Brick blocks are one of the most popular building materials. They make walls that bear the main load, and partitions. In areas with a cold climate or with significant temperature changes, it is advisable to make thick masonry so that the heat is better retained inside. At the same time, it is possible to reduce the weight of the building and the costs of its construction by using hollow bricks.
Material features and typical block sizes

Hollow brick is made a little more difficultthan solid, but its lower price due to lower weight... Raw materials for ceramics are clay with various additives. In this case, it is important that the composition has low humidity (no more than 15%)... In accordance with GOST, products are considered to be hollow if cavities occupy more than 15% of the total volume... Sometimes their percentage reaches 30-40%.
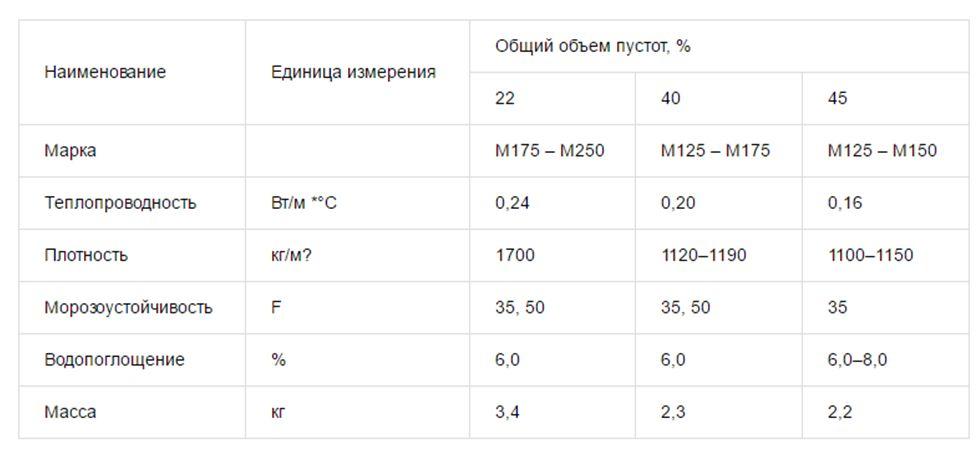
When choosing a ceramic hollow brick, you need to pay attention to the marking. The most informative are the following characteristics:
- Frost resistance, denoted by the letter F and a number. The latter indicates the number of freeze and thaw cycles that the material is capable of transferring. In most of the territory of Russia, it is worth using a brick, in which this number is not less than 35.
- Strength denoted by the letter M in combination with a number. This indicator is also called a brand. The larger the number, the stronger the product. If you plan to build a building with several floors, it is worth taking a brick of grade 150-200.
- Propensity to absorb moisture... The more pronounced it is, the greater the likelihood of cracks in the material. They arise due to the fact that the accumulated water turns into ice floes in winter, which begin to press on the material from the inside. The water absorption indicator is also associated with frost resistance.
- The percentage of hollow areas in the volume of the product... It directly affects the strength: the more voids, the smaller it is. For example, the grade of blocks with 45% of cavities is never higher than 150. But a large number of voids reduces the thermal conductivity of the product.
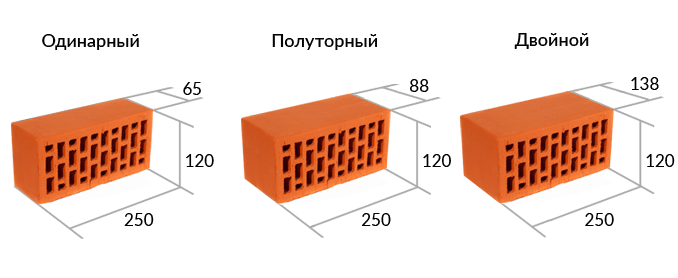
The dimensions of ordinary hollow ceramic bricks (and other types of blocks) are regulated by GOST. Typical options are single (25x12x6.5 cm), one and a half (25x12x8.8 cm) and double (25x12x13.8 cm). In addition to them, products of other dimensions are also produced, for example, thickened (51x25.3x21.9 cm) and additional ones. The use of double blocks helps to carry out construction work faster. The mass of products depends on their dimensions, the percentage of voids and the material used. One-and-a-half ceramic bricks have a weight of 2100-2500 g.
