Mastic is a material for filling cracks and waterproofing surfaces, obtained by mixing different components. The purpose of the treatment is to create a waterproof layer or joint of elements. After application, the coating hardens due to the evaporation of the thinner or as a result of the interaction of its components. The consumption of bitumen mastic for 1 m² of waterproofing must be known for each application in order to correctly calculate the volume for the purchase.
What is bituminous mastic
The mix for production includes Components:
- binder based on bituminous resin;
- rubber granule particles;
- polymer additives;
- synthetic oils;
- antiseptics, herbicides;
- fillers made of chalk, sand, gypsum, lime and other materials.
The mastic is produced in the form homogeneous plastic mass with synthetic or organic fillers. The mixture is modified with additives, therefore, the modern version of the insulating mastic is distinguished by good performance and improved technical characteristics.
Bituminous mastic for waterproofing is applied to rusty metal on a damp roof plane. A high-quality mixture quickly sets, dries, and reinforcing threads are present in its composition to compensate for vibrations of the roofing or road base.
Properties

Bituminous waterproofing is a frequently used technology that effectively copes with the task of protecting against moisture, while not requiring large costs for arrangement.
Mix qualities sets bitumen:
- excellent adhesion to concrete, wood, metal, strong connection with ceramics, foam blocks, adhesion strength is 0.2 - 1.5 MPa;
- complete waterproofness due to its dense (non-porous) structure;
- under dynamic forces, the material shows flexibility, does not collapse when the gap between the roofing sheets is compressed and diverged;
- durability service without repair depends on the operating conditions, and ranges from 5 to 25 years.
Acting maintaining the flexibility of the layer in frost... Such efforts are regarded as tensile strength at low temperatures. The test parameter indicates the degree of elasticity during boundary cooling, asserts the lower indicator of the operating range.
Application
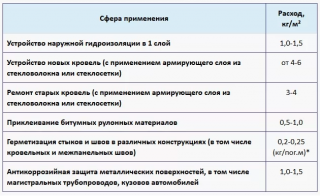
Other use cases material:
- when installing road surfaces as waterproofing;
- for vapor and moisture insulation of strip-type foundations, piles, pillars, grillages, foundation beams;
- as a waterproofing layer on interfloor ceilings, especially in the area of the location of bathrooms and kitchens;
- when insulating the walls of the bathroom, other damp rooms;
- during the construction of swimming pools, reservoirs, various tunnels, external pipelines;
- inside the basement for waterproofing walls from soil moisture, under the floor screed.
The material can be classified as a universal type.It is used in places where it is difficult to apply an adhesive film due to the complex shape of the structures. Hot bitumen roofing mastic is a material that can be applied to curved and complex surfaces.
Varieties of bituminous mastic
By layer overlay method share types:
- cold solvent-based mastic;
- cold bitumen, diluted with water;
- bitumen-polymer;
- bitumen-rubber;
- bituminous waterproofing.
Solvent-based cold mastic includes modifiers, organic solvent (up to 80%) and fillers. The mixture is not heated before work; rollers, brushes, spatulas are used for rolling. The application process is faster.
Cold mastics on water consist of an aqueous emulsion of resin, fillers, emulsifiers, polymers and processing aids. The composition contains about 20 - 70% of oil products. The result is a non-toxic, fire-safe coating. This mastic can be used in residential buildings, rooms.
Waterproofing mastic differs in that over time volatile components are removed from the mass, therefore fragility appears, especially in winter.
Bituminous rubber the materials contain tar crumbs in the structure, which gives the mass improved qualities in the form of increased flexibility, stretchability, and resistance to external influences.
The introduction of polymers also increases elasticity, resistance to temperature changes, chemical and thermal resistance. Have polymer-bitumen of compounds, the resistance to deformation is increased, the material has the longest service life.
How to determine the expense

