Metal tiles are one of the most popular materials that are used in arranging the roof of private houses, summer cottages, cottages, salons, gazebos and pavilions. The coating is distinguished by its presentable appearance, strength, practicality and long service life. Roof waterproofing under metal tiles is critical to ensure the durability of the truss system and to protect the building from moisture.
Why is it needed and how is waterproofing arranged

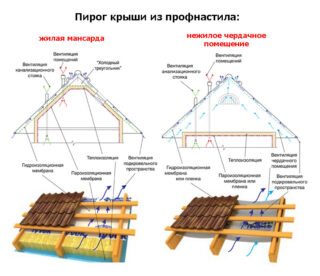
Installation of waterproofing under metal tiles should be carried out for warm and cold attics. The metal coating has high thermal conductivity. The temperature difference between the under-roof space and the street leads to the formation of condensation, and the risk of leaks cannot be ruled out.
The lack of waterproofing on the roof under the metal tile is fraught with the following problems:
- Damage to the rafters with their subsequent destruction. Water is absorbed into the wood, causing mold and decay. Changing the roof frame is difficult and expensive.
- Thermal insulation getting wet. From this, it loses its properties, ceases to protect the building from heat and cold. Even after drying, the thermal insulation is not restored.
- The appearance of rust. Without insulation under the metal tile, condensation accumulates on it, which leads to corrosion. Most quickly, it begins at the points of contact of the cladding with the crate and holes for self-tapping screws.
Moisture also negatively affects the interior of the attic. From its impact, furniture, cladding, household items and household appliances deteriorate.
General requirements for waterproofing metal tiles

According to the technology of roof installation, waterproofing under the metal tile is laid on the counter batten and pressed against the battens of the sheathing. This creates a gap for air circulation and moisture removal.
Waterproofing materials must have the following properties:
- absolute waterproofness and tightness;
- lack of attractiveness for birds, rodents and insects;
- UV resistance;
- sufficient strength and durability to resist constant air movement;
- immunity to temperature changes;
- the ability to do it yourself;
- incombustibility;
- ecological cleanliness;
- durability.
It is necessary to use a waterproofing material, the service life of which exceeds the resource of the roofing, so as not to carry out its removal and subsequent installation to replace the intermediate layer.
Materials used
To make the roof waterproof, materials of different structure and composition are used.
- Bitumen. A petrochemical product with excellent hermetic properties. Modifiers and oxygen treatment are used to provide resistance to temperature changes.
- Rubber-impregnated geotextile fabric. The canvases have sufficient strength, durability and flexibility, practically immune to heat and frost.
- Liquid rubber. The rubber-based product is used both independently and in conjunction with woven fabrics as an impregnation.
The choice of waterproofing is determined by the roof structure and the climatic conditions in which it will be used.
Types of waterproofing films
The following types of waterproof materials are used in construction:
- Membranes. Canvases that allow moisture to enter the street and block its penetration into the attic. The membrane under the metal tile is usually laid when using insulation.
- Painting. They are used on solid battens made of chipboard, plywood or boards made of boards. Can be applied directly to the back of the roof covering.
- Coating. Also used on sealed panels, including sheet metal and concrete.
- Film. Cloths based on polyethylene. It is best to purchase reinforced fabrics.
- Oleechnye. They are applied to the counter batten with glue or by melting the bonding layers. Forms a monolithic waterproof coating.
- Sprayable. Polyurethane foam forms a durable layer that protects the room under the roof not only from moisture, but also from temperature changes.
The choice of film is determined by the financial side of the issue, the purpose of the building and its estimated service life.
Waterproofing for roofs with and without insulation
An anti-condensation film is placed under the metal tile when mineral or cellulose wool, expanded clay or sawdust are used as insulation. This design forms a second gap that serves to drain off steam entering the filler from the rooms below.
When fixing the film, you need to think about the issues of its integrity and tightness. Laying is carried out from bottom to top with an overlap of at least 20 cm. The joints are glued. If a stapler was used to fix the membrane, the staples are sealed with mounting tape. Otherwise, the metal will rust and water will seep into the holes.
A cold room under the roof also needs waterproofing. This is justified by the fact that the joints between the panels are leaky. There is always the possibility of water getting into them during a rainstorm with a strong wind. Condensation is inevitable. The foil can be attached directly to the batten, on top of which the tiles are to be laid. This technique provides complete protection of wood from moisture.
Can I use roofing material
The coating is sold in rolls with slate or stone chips applied to the front side. The strips are highly durable and resistant to mechanical stress. Since roofing material does not allow steam to pass through, it is used only in cold-type roofs. Today, special gasket types of insulators are produced for internal work. They can be called in different ways, but they are distinguished by the absence of an external protective layer.
Vapor barrier for metal tiles
Superdiffusion membranes have the best performance characteristics. The canvases are attached from the inside of the rafters and covered with trim on top - plywood, clapboard, drywall, plastic panels or siding. A good vapor barrier allows moisture to pass through itself and prevents water and insulation fibers from getting inside the room. Fastening is carried out with staples, followed by sealing with tape.