The structure of the cavities this brick is different. In section, they can be in the form of a circle, oval or quadrangle. Voids can be both longitudinal and transverse. In addition to products with through cavities, bricks with grooves on one side can be found on sale.
Variants with horizontal voids have low strength, so their scope is limited.They are used in the construction of monolithic-frame structures for the arrangement of partitions.
Hollow brick classification
If the ceramic brick is red hollow, it can have a strength grade M150-200, then unburned, as a rule, cannot be assigned even M50... However, the low price and ease of production of raw brick (you can even mold it yourself) make it popular in dry areas with warm weather.
Less common options include:
- Foam diatomite blocks, well withstand elevated temperatures. Thanks to this property, they are suitable for laying out fireplaces and stoves. You can make buildings out of them, but this is usually not practiced, since their cost is higher than that of the usual bricks.
- Textured productshaving embossed patterns on the surface and having increased decorative qualities.
- Face brickused for facades.
- Shaped options with beveled corners. They are purchased for the installation of arched and other decorative structures.
Large-sized products are usually called blocks. Their buildings are built faster than using standard sized bricks. Other advantages of the blocks are good thermal insulation properties, strength and reduced cement consumption during installation.
Laying technology and mortar proportions

They work with hollow material using the same technology as with corpulent material. But the presence of cavities in the block structure requires the use of less fluid solution... Otherwise, the latter can brick up the voids, reducing the thermal insulation characteristics of the masonry. If work is in progress in winter, add to the solution plasticizing additives.
The suitable plasticity of the mixture for blocks with cavities is 7-8 cm. It is prepared from 1 part of cement grade M400 and 4 parts of sand... The latter is better to take a small fraction. The ingredients are mixed until smooth, and then water is gradually introduced. Correction of mobility is carried out by the introduction of the required amount of dry or liquid ingredients.
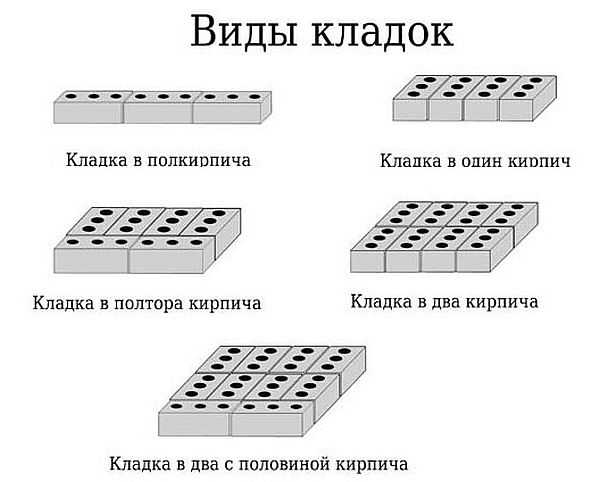
Before you start laying out bricks, you need check horizontality basement or basement of the house. It is covered with a two-layer waterproofingto prevent premature destruction of the material. There are several ways of laying. The half-brick method is used for facing work and involves the installation of a reinforcing mesh every 4-5 rows. Layout in a solid block chosen when constructing partitions. Bearing walls are made thick 1.5-2.5 bricks.
Partitions are easier to buildthan the outer walls, as they do not have corners that require special attention. It is for interior structures that a brick with voids, which has good soundproofing qualities, is best suited. Pre-installed on floor and wall surfaces mark out the installation area partitions. Flatness control provided with a cord stretched between the slats (this method is also suitable for guiding rows when laying out supporting structures).