The progress of the chemical industry makes it possible to create building materials that are superior in their properties to products made from natural raw materials. Various types of polycarbonate are widely used due to their high consumer qualities and technical characteristics.
- What is polycarbonate
- History of appearance
- Consumer properties and technical characteristics
- Benefits
- Chemical properties
- Optimizing performance
- UV protection
- Light scattering additive
- Flame retardant additives
- Preventing condensation
- Features of industrial polycarbonates
- Application of polycarbonate
- Cell type
- Monolithic polycarbonate
- Reliable manufacturers
What is polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a synthetic polymer obtained from linear polyesters of carbonic acid and diatomic phenols when heated to 180-300 ° C.
Physically, the substance looks like a colorless transparent mass.
History of appearance
For the first time, the process of obtaining a product resembling polycarbonate in characteristics and composition was described in 1898 by the German chemist and inventor of novocaine Alfred Einhorn. However, manufacturers were not interested in the substance, as there were no technologies for obtaining components and finished products on an industrial scale at an affordable price.
In 1953, within a few days, the compounds of carbonic acid were obtained by Herman Schnell of the BAYER Corporation, and Daniel Fox (General Electric).
As a result of patent disputes, the German polycarbonate was named "Macrolon", and the American "Lexan". The substance was obtained in the form of a powder.
In the early 70s of the last century, during the period of active development of greenhouses, Israeli scientists were looking for a replacement for glass and acrylic. As a result, the first sheets of cellular and monolithic polycarbonate were produced.
Consumer properties and technical characteristics
Benefits
For the end user, the best material qualities are important in comparison with traditional glass:
- Weight. The density of cellular polycarbonate is 0.5–0.8 g / cm³, cast polycarbonate is 1.1–1.3 g / cm³. The specific gravity of the glass is 2.2–2.8 g / cm³.
- Thermal conductivity is about 1.5 times lower than that of glass, which saves energy for heating greenhouses and other buildings.
- Color and light transmission. Up to 86% of light passes through honeycomb models, about 96% through monolithic ones (85% for glass).
- Resistance to mechanical stress (impact strength) is 10 times better than that of silicate glass at temperatures up to minus 60 ° C.
- Large geometric dimensions of the sheets - up to 12 m long and 210 cm wide, which speeds up construction.
- The bending radius is from 0.6 to 2.8 m., Depending on the thickness of the sheets, it contributes to the manufacture of not only rectilinear structures.
- Sheets of cellular polycarbonate can have 5 chambers, which significantly increases the ability to retain heat in a building.
There are several manufacturers on the market that use different raw materials, therefore, the exact information about the characteristics will be learned from the certificates that the seller must provide.
Thanks to the positive properties of polycarbonate, manufacturability is achieved in construction and in the production of lighting equipment.
Chemical properties
When installing and maintaining structures, it is necessary to take into account the ability of the material to resist the effects of chemicals:
Polycarbonate:
- resistant to salt solutions and mineral oils;
- shows moderate resistance to weak acids at temperatures up to 60 ° C;
- quickly destroyed by alkalis, ammonia, aldehydes, ethyl alcohol;
- does not show resistance to gasoline, kerosene, varnishes and solvents.
During the operation of buildings, it is not always possible to see damage with a glance. Sometimes the material softens and becomes vulnerable to mechanical stress. Microcracks result in light scattering and less light transmission.
Polycarbonate collapses when exposed to water at temperatures above 60 ° C, therefore, structures cannot be washed with hot water and in hot weather.
Optimizing performance
To eliminate harm or reduce negative consequences, manufacturers reduce their impact in various ways.
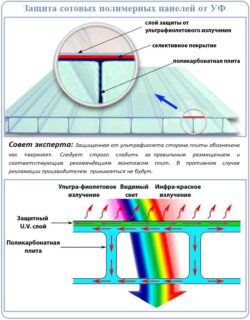
UV protection
Sunlight contains four groups of ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of rays, polycarbonate turns yellow, becomes cloudy, transmits less light and gradually collapses.
Ultraviolet light is harmful to plants and people.
To protect the material, a thin protective film is applied to the outer surface of the sheets.
The outdated technology consisted in the spraying of transparent varnishes, which quickly deteriorated and became cloudy, which ultimately led to the loss of characteristics of the slabs within 4–5 years.
Counterfeit products are still manufactured with varnish protection technology. You cannot purchase products from little-known manufacturers.
Quality products are protected by a protective shell fused into the outer surface. It remains functional for the entire period of operation. The method is called coextrusion.
The shell is the same polycarbonate, but with an ultraviolet stabilizer introduced into the composition.
It is impossible to see the presence of a stabilizing layer. For determination, a special substance has also been introduced into the composition, which can glow under a UV lamp. Reliable manufacturers indicate information in the technical documentation.
The side with a protective layer is marked with the word "top" and is covered with a film for protection during transportation, which is removed after installation.
