Brick walls are erected all year round, regardless of the weather, but in winter, the masonry has its own characteristics. At negative temperatures, cement and liquid freeze and lose their working properties. Additives that slow down icing are added to the composition, the solution is heated in various ways. Such procedures are necessary, especially if the brickwork is done by hand.
Features of winter masonry

In frost, the reaction of cement and water is disrupted, as a result, the mixture does not thicken or harden. After thawing, a mass is obtained that does not withstand the loads. Building elements in the solution do not adhere properly, therefore, the stability of the structure suffers.
The building design (working part) contains certain recommendationif brick laying on the street is planned for the winter:
- given permissible wall height for a specific thickness to which structures can be erected in winter at temperatures below 0 ° C;
- advises on the device of temporary devices to support the walls during thawing;
- described specifics of work, a list of necessary additives, the composition of the solution, instructions are given on the brands of cement.
The structure of the bricks collapses when moisture freezes in them. An ice crust forms on the surface of the components of the solution, which prevents the interaction of, for example, cement with sand.
Solution requirements:
- when the temperature drops below -20 ° С, the temperature of the mixture should be approximately + 15 ° С;
- when working in a gusty wind of more than 10 m / s, the temperature of the composition is increased by another 5 ° C above the recommended indicator;
- to prepare the mixture, you must not take water heated to more than + 80 ° C and sand with a temperature of more than + 60 ° C.

The reasons for the deterioration of the properties of the solution and the resulting risks

Hardening begins when a chemical reaction occurs between water and cement molecules. The reaction slows down with a decrease in temperature, and at 0 ° C it completely stops. A drop in temperature below zero degrees leads to freezing of free water, which will no longer interact with cement.
Processes take place in the mixture:
- the solution ceases to set as long as there is liquid in it in the form of ice;
- frozen water increases its volume (up to 9% of the total cubic capacity), pressure rises in the pores, the structure of the cement composition is destroyed;
- if the solution managed to gain some strength before frost, the violation of structural bonds leads to a persistent decrease in this indicator;
- the set of strength stops completely, if in the next 28 days (the time of formation of one hundred percent strength) the temperature does not rise above 0 ° C.
At the moment the liquid crystals thaw, the hardening process could resume.But the destroyed structure and numerous voids do not allow this to be done fully, although some positive dynamics can be noted. The obtained strength after thawing is insufficient to contain the bricks in the masonry. The mixture loses its elasticity, becomes brittle, cracks when forces occur, for example, if floor slabs or beams are being installed on the wall.

When preparing the composition for work in frost use additives... Bricklaying in winter is carried out in compliance with receptions:
- the thickness of the seam is kept stable on all plots in horizontal and vertical rows, they perform bandaging of the seams, strictly observe the ordering scheme;
- when stopping masonry even for a short period of time, vertical joints are filled with mortar between the butt and spoon walls;
- unfinished area is covered with roofing material.
When the work is resumed, the frozen cement mixture and ice are knocked down with a trowel or other tool, they pay attention to the strict observance of the verticality of the fences.
Brickwork technology at subzero temperatures

The temperature for laying bricks on the street should be above zero, but if a cold snap has come to the region, a heated mixture is used, dry ingredients are introduced during cooking, and the ice crust and adhered snow are checked and removed on the bricks.
Additionally use one of the ways:
- masonry in thermoses;
- the device of greenhouses;
- freezing method;
- heated masonry;
- introduction of additives.
Each of the options helps to maintain the most convenient conditions for the start of the reaction of cement particles with liquid molecules... With such procedures, brickwork becomes possible in cold weather at temperatures below zero.
Recommend application the same brand of mixture along the entire length of the walls, it cannot be changed on different masonry plots. Other recommendations:
- the heated solution is produced within half an hour;
- defrosted compositions are not reused, and hot water is also not added to the cooled solution;
- for preparation, take sand that was stored in a warehouse, and if it was in an open space, it is heated before introduction.
If the option with antifreeze additives is chosen, the proportions according to the manufacturer's recommendation, as well as the technology for adding to the cement composition, are clearly observed.
Masonry in thermoses

