Slate is a sheet of finishing material used for arranging roofs and cladding facades. They make it from asbestos and cement. There are straight and wave slate.
What is flat slate

The building material is in the form of thin rectangular sheets or slabs of small thickness. If corrugated products are used almost exclusively for the installation of roofs, then sheets with a flat surface have a wider range of applications. The material is strong and durable, does not deteriorate under the influence of moisture. It may crack in the event of a fire, but it does not ignite. These properties determine its prevalence as a roofing coating.
Features of the composition
The material consists of Portland cement and 10-20% chrysotile asbestos. The latter component, being rigid and fibrous, acts as a reinforcing element, imparting mechanical strength and resistance to wear.
Since asbestos, which is part of the slate, is classified by WHO as a carcinogen, the question arises about the harmfulness of the material and the restrictions associated with its use. Safety regulations instruct builders to cut and mount slate in special respirators. This is due to the fact that during work there is a high risk of asbestos dust getting into the lungs. Slate roofing does not pose a threat to the health of residents. In this case, evaporation to the external environment does not occur, since the fibers are tightly bound to the cement.
In the past, amphibole asbestos was used to make slate, which is more carcinogenic than chrysotile. Now its use in the countries of the European Union is prohibited.
You can find slate-free options in asbestos-free options, for example, slate, which is excellent for roofing, and polycarbonate, used to create gazebos.
Scope of application

Smooth surface, strength and durability allow the material to be used for different purposes. Flat sheets, like corrugated sheets, are widely used for roofing. In addition, other structures are made of them:
- fences for loggias and balcony rooms;
- permanent formwork for the foundation or walls when pouring concrete;
- fences;
- paths on the territory of the site;
- facade cladding of buildings (including non-residential).
Insulated wall blocks like a sandwich can be made from slate sheets. They are used both for the construction of residential buildings and for buildings for economic or commercial purposes.
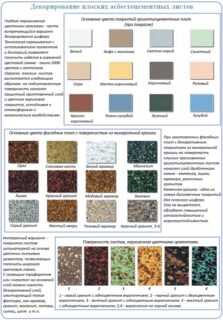
Colors and textures
Polycarbonate slate has an even wider range of shades. In addition, it is transparent.
In addition to the traditional smooth material, there are options for sale with a textured surface. One example is the coating with crumbs of ornamental stones (for example, jasper) or marble, on which varnish is applied on top. Sometimes the texture is given using relief embossing.
A color similar to a particular metal can be obtained using iron oxide compounds.
The use of decorative coatings improves the appearance and makes the material more durable due to their protective properties. Such slate is used for the construction of fences, facades and other objects, when it is important to combine aesthetics and resistance to environmental influences.
Pressed and unpressed
Flat slate can be pressed and not pressed. Materials differ in manufacturing method and characteristics.
The first option is obtained using a press. Of all the varieties of slate, it has the greatest strength and toughness.
The second type is made without the use of a press, its indicators for the main characteristics are noticeably lower. It can transfer 25 shifts of high temperature to low temperature. At the same time, changes in dimensions are more pronounced for him than for pressed products. The latter are able to withstand 50 temperature jumps, after which their strength is reduced by almost half.
Sheet marking
On sale, the most common standard sizes of flat slate. Knowing the dimensions of the sheets, you can calculate how much material is required to cover the roof area or carry out other work.
According to GOST, it is customary to mark the plates with a combination of letters and numbers. At the beginning of the code, the letters LP-P or LP-NP are written, which means, respectively, pressed and unpressed types of products. This is followed by dimensions in the format length (in meters) x width (in meters) x thickness (in millimeters).
After these data, the GOST number is written through a space, in accordance with which the product is manufactured. For example, marking LP-P-3x1.5x6 denotes pressed products 3 m long, 1.5 m wide and 6 mm thick.
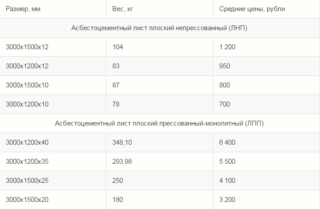
The typical size of a flat slate sheet in width is 1.2 or 1.5 m. The minimum thickness will be 6 mm, and the upper limit depends on the type of material. For pressed products, it can reach 4 cm, and for ordinary ones, as a rule, it does not exceed 1.2 cm. In private construction, sheets of small thickness are used. The most common lengths are 2.5 and 3 m. Occasionally, you can also find rectangular slabs of small dimensions (for example, 0.4x0.6 m), used only for installing the roof.
The weight of the sheet depends on its dimensions and manufacturing method. Pressed products are noticeably heavier due to their greater strength. The largest typical dimensions of such a product are 3x1.2x40, and its weight will be 348 kg. The largest non-pressed sheet (3x1.5x12) is more than three times lighter. It weighs only 104 kg.
The mass of the slate is important when preparing the lathing frame for covering.