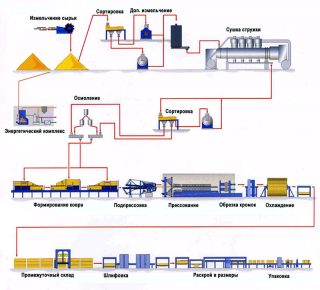
Hardboard is manufactured at the factory by hot pressing under pressure. The raw material is waste from the woodworking industry, combined with synthetic resins with the use of additives. The material belongs to the category of fiberboard, while the thickness of hardboard can be more than standard fiberboard, technical characteristics are also different.
- Material description
- What it consists of and how it is made
- Difference from fiberboard
- Characteristics and varieties
- Features of laminated hardboard
- Material type by density
- Other specifications
- Sheet sizes
- Marking and decoding
- Application and design
- How to choose
- Rules for mounting hardboard on a frame
- Is it possible to cut and what
- How to fix
- Features of storage and operation
Material description
The strength of the sheets depends on factors:
- thickness;
- varieties.
Grade increases with increasing densityThe thickening gives the material additional flexural strength and rigidity. Compressive and abrasion strengths correspond to the values of OSB (approximate strand board) and natural sawn timber. High performance allows the use of hardboard for a finishing layer on floors.
What it consists of and how it is made

Wood chips, campfire plants, processed in defibrators to obtain fibers, which are used as a base. For the outer layer, apply fine sawdust, sanding dust.
The addition of modifiers and binders improves performance:
- binder are formaldehyde and synthetic resins, which form a dense structure;
- polymer additives increase strength and resistance to mechanical stress;
- water repellents, for example, rosin, paraffin, increase the resistance to water;
- flame retardants increase fire resistance.
Sometimes binder resins are not used if wood fibers with a high content are added to the composition of the mass. lignin... The substance melts under the action of heating, joins the particles of the base.
- drying of raw materials in chambers, sorting by size;
- combining wood particles with binders in mixers;
- transfer of the mixture to the forming department of the equipment for the formation of a three-layer carpet;
- pressing the workpiece (temperature +200 - 220 ° С, pressure 30 - 45 kg / cm²);
- cooling in the sections of the fan-shaped mode of action.
The workpieces are sawn to size, trimmed, then sanded, and a perfectly flat plane of the panels is obtained. The material is stored before shipment on pallets in a warehouse with the optimal temperature and humidity of the atmosphere.
Difference from fiberboard