Light scattering additive
In greenhouses and in places where people stay, it is desirable to have diffused light:
- the property allows you to evenly distribute the rays throughout the greenhouse as the sun advances during the day;
- the stream of light is reflected from the inner surface of the plates and remains in the greenhouse, which also increases insolation (lighting during the day);
- scattering eliminates burns of plant leaves and human skin.
The LD diffuser additive included in the composition refracts and scatters light. It is its content that distinguishes polycarbonate, produced specifically for greenhouses.
Flame retardant additives
Pure polycarbonate supports combustion, therefore special additives are added to the polycarbonate composition to reduce the likelihood of fires and reduce the rate of fire propagation.
When buying, pay attention to the ignition group indicated in the accompanying documentation:
- G1 means slightly flammable, they die out when the exposure to an open flame is stopped;
- G2 - moderately flammable, go out in less than 30 seconds.
As a rule, cellular polycarbonate belongs to the G1 group, and monolithic polycarbonate belongs to the G2 group.
Preventing condensation
In closed greenhouses and swimming pools covered with polycarbonate, condensation forms on the inner surface. Drops of water reduce the light transmittance, and falling on the leaves, cause disease.
On modern panels, a special coating is applied to the entire inner surface - antifog, which prevents the formation of large drops. The information is contained in the product data sheets.
Features of industrial polycarbonates
Used in extreme or difficult conditions, polycarbonates are produced in a special industrial version.
Increases stiffness, high temperature resistance and toughness.
To improve the properties of the plate, they are reinforced with fiberglass, additives are introduced against combustion and for thermal stabilization (preservation of parameters at high temperatures). The addition of graphite, molybdenum, Teflon increases the abrasion resistance.
The increased content of bisphenone S multiplies the impact strength, which increases the resistance to mechanical stress.
Application of polycarbonate
The operating conditions and the purpose of the structure directly affect the choice of the type of polycarbonate. In construction, two types of plates are used: monolithic and honeycomb.
Cell type
The characteristics, geometry, areas of use of products are determined by GOST 56712, approved in 2015. The document is called "Multilayer Polycarbonate Panels".
The document identifies several types of cellular polycarbonate on the basis of:
- the number of layers;
- locations of channels and stiffening ribs: rectangular (P), honeycomb (C), triangular (T), cruciform (K);
- colors: colorless, colored in the mass, colored by applying a colored coextrusion layer;
- UV protection, on one (outside) side, on the outside and inside;
- thickness - from 4 to 32 mm.
The material is used for glazing:
- winter gardens, greenhouses, verandas;
- roofs of sports facilities, industrial and public buildings;
- pools and greenhouses.
Cellular polycarbonate replaces glass in the manufacture of:
- stopping pavilions, canopies, awnings;
- soundproof screens;
- partitions;
- filling fences;
- skylights with increased protection against temperature extremes.
Clause 10 of GOST R 56712 establishes the requirements for installation and operation, in which the cellular variety of polycarbonate will last a long time without losing technical characteristics:
- the panels are installed outside with a protective layer;
- longitudinal stiffening ribs are placed vertically or at an angle to drain condensate from internal cavities;
- cleaning is carried out with a high pressure of water without the use of chemicals, small ones are washed with water soapy solution;
- do not use metallized fabrics for maintenance;
- do not wash surfaces heated by the sun;
- the panels are sawn with a circular or hand saw, a hand saw or a jigsaw, products up to 8 mm are allowed to be cut with a knife;
- to make holes, you must use drills for metal;
- during installation, gaps for thermal expansion are provided, and the diameter of the hole in the panel should be greater than the thickness of the hardware;
- PVC film, which covers the edges of the panels, is removed after installation;
- the ends with open channels are sealed with a perforated sludge sealing tape to prevent moisture from entering the cavities;
- do not allow heating panels with a transport protective film applied to the surface - difficulties may arise when removing it;
Honeycomb panels are bent parallel to the stiffening ribs, the bending radius should not be less than that specified in the accompanying documentation.
Monolithic polycarbonate
The main advantages of the material required in construction are transparency, strength, flexibility. Externally, the panel may not differ from plexiglass or transparent plastic, but it is much superior to them in all important characteristics.
The scope of application is the same as for honeycomb material.
The most important advantage is the monolithic structure of thick walls, which perfectly resist shock loads. Because of this, products are more often used to make structures located in public places.
Geometrical dimensions are specified according to the prices of sellers. For large customers, manufacturers can produce panels of the required length and width.
Reliable manufacturers
On the Russian market, you can buy polycarbonate of domestic and foreign performers. Materials can vary in quality, but imported counterparts can cost 1.5–2 times more.
Reliable domestic enterprises include products manufactured:
- Novattro;
- Polinex;
- Sellex;
- Kronos;
- Carboglas;
- Carat.
Most of the factories use imported equipment and technologies, and the low price is due to customs duties and the cost of delivery across the country.