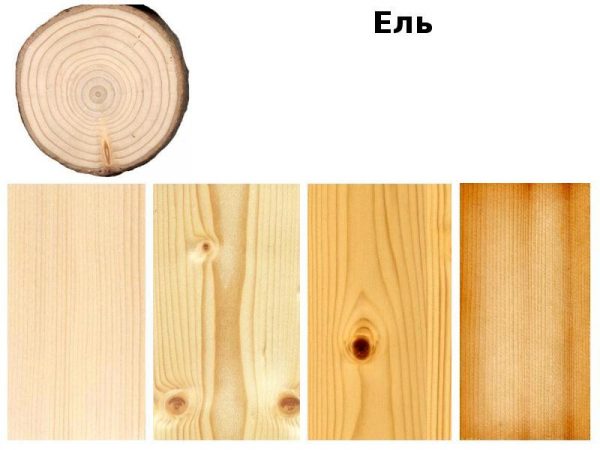
Round logs are sawn in the longitudinal direction, the resulting parts are processed on special equipment to obtain lumber. Distinguish between unedged, partially and fully edged products. Softwood lumber is in demand due to its high technical characteristics and reasonable cost.
Description of coniferous materials
- timber;
- bar;
- board;
- fence;
- sleeper;
- lagging;
- croaker.
TO timber include products whose width and thickness are more than 100 mm. Products are made from solid wood or made from individual boards by gluing. Two-edged beams are represented by products in which the opposite planes are processed. For three-edged and four-edged types, three and four planes are machined. Calibrated bars are dried products and sawn to size.
Bar - material whose thickness does not exceed 100 mm, and the width cannot be more than twice the thickness. Bars are made from thick boards. The planed view involves the processing of one longitudinal or two planes. Calibrated type - wood with minimum moisture content, dimensions according to standard. Produce solid bars, and assembled lengthwise from separate parts.
Bars of sizes are obtained from conifers:
- thickness and width - 75, 60, 50, 44, 40, 32, 25, 22, 19, 16 mm;
- length - 1.0 - 6.5 m graduated every 0.25 m.
Boards - sawn materials from beams or logs with a thickness of up to 100 mm, while the width is always greater than twice the thickness. There are edged, one-sided-edged and unedged products - the groups are divided according to the degree of edge processing, the presence of wane. Distinguish between planed and not planed boards.
The picket fence is cut out in the form of fence parts, the product is represented by uniform vertical or horizontal strips of the same section. Sleepers are made in the form of beams, using a structural (durable) type of wood.
Obapol and croaker obtained after sawing a square bar from a round trunk (lateral parts of the trunk). They are distinguished depending on the degree of sawing of the outer planes. There are elements with a half-sawn surface, with one plane removed, while the ends differ in different widths.
What belongs to lumber

The category includes products that have two or more parallel planes... The structural group is characterized by increased strength; it is used for load-bearing elements.
After making materials sorted in two ways:
- by machines - take into account the relationship between elasticity and strength in bending, compression, tension;
- manually - determine the dimensional accuracy, geometry, the presence of wood defects and their location on the product.
Distinguish trimmed and non-trimmed products... In the first case, the lumber is divided by length into the desired lengths. In the second, the products are left as long as the trunk was.
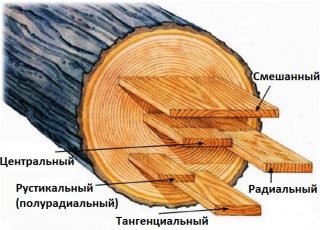
- radial cut - the elements are produced by dividing the logs along the radius of the annual rings;
- tangential sawing - the bars or trunks are divided along a tangent line relative to the annual rings;
- rustic - a group of mixed products, in which the features of the first two types are combined.
What types of wood are used
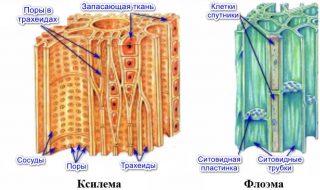
Conifers are composed of:
- tracheids - provide mechanical strength;
- parenchyma - store and distribute nutrients.
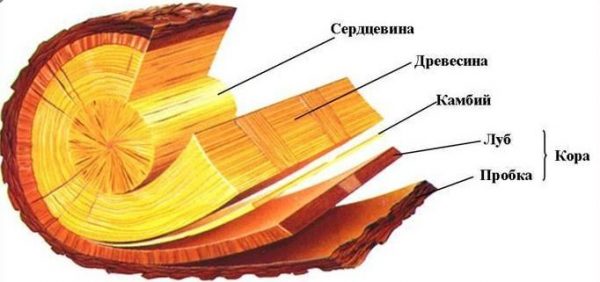
Resin ducts develop in the thickness of parenchymal cells. Spruce and pine have such formations, while yew and fir are absent. The section between bark and wood is called cambium.
