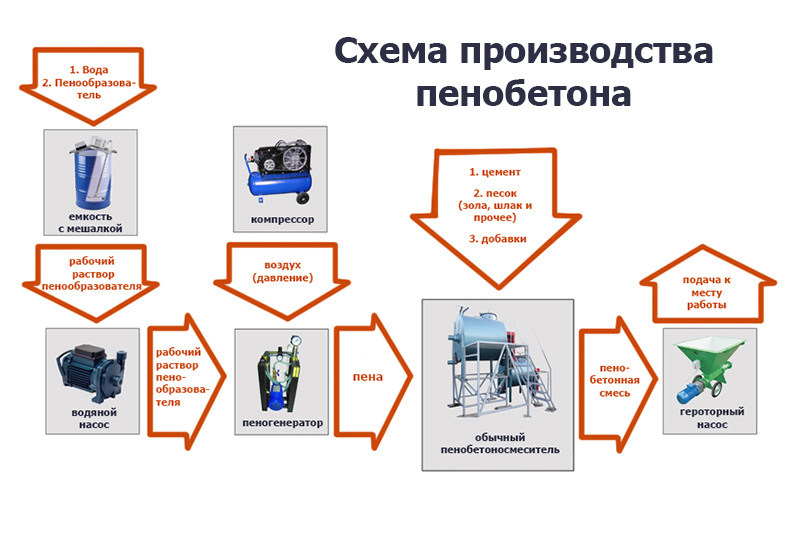
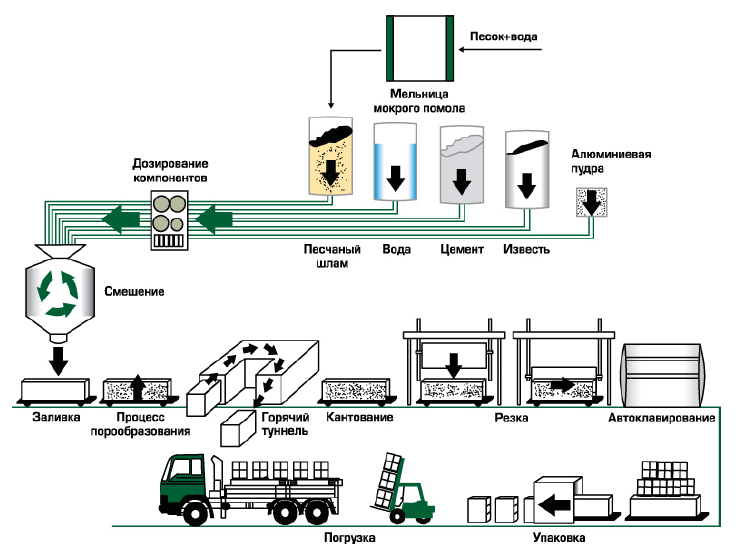
Developers who decide to build warm houses pay attention to foam concrete and aerated concrete, since it is low thermal conductivity that is one of the characteristics of materials. However, the blocks have different operational properties, which you need to know about already at the stage of construction planning.
General information

Aerated concrete is material with open small (1-3 mm) air pores, which communicate with each other and are located throughout the volume of the blocks. The open structure leads to the rapid absorption of moisture, which is why the walls must be subjected to a finishing covering finish.
In foam concrete, the pores are closed (except for those cut along the surface), which reduces water absorption, but does not cancel the protection of the surface of buildings.
Building materials are produced using different technologies from different raw materials, which implies differences in the construction of buildings, decoration and operation.
Raw materials and production
Both materials classified as lightweight fine-mesh concrete, however, the difference between foam concrete and aerated concrete lies in the composition of raw materials for production, strength and other important characteristics.
Difference between foam concrete and aerated concrete is in the way of forming a porous structure... In aerated concrete, bubbles are obtained as a result of a chemical reaction between lime and aluminum powder (paste), a previously prepared foam is introduced into the foam concrete.
Foam blocks
Two production technologies involve obtaining a porous structure due to the introduction of a foaming agent or ready-made foam obtained in foam generators into the blocks.
Classic technology:
- A foaming agent is poured into the foam generator.
- Cement and sand are mixed in the required proportions to obtain blocks of the required strength.
- Water and foam from a foam generator are introduced into the mixture.
- Stirring takes several minutes.
- The finished mixture is poured into containers for settling and hardening, which last about 12 hours.
The molds can be the size of one finished block or have a capacity of about 1 m3. In the second case, after the composition has solidified, the material is cut into products of the required size.
Barotechnology assumes the rejection of the foam generator, the foam concentrate is added immediately to the mixture with stirring. The small dimensions of the equipment make it possible to produce blocks at the construction site, but at the same time, the consumption of the chemical composition is significantly increased.
