forbidden to be used in the construction of the foundation, therefore, only the area of the walls is taken into account in the calculations.
Construction features
Gas block laying is performed 2 ways.
- For cement mortar - a standard mixture is used. The composition is applied to the front surface of the block and to the side. However, this method is not recommended for gas blocks.
- On glue - a special mixture is used for laying aerated concrete. The composition is chosen taking into account the construction time - winter or summer, and the temperature in winter. If you are building a house in the cold season, you need to take frost-resistant glue.

Masonry technology for the first and subsequent rows
When constructing buildings from aerated concrete, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of this material. Step by step instructions includes the following recommendations.
- The foundation is carefully waterproofed, otherwise the porous material will draw water from the soil.
- The first row is placed on a cement-sand mortar. The mixture allows you to even out the slightest irregularities and differences in the height of the foundation.
- The corner blocks are laid first and carefully leveled. The stones are connected with a cord and the rest of the bricks are laid on it. Correct the position of the stones with a rubber mallet. The first row should be perfectly centered both horizontally and vertically, as it defines the masonry of the rest of the wall.
- The first row must be reinforced. Steel rods are usually used, but perforated steel tape and, in some cases, fiberglass are acceptable.
- The second and all subsequent rows are put on glue. The composition is applied in the thinnest possible layer.
If necessary, the surface of the row can be leveled using an aerated concrete plane.
Overlapping systems
The structure of the roof doesn't really matter, but the less weight the better. Mount under the roof or ceiling in the last row reinforcing belt... Usually a more massive rod is taken for him. The task of the belt is evenly distribute the load from the roof.
The reinforcing belt must be placed not only under the slopes, but also under the gables.
Options for finishing the facade of a house made of aerated concrete
Since gas blocks have increased hygroscopicity, the walls of a building made of this material need protect from rain and wind.
- Plastering - the composition has high vapor permeability and copes with its role perfectly. It prevents moisture from entering the pores of the stone, but at the same time does not interfere with the removal of moisture from aerated concrete.
- Staining - mineral, silicone or silicate paint is used - compositions with high vapor permeability. It is impossible to "plug" moisture inside the stone.
- Clinker cladding - has similar parameters in terms of vapor permeability, but does not absorb moisture at all, is not afraid of either the sun or frost. Great option, but expensive.
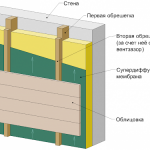
- Ventilated facade Is also an expensive solution. Siding, porcelain stoneware panels, stone are fixed on a pre-assembled frame. At the same time, a gap remains between the aerated concrete wall and the cladding in which air circulates.