Transparent polycarbonate is an alternative to silicate glass. It is used in the construction of greenhouses, greenhouses, glazing in gazebos and terraces. Its special brands have found application in radio devices and even in optics.
Material description

Transparency is the main feature of polycarbonate. This allows it to be used as a substitute for silicate glass. The property depends on the type of plastic, its structure and color.
Transparent clear plastic is rarely produced. For its manufacture, a special technology is used, which assumes a high level of purification of raw materials. Such polycarbonate is expensive, but has high optical qualities. The light transmission coefficient of such a material ranges from 95 to 98%.
For construction work, they use less high-quality, but more affordable plastic. However, due to its extremely high strength and lack of fragility, the field of application of the material is much wider. Colored polycarbonate allows you to create a variety of decorative designs.
The light transmittance depends on the color shade and its intensity. There are 4 categories.
- Transparent - transmits more than 85% of the light. Such panels are completely colorless and are used for glazing greenhouses and greenhouses.
- Conditionally transparent - this is the name for colorless, but not so transparent plastics. The light transmittance here ranges from 40 to 85%. These are translucent silvery panels, "opal", "pearl".
- Conditionally ghostly color - the level of light transmission is from 25 to 75%, but at the same time they are painted in different colors.
- Opaque - no more than 20-30% of light passes through the material. They produce white panels - dairy, "say" - and painted. Most often they use a material of a cold shade - silver, gold, snow.
The light transmission coefficient depends on the thickness of the plastic and its structure.
Varieties, sizes and nuances of application
Polycarbonate is produced in the form of sheets - monolithic and honeycomb. The configuration and dimensions of the sheet also vary. This determines the purpose and way of using the materials.
Cellular

This material is 2 thin sheets of polycarbonate, interconnected by numerous partitions. In section, it resembles a honeycomb, for which it got its name. Partitions can be perpendicular or inclined, which determines the stiffness of the sheet.
Cellular polycarbonate has almost the same resistance to mechanical stress and is only slightly inferior in strength. At the same time, it retains heat much better and dampens sound due to the fact that a layer of air remains between the two sheets of plastic. The material is very flexible and light, you can build a greenhouse out of it with your own hands in a couple of hours.
Compared to monolithic, cellular has only one drawback. The ends of the slab are open, which means that moisture or debris can easily get into the sheet. Therefore, during installation, the sheets must be closed from the ends.
There are several types of panels.
- 2H - two-layer sheet with rectangular honeycomb. The distance between the partitions is from 0.4 to 1 cm, which determines the different density of the material.
- 3X - a three-layer panel in which straight and inclined partitions are combined. The material is durable and resistant to deformation.
- 3H - three-layer sheet with rectangular honeycombs. Its thickness reaches 5–10 mm.
- 5W - five-layer panels with straight baffles. Designed for high bearing loads.
- 5X is a five-layer material with straight and inclined partitions. Differs in an exceptional combination of strength and flexibility.
The width of the honeycomb sheet is 210 cm. The exception is panels with a thickness of more than 2 cm, while the length ranges from 6 to 12 m. The dimensions of polycarbonate correspond to the thickness of the sheet.
Cellular plastic is not resistant to ultraviolet light. It is covered with a protective colorless layer.
Monolithic

Monolithic polycarbonate is a dense solid material with a thickness of 0.2 to 0.6 cm. It most often serves as a substitute for silicate glass, as it has a higher translucency.
Monolithic polycarbonate is 200 times stronger than silicate glass, not so fragile, retains heat and is not afraid of ultraviolet radiation. It is ideal for a greenhouse or greenhouse, although it is heavier than cellular polycarbonate.
A monolith is more difficult to install if it is faced with structures that are complex in configuration. Sheets are heavier and denser than honeycomb, so it is more difficult to bend them, the bending radius is smaller.
The inclusion of modifying additives significantly changes the properties of monolithic polycarbonate. There are several of the most popular brands.
- PC-5 is translucent, smooth, prevents the growth of bacteria and perfectly tolerates disinfection. Used for medical needs.
- PK-6 - has the highest translucency. It is used in optics and radio engineering.
- PK-M-1 is a variant characterized by minimal friction.
- PK-M-2 is the only polycarbonate that is not afraid of fire and does not form cracks. It is rare in everyday life.
- PK-LT-12 is a material with low viscosity. Used for sheathing flat surfaces.
- PK-2 - sheets with medium viscosity. They are used for glazing verandas, gazebos, arranging canopies with a curved configuration.
The dimensions of the polycarbonate sheets are relatively small. The standard is considered to be a length of up to 305 cm and a width of up to 205 cm. The usual thickness is 0.2–0.6 cm, but material is produced with a thickness of up to 1.2 cm.
There is a special material for the roof - profiled polycarbonate. It reproduces the undulating configuration of slate or metal tiles. At the same time, the sheets retain some transparency. Used to overlap verandas, garden pavilions, park sheds.
Transparent honeycomb polycarbonate for greenhouses

Transparent polycarbonate sheet is used for greenhouses and greenhouses due to the following characteristics.
- High transparency - 85% and higher. In terms of transparency, it is in no way inferior to ordinary sheet silicate glass.
- Plastic transmits ultraviolet light, which plants need for normal development, but at the same time retains heat waves, unlike silicate material. A spring greenhouse made of polycarbonate, unlike a glass one, does not need heating at all - it is enough to be warmed up by the sun. The winter greenhouse needs to be heated, since the sunny day is too short in winter, but the heating costs are much lower.
- Polycarbonate dampens sound.
- Installation of polycarbonate cladding is much easier. The sheets are lightweight even at large sizes, impact-resistant, resistant to mechanical stress. The panels with a lower thickness can withstand high wind and rain loads.
- Thanks to the flexibility of the plastic, the greenhouse can have a more ergonomic, rounded shape.
Coloring in any color reduces the light transmittance to 75% and below. Therefore, a transparent version is needed for a greenhouse.
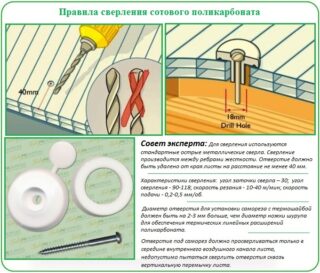
Polycarbonate glazing rules
- Bending sheets can only be up to a certain degree.The indicator is usually indicated on the packaging and is related to the thickness of the panel.
- The sheets are fastened end-to-end using a special profile. It is not enough to simply connect the panels and fill the joint with silicone sealants.
- For fasteners, take only hexagonal self-tapping screws with a press washer. A rubber gasket under the head prevents sheet deformation when the temperature rises.
- Cannot be fixed rigidly. Even special self-tapping screws are tightened so that a technical gap remains between the cap and the sheet.
- The sheet connector is installed on the frame. A loose profile will sag, since such a load is excessive for cellular polycarbonate.
Since the ends of the sheet are open, the installation of cellular polycarbonate begins with determining which edge of the panel is considered the top and which is the bottom. When laying, the top is sealed with a continuous tape to prevent moisture and debris from getting inside. The bottom edge is sealed with a perforated strip that allows condensation to drain out.