Materials fall into a general category, but they form different groups. Specialists called hardboard painted, varnished wood fiber panels or with another type of coating (laminated film, veneer, plastic).
Differences from fiberboard:
- higher strength;
- increased density;
- higher resistance to moisture thanks to the film.
Soft sheets belong to the fiberboard group, and hard sheets - to hardboard.
Characteristics and varieties
Light and soft varieties:
- LDF - 450 - 640 kg / m³;
- MDF - 640 - 840 kg / m³;
- HDF - 840 - 1000 kg / m³.
The corrugated layer on the back of the panels promotes good adhesion to the wall or floor.
Hardboard products are covered with veneer from two sides, since a one-sided coating will upset the balance of strength indicators of surfaces during operation, leading to deformation.
Material cost depends on hardness - the higher the indicator, the higher the price.
Features of laminated hardboard
Laminated film increases the strength of the material, makes it possible to apply a variety of drawings with imitation of natural materials... Laminated hardboard has a higher cost due to improved characteristics and long service life. Surface finishing layer allows wet cleaning using standard detergents.
Material type by density
Low density sheets weigh less, so they are installed if the wall cannot be overloaded, which transfers the load to the foundation of the house. Hardboard is also divided according to the thickness of the finishing layer, which can be from 2 to 4 mm.
Distinguish hardboard grades by density:
- T - soft versions with a density index of up to 1000 kg / m³;
- H - slabs of medium density up to 1100 kg / m³;
- FROM - material with the highest density up to 1200 kg / m³.
A square of sheets with a thickness of 2.5 - 3.2 mm weighs 0.5 - 3.52 kg, with a thickness of 4 - 5 mm has a mass of 0.8 - 5.5 kg. The difference in weight is due to the different density of the material. A square meter of slabs with a thickness of 6 - 8 mm has a weight of 1.2 - 8.8 kg, and with a thickness of 12 - 14 mm - 2.8 - 15.4 kg.
Other specifications
- semi-solid brands increase in size by 40% per day;
- solid ones swell by 20 - 25%;
- superhard - by 14%;
- with a refined plane increase by 10% of the original dimensions in thickness.
The moisture-resistant material is still not 100% protected, so it is not used in rooms where there is a direct hit of water on the finish. The edges of the material are especially at risk.
Ultimate tensile strength, the bend is different for each grade of hardboard:
- tensile strength for soft and semi-hard varieties is not determined, for hard ones - 0.3 MPa, superhard - 0.32 MPa;
- bending for soft sheets - 0.4 - 1.8 MPa, semi-hard - 15 MPa, hard - 33-38 MPa, superhard - 40-47 MPa.
Thermal conductivity material at the level of 0.045 - 0.095 W / mK.
Sheet sizes
Size range panels depending on density:
- soft material - length 3000, 2700, 2500, 1800, 1600, 1200 mm, width - 1200 mm;
- superhard, hard and semi-hard produced in lengths of 3360, 3050, 2740, 2500, 2000, 1800, 1700, 1200 mm, width - 2400, 1800, 1500, 1200, 610 mm.
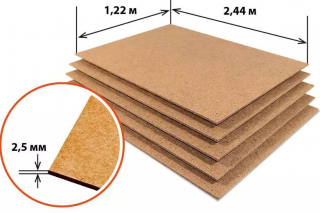
Most often, slabs with dimensions of 1200 x 2500 mm and 1200 x 2700 mm are ordered. For industrial use, the width of the slabs is 1800 mm, and the length reaches 6000 mm.
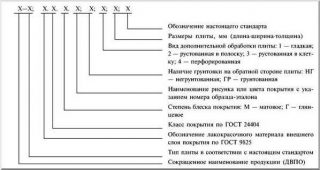
Marking and decoding
Grades are determined by the physical and mechanical properties of the material.
- letter M - soft material;
- PT or NT - semi-solid;
- T - solid with an untreated plane;
- TS - solid with surface finish;
- TSP - hard, with a thin woody layer and dyed;
- TP - solid with a painted surface;
- Tv - moisture resistant, untreated;
- TSV - moisture resistant with a decorative film;
- ST - superhard sheet;
- STS - super hard with laminated film.
The numbers next to the letters indicate the tensile strength. For example, CTC 250 means that the sheet is superhard, with decorative processing, it can withstand 300 kg per cm2.
Application and design
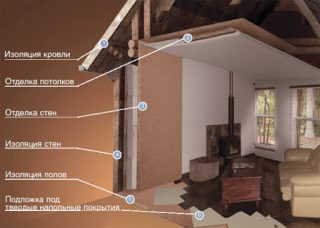
Hardboard is used in many areas, since they produce a variety of varieties that differ in decorative surface.
The material is used:
- as cladding of walls and ceilings, sheathing of partitions;
- as a substrate and floor finish;
- for the manufacture of furniture, the material of reduced density is placed on the walls, bottom and backs of the boxes;
- as a basis for oil paintings;
- for structures, in dry and moderately damp conditions;
- in the manufacture of doors;
- in the inner lining of cars, wagons;
- for the manufacture of containers, packaging.
Laminated film imitates various natural materials: marble, granite, basalt, sandstone. Many finishes in the form of different types of wood. There are drawings of stone and brickwork, concrete surfaces, fabrics, straw, and reeds.
How to choose
Hardboard contains synthetic resins and formaldehyde, therefore, for residential premises, a material with a low content of components is chosen (at a rate of no more than 1.3% of the total mass). This information is contained in the certificate of conformity provided by the supplier.
When buying, check chips on the surface, curvature of panels, delamination of the decorative layer. Irregularities indicate that the product has been exposed to moisture. Take into account the type of hardboard that is suitable for a particular job.
Rules for mounting hardboard on a frame

Frame method involves the use wooden slats with a section of 40 x 25 or 50 x 25, which is impregnated with linseed oil before installation.
In another embodiment, use galvanized profiles:
- CD - 60 - bearing profile;
- UD - 27 - strapping;
- Staple ES lengths 90, 120, 150 mm for installation and alignment of profiles.
The space of the frame makes it possible to add an insulating layer, sound protection, vapor barrier and waterproofing membrane. Installation step the slats are chosen so that the edges of the sheet are connected on the support, but the distance was in the range of 40 - 50 cm.
Is it possible to cut and what
Manual tools for cutting sheets to size are not used, even for low-density products. A saw with fine teeth and sharpening for metal is ineffective.
Use electrical tools:
- circular saw with a circle for wood;
- jigsaw with a nail file for wood.
Specialized suppliers (shops) provide services for cutting hardboard. Smaller dimensions make it easy to transport the slabs to the work site.
How to fix
Install panels on the frame and on the glue... For the second option, it is necessary to level the wall, floor or ceiling so that there is no distortion during installation.
Use compositions of various types:
- cement;
- polyurethane;
- bituminous;
- casein.

Features of storage and operation
Store slabs horizontally with wood lining, which are placed across the products. The length of the bars is equal to the width of the slabs, and they are placed in increments of 50 - 70 cm, so that the upper intermediate slats are above the lower ones. In large warehouses, special racks are installed. The sheets are transferred by turning them "on the edge".
Material care depends on the variety. Uncoated sheets are treated with paints and varnishes in order to be able to do wet cleaning. Boards with a film or plastic layer may be washed with a damp cloth, so that moisture does not get into the seams.