Dry mineralization method used in large industrial enterprises. Production is ongoing. Due to the introduction of surfactants into the composition, the finished product has ideally smooth walls.
Gas blocks
- Portland cement of grades M400 or M500 (up to 40%);
- very fine quartz sand (35%);
- lime powder (1%);
- aluminum powder (up to 0.05%);
- purified or distilled water (up to 30%).
In the manufacturing process tothe components are mixed. The chemical reaction of the interaction of lime and aluminum powder leads to the formation of gas bubbles, which creates a porous structure.
The composition is poured into containers.After the initial setting, the mass is cut into blocks of the required size.
To speed up the set of strength by blocks and preserve the structure, a 12-hour autoclaving at a temperature of 180 ° С.
When processing in an autoclave, shrinkage is reduced or completely absent, the blocks are stronger than when drying in air.
Comparison of materials
The foam block differs from the aerated block in consumer properties, technology for the implementation of masonry and finishing.
Advantages and disadvantages of foam concrete
Foam concrete is used for the construction of low-rise buildings. Due to its positive properties, it is popular with private developers.
During transportation, loading, unloading and masonry, care must be taken, since foam blocks easily break, chips and cracks appear.
Pros and cons of aerated concrete
Aerated concrete is relatively has recently become widespread. Discussion continues among builders and homeowners about the properties of the material, based on real-life operating experience.
The walls of aerated concrete blocks must be impregnated with deep penetration water-repellent primers and closed with a waterproof finish - this leads to an increase in the cost of construction.
Comparison of characteristics
It is appropriate to hold comparisonwhat is better to choose for construction: expanded clay concrete blocks, silicate or red brick, foam block or aerated block, since the construction technologies are similar.
The important parameters are summarized in a table.
| Characteristic | Foam concrete | Aerated concrete | Silicate brick | Ceramic brick | Expanded clay concrete |
| Density, t / m³ | 0,3 – 1,0 | 0,5 — 1,2 | 0,9 – 1,6 | 0,7 – 2,4 | 0,3 – 1,8 |
| Strength, kg / cm³ | 10 – 50 | 15 – 35 | 100 – 200 | 100 – 300 | 35 – 150 |
| Thermal conductivity, W / m ° С | 0,1 – 0,4 | 0,1 — 0,14 | 0,65 – 0,81 | 0,12 – 0,57 | 0,15 – 0,45 |
| Frost resistance | F50 –F200 | F35 - F 100 | F35 - F75 | F25 - F100 | 35 – 200 |
| Water absorption,% | 80 | 100 | Until 6 | Up to 12 | 50 |
Assessing the characteristics of materials, you can do the following conclusions:
- The strength of foam and aerated concrete blocks is approximately equal to, but not sufficient for the construction of buildings over two floors. For high-rise buildings, you should choose ceramic silt-silicate bricks, as well as expanded clay concrete blocks.
- It is more convenient to use foam blocks or aerated concrete, since the low specific gravity makes it possible to make products more overall, which means that the speed of laying will increase.
- The thermal conductivity of foam and aerated concrete is lower, which means less energy will be spent on heating. Modern materials are not inferior in frost resistance to classic and proven bricks and expanded clay concrete, which, with the correct construction and finishing technology, allows you to build durable houses.
- High water absorption involves the cost of protecting walls made of aerated and foam concrete from moisture, which increases construction costs.
Considering that the goods are packed and placed on pallets, the cost of delivering materials to the construction site will be approximately the same.
Basic requirements for use
Summarizing the experience in the construction of residential buildings and industrial facilities from foam blocks and aerated concrete, one can single out features of the use of materials:
- The foundation is calculated with a 50% safety factor. The material of the blocks actively absorbs water, increasing in mass. The fragility of the blocks does not allow guaranteeing the absence of cracks even with a slight deformation of the foundation.
- Blocks do not use for construction basements and basements.
- Walls are separated from the foundation reliable waterproofing due to high water absorption by blocks and reduced durability due to regular freeze / thaw cycles.
- For adjusting sizes use hand saws, drilling hold with a concrete tool. For wall mounting items use special dowels.
- Foam blocks stack for cement-sand mortar or special adhesive composition, gas blocks exclusively on glue.
- No houses are built in winter, aerated concrete is covered with a waterproof film.
- For plaster use special compounds based on gypsum or cement.
- For the construction of interior partitions acquire blocks of less thickness than for walls.
Compliance with the conditions is important for the safety of the building to increase the service life.

Blocks are easy to crack under vertical loads... A house built in a "half block" will crack over time. Based on this, the walls are laid with a bandage, which increases their thickness to 60 cm.
Baths and other rooms with high humidity are not built from gas and foam blocks - this is due to the hygroscopicity of materials.
These requirements are relevant for residential buildings or buildings with a constant presence of people. For outbuildings - sheds, chicken coops - half-block masonry is enough.