For the manufacture of lumber use tree species:
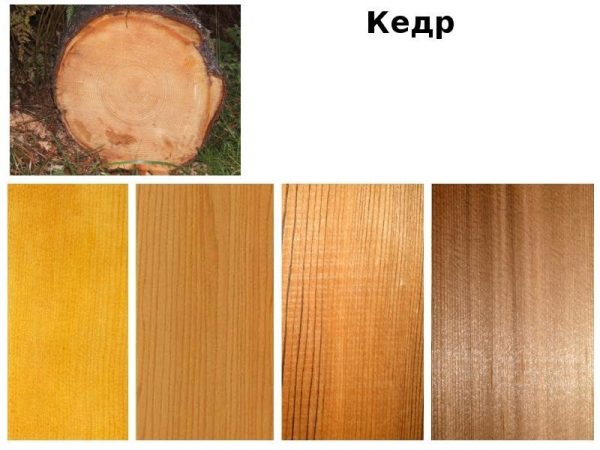
- cedar;
- larch;
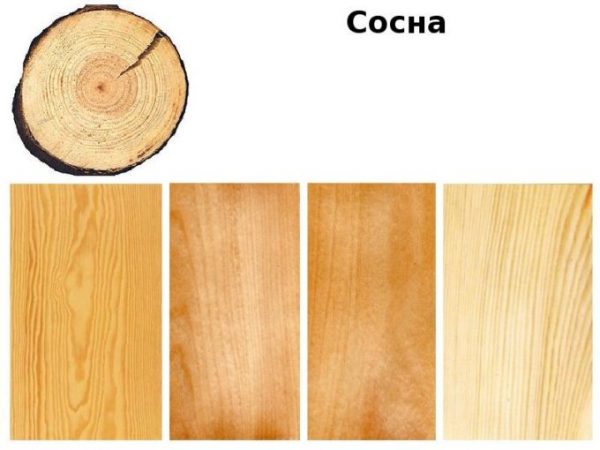
- Pine;
- spruce.
Wood cedar belongs to the category of natural antiseptics. There are no bacteria in houses from it, the air has signs of sterility. The wood is soft, with an expressive texture, smooth, poorly conducts heat. The breed is suitable for the manufacture of lining, floorboards, finishing materials.
Larch it is characterized by high strength (105 N / mm²), therefore it is used for decking and floor boards, decoration. The high content of resinous components allows larch products to serve for a long time even in humid conditions. Load-bearing structural elements are made of this rock; the rock has the lowest hygroscopicity.
Pine has a lower strength (100 N / mm²), but this difference makes processing easier. Pine sawn timber is classified as a universal type, it is used for various products, thanks to the resins in the wood, elasticity. Protective impregnations penetrate deeply due to their low density.
Spruce has a strength of 80 N / mm², but its ductility is superior to other types of softwood. The increased resinousness protects against moisture and fungi. The material is used to create handrails, decorate hallways loggias. Spruce is used to make musical instruments.
Scope of application
Due to its texture, strength and pliability in processing, wood is considered a practical and versatile material. for production:
- building materials;
- joinery products;
- decorative and finishing cladding;
- furniture;
- household and cultural items.
Under normal conditions, with good processing and protective impregnation, wooden products serve for several decades. They are obtained by milling, turning, sawing, planing.
- frame frame of the house (racks, lintels, ties, lower and upper strapping belts);
- overlapping and roofing (mauerlat, beams, purlins, trusses, rafters, lathing);
- door and window fillings (boxes, lintels, canvases, transoms, sashes);
- finishing elements (lining, block house, chipboard, fibreboard, cement chipboard);
- frame of partitions, panels for sheathing of internal walls, ceiling, floor, parquet, board;
- running products (cornices, stair railings, handrails, fillets, glazing beads, slats, skirting boards);
- fences, gazebos, awnings, arches, terraces, garages, sheds, and other yard structures.
For each type of product, coniferous wood of a certain type, moisture content is used. Wood quality and grade are determined by many parameters.
What are GOSTs for?

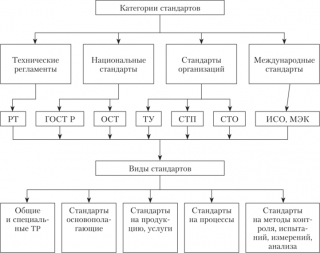
State standard contains list of quality requirements commercial products of sawn timber, it spelled out the standards for services and work of inter-industry significance. GOSTs are developed on the basis of scientific discoveries and practical experiments, taking into account the current international standards. GOST confirms that commercial products are checked for compliance with standards and meet safety requirements.
GOST differs from other documents that also contain regulatory requirements:
- TU (technical conditions);
- technical regulations;
- OST (industry standard).
Technical regulations contains a list of norms that ensure the preservation of health and life of people when using sawn timber. It spelled out the requirements for the transportation, storage, and sale of products. The GOST contains the dimensions of lumber, quantitative parameters, and the technical regulations determine the conditions of use.
OST regulates the requirements for softwood products at the industry level. Such documents are developed if it is necessary to clarify certain provisions that are not accurately spelled out in GOST. The requirements apply only to one branch of the economy or related divisions.
GOST 24454 80
The text indicates tolerances for sawn timber:
- by lenght upwards no more than 50 mm, downwards - 25 mm;
- by thickness with dimensions up to 32 mm - ± 1 mm, dimensions 40 - 100 mm - ± 2 mm, more than 100 mm - ± 3 mm;
- in width for edged products with dimensions up to 100 mm - ± 2 mm, more than 100 mm - ± 3 mm;
- no tolerances are indicated for materials up to 1.5 in length.
The tables show the nominal parameters for the width and thickness of lumber with parallel (edged) and non-parallel edges (unedged). If the consumer needs other sizes, it is allowed to produce sawn timber to order.
GOST 8486 86
By the quality of wood and processing, lumber is divided into several varieties:
- selective;
- first;
- second;
- the third;
- fourth.
There are technical requirements for moisture and antiseptic treatment. Recommendations for the choice of wood species for each type of sawn timber are indicated. There is a special table in the appendix with recommendations for the appointment of products.