The brand of brick or stone is an indicator that directly reveals the main characteristics of the product. In addition, marking is carried out taking into account state standardization to indicate additional qualities of the material.
What does a brick brand mean?

GOST 530-2012 defines the basic parameters of bricks and stones. Among these indicators, the following characteristics are taken into account:
- dimensions;
- strength;
- water absorption;
- frost resistance;
- fullness.
Each batch of building materials is marked with an alphanumeric code that contains information about the product. This allows it to be used in accordance with the purpose and operating conditions.
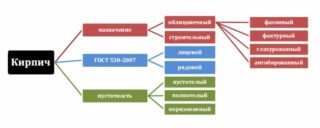
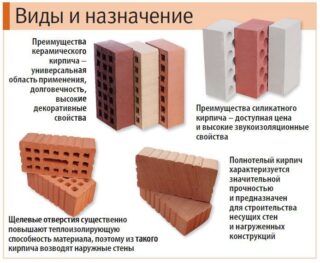
According to the method of manufacturing technology and material, bricks are: K - ceramic, S - silicate, W - fireclay. They are used in various construction industries, for the construction of special parts of buildings, as well as in cladding and other works. They differ in the way of production and resistance to extreme temperatures and loads.
The most fragile and unsuitable for the construction of structures is silicate brick. Ceramic is the most common. This is due to its high indicators of reliability, resistance to loads, as well as temperature changes. However, these indicators may differ depending on the brand, as well as the presence of additional impurities in the composition.
Fireclay or special bricks are mainly used for masonry structures exposed to extreme temperatures.
Type and characteristics marking
- KR - brick;
- KRG - brick with horizontal voids;
- KM - stone;
- KMD - additional stone.
The area of application is also indicated in the labeling. It can be P - ordinary brick, which is used for masonry, or L - front, used in facing work.
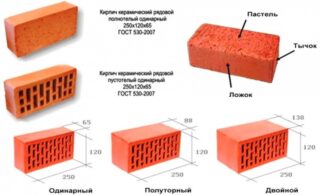
- O - single;
- E - "euro";
- M - modular;
- U - one and a half;
- IG - thickened with horizontal voids;
- K - stone, double brick;
- KK - large-format stone;
- KG is a stone with horizontal voids.
These markings indicate the dimensions of the product. The thicker it is, the easier it is to build walls from it. However, weight and cost increase with size.
Letters are used in the marking, indicating the features of the molding: PO - full-bodied and PU - hollow.
Solid brick has voids up to 13%. This does not allow it to be used as the only material for masonry exterior walls. This state of affairs is due to the increased thermal conductivity of the material. Hollow bricks have voids up to 45%. This improves the performance of thermal insulation and makes the product lighter. However, the strength is reduced. It is used for laying lightweight walls.
Brick standardization
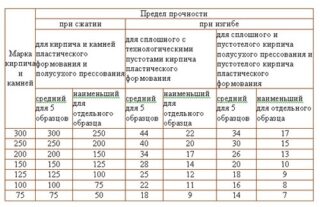
A batch of bricks undergoes mandatory tests for compliance with the strength and frost resistance indicators. As a result of these tests, a specific brand is assigned. To check, 5 items are randomly selected from a brick lot. Strength is determined by the ultimate loads applied to the product. For cold resistance tests, a brick is taken and soaked in water for 8 hours. After that, freezing is performed and the cycle is repeated until its characteristics change.The more cycles it withstands, the higher the indicator in the marking.
Strength grade
The strength grade of ceramic bricks is determined by the bending compression ratio. It is denoted by the letter M, supplemented with a digital code indicating the level of load that an ordinary brick can withstand by 1 square centimeter. To date, 8 grades have been established in terms of strength - from 75 to 200 with a step of 25 and extra strong bricks - M-250 and M300.
There are special heavy-duty bricks that are used in responsible construction. In the framework of ordinary urban planning, such products are not in demand due to their high price.
Frost resistance
This indicator indicates the resistance of the product to freeze-thaw cycles in moisture-saturated conditions. There are a large number of frost resistance markings - from F15 to F-300. The higher the number, the more cycles of complete freezing-thawing the brick can withstand without damaging its structure. These indicators are extremely important when building in areas with extremely low temperatures.
For the middle lane, when building conventional structures, this indicator does not have to be the maximum. Enough average values for the exterior and less for the interior.
Use in construction
Silicate brick is made from a mixture of quartz sand, water and lime. After molding, the brick mass is autoclaved. It is exposed to steam and increased pressure. Its main disadvantage is its high weight and high thermal conductivity, coupled with low moisture resistance. Silicate brick is most often used for the manufacture of load-bearing structures, but its low water and heat resistance rates do not allow it to be used for laying the inside of chimneys, as well as for erecting walls in rooms with a high level of humidity. This product is cheaper than ceramic.
Special bricks - fireclay, stove bricks are used as material for laying stoves, fireplaces and internal parts of chimneys. Their feature is an increased level of heat resistance. They are able to withstand extremely high temperatures in excess of 1000 degrees Celsius without modification.