Bituminous mastic is a waterproofing material that has replaced hot bitumen. It retains its plasticity for a long time, which facilitates application. After polymerization, it forms a waterproof, resistant layer.
Description and purpose of bituminous mastic
The main inconvenience when working with natural bitumen is the need to heat the substance and apply it hot. The mastic can be applied cold, since it retains its plasticity longer and is more resistant to low temperatures. These properties are obtained by adding the following compounds to bitumen:
- dusty asbestos, brick or limestone powder - these solid components provide greater strength and hardness of the solidified layer;
- ground asbestos, chalk, peat chips - thickeners, imparting volume to the viscous composition;
- fibrous fillers, imparting bending and tensile strength to the coating.
According to the initial composition, they are distinguished several types of mastic.
- Regular - do not include modifying ingredients. They are used for coatings that are operated at a stable temperature without extreme cold or heat.
- Bituminous-polymer - are distinguished by a high degree of adhesion and good water resistance. The degree of polymerization on curing is higher here, which allows for a more reliable coating.
- Bituminous rubber - have anti-corrosion properties. They are used for waterproofing metal structures.
- Rubber - liquid rubber. Differs in the highest elasticity and durability.

Unlike bitumen, mastic does not need to be pre-diluted. This is a finished product that you can use right away.
Properties and characteristics
Mastic hot application when applied first heats up to + 150 ° С... This is the first analogue that began to be used instead of bitumen. Nowadays it is used very rarely, usually in order to glue roll roofing material to the base.
Mastic apply only on a horizontal surfaceb, because it spreads. Layer thickness no more than 2 mm... The advantages include the high strength of such a layer, elasticity and the complete absence of shrinkage.
Bituminous mastic cold applied used much more broadly. It does not need to be heated, it is ready for use. The mixture spreads poorly, so it can be taken for waterproofing horizontal and inclined surfaces.
Cold mastic is fireproof, it is used even when working in the cold. At very low temperatures, the mixture must be warmed up to + 30– + 40 ° С... The composition is used as a roofing material, as a coating waterproofing, as a filler and sealant for seams and joints.
Comparative characteristics of cold and hot bitumen mastic are given in the table.
| Solvent-based cold mastic | Cold water based mastic | Hot mastic | Bitumen | |||
| Parameters | Roof | Foundation | Roof | Foundation | Roof | Foundation |
| Thickness of 1 layer, mm | 1,0 | 0,5-1,0 | 1,0 | 0,5-1,0 | 2,0 | 1,0 |
| Consumption per layer, kg / m2 | 1,0-2,0 | 1,0-1,5 | 1,5 | 1,0-1,5 | 2,0-2,5 | 1,0 |
| How long does it dry at 20 ° C and 50% humidity, hours | 24 | 24 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 24 |
| Temperature at which work can be performed, ° C | -10 to +40 | -10 to +40 | +5 to +40 | +5 to +40 | +5 to +40 | +5 to +40 |
| Substrate moisture content, not more,% | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 |
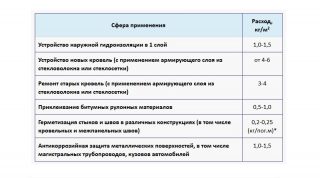
Areas of use
- for covering flat and pitched roofs, both as a roofing material and a substrate under the flooring;
- for waterproofing foundation, concrete sites, pipelines;
- for insulation of pools, fountains, artificial ponds and other hydraulic structures;
- for sealing joints and waterproofing coatings under the screed and self-leveling floor, under the ceilings, under the floor on balconies, in garages, in sheds.
Mastic is often used as a bonding layer when laying soft roofing materials such as ondulin, bituminous shingles or when laying a substrate on the floor.
How to work with bituminous mastic
Working with mastic starts with surface preparation. It must be clean and completely dry. Remove dust and dirt, wash. After the surface has completely dried, a primer is applied.
After the primer layer has frozen, they begin to apply the mastic.
How to dilute
Usually solvent addition is 10–20%... If there is too much of it, the mastic will turn out to be liquid, and it is quite difficult to thicken it - you need to add the filler that is part of the composition.
The composition based on organic solvents does not need to be diluted.
How to calculate consumption
- If the angle of inclination is up to 10 degrees, the mastic is applied in 3 layers... Each layer is applied after the previous one has dried, and a reinforcing fiberglass mesh is placed between 1 and 2. The layer thickness is 3-4 mm. To calculate the consumption, you need to calculate the roof area, multiply by the layer thickness and increase by 3 times.
- If the roof is tilted at an angle 10-20 degrees, the mastic is applied in 2 layers... The thickness is the same.
- If the angle of inclination more than 20 С, 1 layer is enough mastics for a reliable coating.
If mastic is required for waterproofing not only the surface, but also individual elements, such as chimneys, ventilation holes, the result of the calculations is increased by 5%.
How to apply correctly
Bituminous mastic can be applied in 2 ways: manually and mechanically.
With the manual method the composition is poured over the surface and leveled with a spatula. For difficult areas, use stiff-bristled brushes and short-haired rollers.
Mechanized method assumes the use of a spray bottle.It delivers the mixture at a pressure of 150 bar, which allows for an even, uniform coating even over very large areas. However, only models designed for viscous liquids are suitable for working with mastic.
Mastic applied according to the following technology.
- Before applying the composition should be kept at room temperature for 1 day. It is not necessary to melt it specially.
- Following the instructions, add a solvent to the mastic, if required... Mix thoroughly. If the mixture is applied by spray, mixing is done directly in the apparatus.
- Pour a certain volume onto the prepared surface and, using a mop, scraper or spatula, distribute the mixture. Layer thickness from 2 to 4 mm.
- A layer of mastic dries from 1 to 3 days... After complete drying apply the second layerif there is a need for it.
The waterproofing layer reaches the same thickness as the covering layer. The adhesive layer is thinner - 1–2 mm.
Helpful Tips for Beginners

To make the mastic last as long as possible, fulfill the following recommendations.
- On vertical surfaces, the material is applied in 2 layers, not less.
- To make the coating even, apply the mastic step by step, in strips from the top of the structure to the bottom.
- A large horizontal area is treated in the same way - stripes.
- When mixing mastic with solvent, it is best to use drill mixer attachment.
- You need to work with mastic in respirator, protective gloves and clothing.
- In the room where waterproofing with mastic is performed, a very good ventilation... But still, every 20 minutes you need to go out into the fresh air.
The material is flammable and fire hazardous. Do not leave cans with the composition near fire or heating objects. It is forbidden to smoke during work and near freshly laid surfaces.