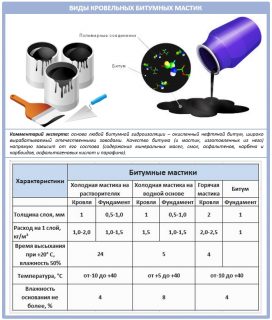
Mastic is characterized by dry residue indicator. It means the volume of a substance on a plane after the mastic has dried and hardened. The index is expressed as a percentage of the total consumption of the material used. The indicator means that a small dry residue leads to an overexpenditure of the original mass in order to obtain a layer of the required thickness according to the technology.
Most materials are characterized by a dry matter index 20 – 70%. The consumption of material with a high percentage will be 3 times less to form the desired thickness than with an indicator of 20%. In addition to the cost, the labor intensity of the work increases.
To find material consumption to the entire surface, you need to know:
- standard layer thickness;
- the amount of dry residue after curing.
For example, if the remainder of the material is 50%, 1 kg of mastic contains 0.5 kg of working substance and 0.5 kg of solvent. After drying, 0.5 kg of waterproofing will remain on the plane when 1 kg of mastic is applied.
After finding the specific consumption, taking into account the residue after curing and the thickness of the coating, determine the number of layers on the surface.
For waterproofing a roof using fiberglass, an amount of 2-3 layers of base material is required. In this case, 3 - 4 layers of bitumen mastic with a thickness of 1.5 - 2 mm will be required.
Consumption depends on the density of the mass and the temperature of the solution.
Consumption rates for different application methods
Thickness standards depending on the cold and hot method:
- mastic layer thickness for material hot lining method is not less than 2 mm;
- cold can be used thick not less than 1 mm.
For one square in one layer, cold material is consumed in a solvent 1 - 2 kg, bitumen cold mastic on water - 1.5 - 2 kg, hot mass will go 2 kg. The square of the coating is multiplied by the consumption of mastic, then multiplied by the number of layers.
Calculation for waterproofing the foundation

Foundations are of different types. It is easiest to calculate the flow rate for tape type... In this case, the squaring of the entire surface is found, which is required to be coated with the composition.
The procedure for determining the area:
- multiply the width of the tape by the length, get the horizontal area;
- the lateral height is multiplied by the length of the tape, then by 2 - the squaring of the lateral planes is obtained;
- sometimes you need to calculate the area of the ends;
- for each separate area, the area is considered, then the indicators are added.
To coat the foundation in one layer per square meter, 1 - 1.5 kg of cold mastic on solvents, 1 - 1.5 kg of cold mastic on water, and 2 kg of hot mastic are used.
The resulting squaring of the treated surface is multiplied by the flow rate squared, then multiplied by the number of layers. Foundation waterproofing involves at least two layers of the coating composition.
Calculation for roof waterproofing
Consumption of mastic paste:
- when laying in a cold way with two layers of fiberglass and three layers of mastic, the total consumption per square will be 3.5 - 6 kg;
- when applied with heating, the total consumption per square of the roof with the same composition will be at the level of 6 kg;
- if joints are to be filled between reinforced concrete floor slabs, then the consumption rate is taken at 145 - 157 kg for every 100 m of the joint (with a slab thickness of 200 mm).
The area of the roof is calculated, multiplied by the standard consumption. Since the maximum indicator is given for several layers at once, it is not necessary to additionally multiply by the number of layers.
Application technology
Further styling process:
- apply the mastic in an even, uniform layer;
- a layer of reinforcing membrane is placed on top of it, the seams are glued with a special tape, it is glued with bitumen;
- the second layer of the membrane is mounted so that the glass fabric overlaps the connecting tape by 20 - 30 cm, bitumen is poured under the liner inserts.
Bituminous cold or hot mastic is indispensable for spot or complete repair of roofing... Such a composition is applied to a damp surface of concrete, slabs, wood - other materials cannot cope with moisture.
Usually, the problematic area of the soft roof is cut with a cross in the problem area, the edges are folded back. Inside, mastic is applied in the required volume, then the edges are again brought to the center, pressed. Apply the mesh to make the patch.
Surface preparation is important in order to apply the mastic evenly. Before work, it is advisable to level the plane with mortars - this way it will be possible to avoid overspending.