Lightweight porous blocks are used for the construction of load-bearing and enclosing vertical structures. The foam block or gas silicate belongs to the group of cellular concrete, their characteristics are very similar. Products differ in the method of production and the composition of raw materials, which explains some of the differences in technical and operational indicators.
Characteristics of porous concrete
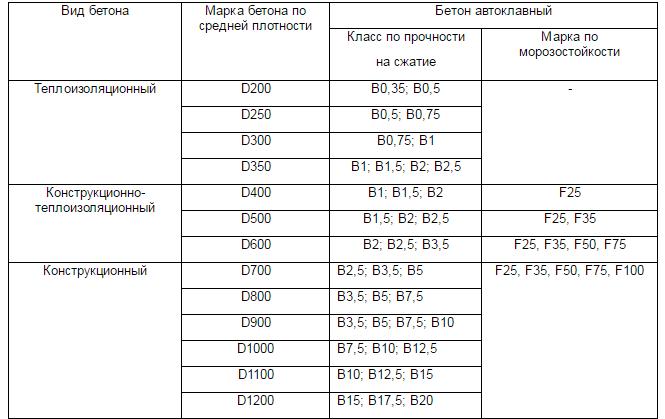
The difference between gas silicate and foam concrete blocks in the purpose of use. Produce products of the following brands:
- structural - D1000, D1100, D1200;
- heat insulating - D300, D350, D400, D500;
- structural and thermal insulation - D500, D600, D800, D900.
Produce cellular materials autoclave and non-autoclave method. In the first case, the expanded mass hardens under pressure in a high-temperature regime, and the second method involves setting in natural conditions.
Difference silicate aerated concrete and aerated concrete in the used astringent... In different cases, lime components, cement, Portland cement, slag, ash, mixed options are used.
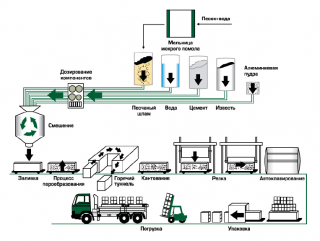
Production of silicate gas blocks
Manufacturing process includes stages:
- dry mixed ingredients are diluted with water, obtained the solution is poured into molds;
- gas-forming component is introduced, as a result of the reaction, hydrogen is released, which increases the volume of the mixture;
- the set mass is removed from the formwork, form product blanks;
- products process steam, dried in electric dryers.
During the production process, modifiers are added to the solution to increase the compressive strength, bending, reduce the degree of moisture absorption, and increase frost resistance.
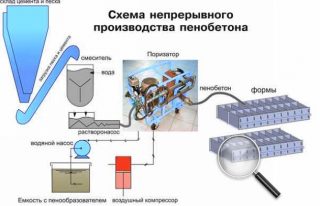
Foam concrete production
Reliable and proven classic way suggests:
- cooking cement-sand dough in mixers of improved action;
- addition foaming agent (organics) to obtain a foamy consistency;
- hardening in an autoclave at high temperatures.
Barotechnology is to apply pressure already at the stage of mixing the components... First, water is fed into the mixer with a foam former, then the remaining components are introduced, then the pressure inside is increased. The mass is transported into forms under pressure, synthetic foaming agents are used. This production method requires baroinstallations.
Choice for building a house
Silicate porous concrete is used in frame construction to fill the gaps between the uprights and crossbars. For multi-storey buildings, this method is suitable if additional stiffening belts are installed. In a free form without a skeleton, blocks and gas silicate are taken for the construction of walls with a height no more than three floors.
- private houses, outbuildings, summer cottages, cottages;
- industrial premises, workshops;
- commercial facilities, stalls, shops, pavilions.
Foam blocks use during construction:
- classic residential buildings;
- with a monolithic construction method;
- for cold insulation of foundations, walls, floors and roofs.

Comparison of the characteristics of aerated concrete and foam concrete
In the first material, pores are formed by gas bubbles constantly rising to the surface, so the cells are interconnected, and gas silicate absorbs water in a humid environment... There are closed isolated bubbles in the structure of foam blocks, so the products are not able to absorb moisture.
Differences and similarities for other characteristics:
- soundproofing better for foam concrete blocks;
- stronger protects from cold gas silicate, but subject to careful waterproofing, since moisture saturation negates any protective properties;
- both materials are excellent resist ignitionbecause non-combustible components are used as raw materials;
- vapor permeability aerated concrete is better, and foam blocks do not "breathe" well.
The main difference between a gas silicate block and a foam block is in the structure of internal cells, hence the mismatch in qualities. The characteristics depend on the brand, density.
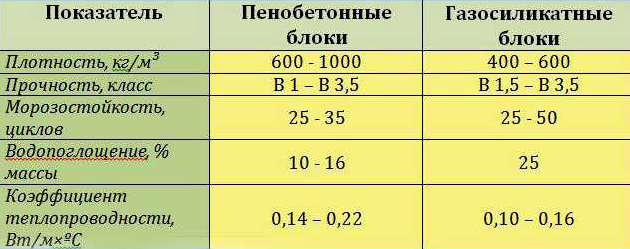
Difference in strength
The strength of gas silicate products is higher, than foam concrete analogs. If we take brands that are equivalent in terms of designation (in terms of density), gas-silicate stones will withstand a stronger load. They keep their original shape, do not crack during transportation and unloading.
The density of handicraft foam blocks may be different in different parts of the product. Gas blocks are distinguished by a homogeneous structure in all areas, since they are not made independently.
Features of choice depending on operating conditions:
- if additional wall treatment is needed, complex architectural structures, smooth surfaces, take aerated concrete;
- for insulation and internal walls, foam concrete stones are used, they are used for laying a basement, isolating foundations, since the products do not conduct moisture.
Aerated concrete is easier to cut, drill with tools without carbide tips. It holds dowels and nails better. Porous materials have less radioactivity - they do not contain mica, granite rubble with natural radiation.
Masonry feature
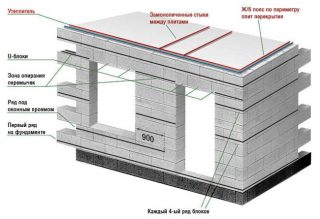
The difference between foam concrete and gas silicate is that the first material can be placed in any weather, for example, in snow, rain. Gas blocks are put into the structure only after complete drying, they cannot be installed in fog, mounted in structures on the shore of fresh water bodies, seas.After laying aerated concrete stones, an insulating film is made from moisture, and a ventilated gap is required to remove condensate.
Reinforcement differences:
- metal rods are laid after the first row in the masonry of their gas blocks, the next reinforcement is performed every 4 rows;
- iron wire, fittings are placed in the foam concrete masonry after the first tier, the subsequent ones are used after 2 - 3 rows.
Along the perimeter of the walls of both materials, a reinforced concrete belt is made in order to support floor slabs or load-bearing beams, trusses on it. For laying gas blocks and foam blocks, a cement-sand mortar or special glue is used. The first row is always put on a solution.
Purchase selection rules

The grade and density of the material is determined by the purpose of use (thermal insulation, partitions or loaded walls).
Pay attention to quality of stones:
- a uniform color speaks of a bona fide manufacturer;
- the evenness of the surface and the observance of geometry are important - such products will save glue or mortar when laying;
- the absence of chips, cracks, blisters indicates compliance with the technology.
The supplier must provide quality certificate... Factories pack products in foil and stack them on pallets to reduce the risk of destruction during transportation. Each pallet is marked with parameters. If the blocks are sold in bulk, the risk of buying handicrafts increases.