Slate is a classic roofing material. They are used to lay the roofs of multi-storey buildings, summer cottages, garages, outbuildings of any kind. Before such work, you need to calculate the required amount of slate.
Slate characteristics
The undoubted advantage of the material is the ability to lay it on slopes with an angle of 12 degrees. The wavy shape allows you to get rid of water and snow even with such an incline. They use material for covering both simple roofs and complex ones - hip and multi-gable.
GOST assumes 2 types of material:
- with a wave height of 40 mm and a step of 150 mm;
- with a ridge height of 54 mm and a length of 200 mm.
Slate sheets are produced not only in accordance with GOST, but also in accordance with TU, therefore, its dimensions vary within much wider limits.
Distinguish material by profile:
- unified: width 1125 mm, length 1750 mm, thickness 5.2-5.8 mm;
- ordinary - width 780 mm, length 1120 mm. thickness 6–7.5 mm;
- reinforced - with a width of 1000 mm, a length of 2800 mm and a thickness of 8 mm.
When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the sheet in order to determine the required amount for overlap. If this is not enough, the slate is laid with an overlap. The amount of overlap along the slope is determined by its slope, and across - only by the features of the material. If the sheets, taking into account the overlap, do not fit in a whole number, you have to cut a lot.
To minimize the number of scraps, you need to consider the format of the sheets. Available in five, six, seven and eight wave sheets. The most profitable are the six- and seven-wave models, since after deducting the area of overlaps, they are characterized by the minimum difference between the usable and the total area in m². In addition, with a small thickness, such slate does not constitute a large load on the walls and foundation.
On roofs with a slope of more than 15 degrees, the overlap is 1 wave, with a slope of less than 15 - 2 waves. On sheets, the last wave has a slightly smaller radius to ensure a tight fit of the material. The amount of overlap when overlapping the lower sheet with the upper one also depends on the slope angle: if it is more than 15 degrees - 160 mm, if less - at least 200 mm.
Laying 5- and 6-wave sheets is more difficult. Due to the smaller slate area, the overlap area has to be increased, which is unprofitable. However, such material usually has a large thickness, is characterized by increased frost resistance and strength. 5- and 6-wave sheets are usually used for roofing industrial buildings, warehouses.
Calculation of material per slope
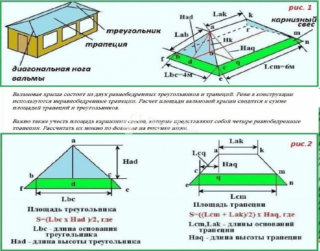
- The length of the ramp is divided by the width of the slate that is going to be used. Add to the 10% overlap rate and get the number of sheets for 1 row. If the roof is gable, the resulting value is simply multiplied by 2.
- The length of the eaves overhang is added to the distance from the ridge to the eaves. Divide the amount by the length of the slate sheet and add 13% to the overlaps. This is how they determine how many rows need to be laid to overlap the ramp.
- The number of sheets in a horizontal or vertical row is multiplied and the total is increased by another 5% for trimming.
This method is used to calculate the volume of material and for more complex structures: hip, half-hip, hip roof and even a mansard roof. For symmetrical options - hipped, it is enough to multiply the calculated amount by 4. In the rest, the amount of material for the short and long slope is calculated separately.
If the calculation of slate is carried out for the attic, it is necessary to take into account the area of the ventilation ducts, dormer windows, and the chimney.
When laying in difficult areas, the sheets sometimes have to be cut very strongly or cut diagonally. In such cases, it is believed that 1 whole sheet is needed to overlap, since its trimmings, and even complex shapes, can hardly be used in another area.
other methods
In such cases, a sketch of the roof is made - each slope separately. Then, rectangles are cut to the size of the slate sheet on the same scale and taking into account the overlaps. In the drawing, rectangles are superimposed on the ramp to determine the number of elements. Here it is not possible to save on pruning and you have to come to terms with the fact that almost 25% of the material will turn into construction waste.
You can calculate the number of slate sheets using online calculators. Most of them calculate roofs with slopes in the form of a rectangle, but this option also saves time.
In order for the online calculator to perform the calculations correctly, it is necessary to enter the maximum of known data: the angle of inclination of the ramp, its width and length, the amount of overhang, and the type of material.
Calculation of other components

When arranging the roof, there is a need for some additional elements. Under the slate, you need to build the correct crate. Take for it bars with a cross section of 5 * 5 cm for a regular sheet, and 7.5 * 7.5 for a reinforced one. Instead of timber, you can use unedged boards.
For the lathing, it is recommended to buy coniferous wood, like spruce, larch, pine. You can take grade 2 or 3.
- Calculations are performed taking into account the installation step. Boards are attached at a distance of 50–60 cm under a regular slate, and 70–80 cm under a reinforced one. The calculation is simple: the length of the slope is divided by the step size and the resulting value is rounded up.
- Each outer corner on the roof is covered with a ridge. For slate, a conventional galvanized sheet of the required width is used. In a gable roof, they simply measure the length of the point of contact between the two slopes and increase it by 5%. If the roof is more complicated - hipped, broken, you need to calculate the required value for each outer corner, and then sum it up.
- The inner corners cover the valley. The calculation scheme is the same: measure the length of the border between the adjoining slopes, taking into account the overhang or cornice.
- The number and length of gutters is more difficult to calculate. The drainage system depends not only on the size of the roof projection - along the perimeter, but also on the angle of inclination, since the latter parameter determines where additional gutters should be located.
It is quite simple to calculate the required amount of slate and additional elements for the roof. The calculation method depends on the complexity of the roof, the angle of inclination, the nature of the material used.