The method is based on the retention of heat, which is released during the chemical interaction of cement with water in the mass. Use thermal insulation shell - this method is relevant at outdoor temperatures up to -5 ° C.
The essence of the technique:
- a large amount of insulation material is required;
- the effect of a thermos is created over the entire surface of the masonry;
- the laid brick is covered with layers of material with low thermal conductivity (every 3-4 rows);
- the solution will release energy during the reaction, but it will not go outside, but will remain in the mass of the masonry;
- as a result, the temperature of the array will turn out to be positive, so the solution will harden under the right conditions.
Initially, a heated cement composition is used, the speed of work is increased compared to the standard situation. To increase efficiency, each brick is heated with a blowtorch or gas torch. So they put silicate and clay ceramic bricks of any kind.
The disadvantages are the possibility of laying only with a slight cold snap and low productivity. The worker spends time heating up piece elements.
Hothouse device

In the area of the construction site they are building frame structure made of wood or metal to protect the site from precipitation and cold. Heating elements are installed inside to increase the internal temperature.
Use units with installation of a step-down transformer:
- on diesel fuel;
- gas convectors;
- electric or infrared heaters.

Freezing method
A warm liquid is used in the batch, while changing the brand depending on the climate outside the window:
- up to -3 ° C, take the solution unchanged;
- the average temperature during the day is -20 ° С - the brand increases by one value;
- frosts below -20 ° С - the brand is increased by 2 values.
The method assumes reliable maturation of thawed and matured masonry. The ambient temperature plays a role.
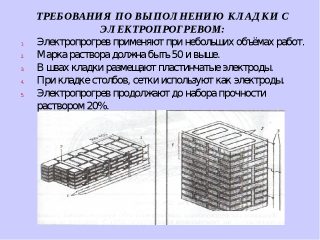
Electrically heated masonry
Process rules:
- steel rods are staggered equidistant from the masonry array at a distance of 21 - 50 cm in every second row;
- the protruding ends of the electrodes are connected into a system that is carefully insulated;
- are connected according to the principle "one rad - one phase" for a uniform change of electrical connections;
- the value of the current is regulated depending on the thickness of the wall, for example, exposure to 220 W will heat the fence 1.5 meters thick by 30 ° C.
According to a preliminary calculation, 75 W of voltage is needed to heat a standard wall of 2 bricks (50 cm), but the calculations are trusted by professionals so as not to end up with a weakened masonry in the spring. The decision in favor of electric heating is made after comparing the efficiency and cost of installing equipment, energy consumption.

Additive injection method
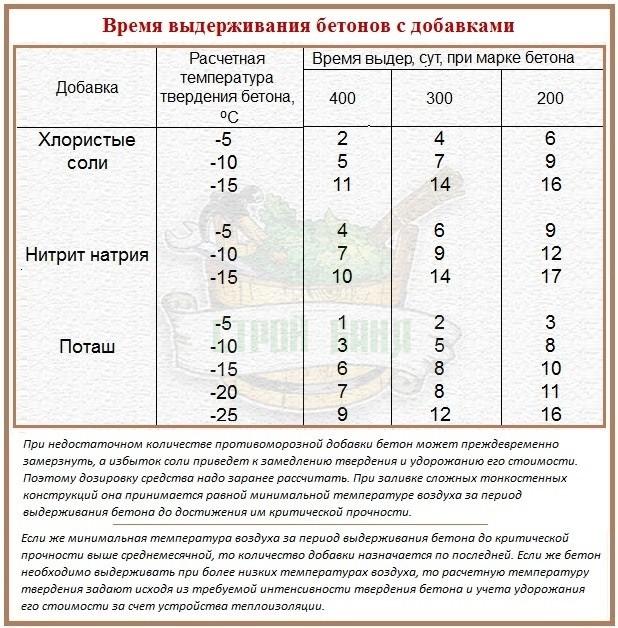
Antifreeze additives are an effective way to keep brickwork at a temperature down to -25 ° C.
Modifiers affect the hardening process:
- reduce the setting time;
- provide normative parameters of hydration;
- increase the mobility of the solution;
- increase the final strength indicators.
The introduction is carried out on the basis of a proven concentration, while safety rules must be observed, respirators are worn. Chemical additives are not used in residential construction in order not to increase the health hazard of harmful emissions.
The solution is used substances:
- calcium chloride;
- sodium nitrate, calcium carbonate (potash);
- calcium and sodium salts (formates).
Potash cannot be used for assembling silicate stones; it reduces their characteristics. If the masonry contains metal reinforcement, sodium chloride and calcium corrode it.
Builders use liquid soap in order to save money on the purchase of professional drugs. It is an inexpensive way to reduce the volume of cracks, cracks and delamination in the mass. Liquid soap does not affect the hydration of the binder.