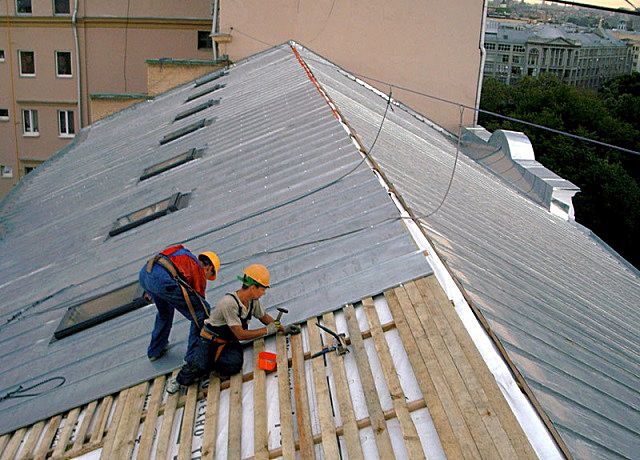
Roofing material is one of the most affordable materials used in the arrangement of roofs and various kinds of waterproofing works. This is due to the prevalence of raw materials and ease of manufacture. Installation is not difficult, as it does not require special skills and tools. Roofing material RKP 350 belongs to the most popular types of material.
Description and transcript

When building roofs, it is often used roofing felt ruberoid RKP 350 or RKP-350b... The technical characteristics of the material and the requirements for it are indicated in GOST 10923-93 or in the TU of the manufacturer... When purchasing a roll, you can request a certificate of conformity for the product to verify its quality. Roofing material 350 is also used for waterproofing the foundations of buildings.
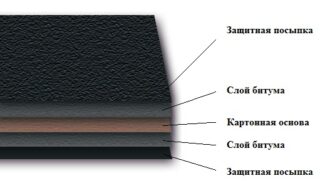
Material is produced from cardboard treated with water-repellent compounds... First, the sheets are impregnated with a low-melting bitumen, and then a thicker grade of this substance is applied to them. A coarse-grained powder with shale inclusions and talc is applied on top of the products. Due to the combination of an affordable price with strength and waterproofing qualities, which this product has better than cardboard materials without powder, roofing material is widely used for arranging roofs and other works where sheet insulation is needed.
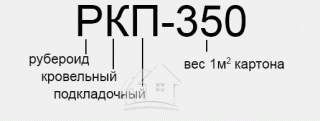
- P - the name of the building material (roofing felt with a cardboard base);
- K - purpose (roofing);
- P - type of powder (dusty);
- 350 is an indicator of the density of the cardboard base (0.35 g / m²).
The material is suitable for use on roofs of different configurations and with different angles of inclination. Usually it is laid in 2-3 layers.
What is the difference from RPP 300
For RPP 300 rolls the letter P marks the lining roofing material, the main scope of which is foundation waterproofing... It has a lower density than roofing material (only 0.3 g / m²). When installing roofs, it is permissible to lay it only as a bottom layer of insulation. In terms of weight, wear resistance, tensile strength, it is noticeable inferior to roofing varieties, and the area of coverage exceeds the RCP by a quarter. RPP is produced in long rolls (20 m - one and a half times more than that of RCP, with the same width of 1 meter).
Both materials have a dust-like powder, as indicated by the last letter P in the marking. In addition, coatings are fine and coarse-grained (example of the first option - products PM 350), as well as scaly. Coarse-grained products are used to organize the top layer of the roof. A similar purpose is for products with scales that have good decorative qualities. Dust-coated rolls are designed to organize the lower layer of the roof.
The density of the cardboard base used for the manufacture of roofing material varies from 300 to 500 g / m². The higher the value, the more suitable this material is for roofing.
Specifications and modifications
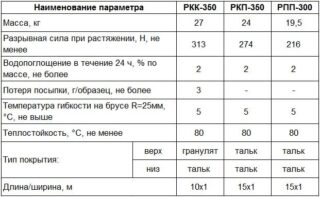
For the production of roofing material RCP is used cardboard base density 0.35 g / m²... Rolls have a meter width, length 15 m and a weight of 26 kg. Weight cover layer is 800 g / m², strength to break - 28 kg / s... The material has good waterproofing properties. It is customary to lay roofing strips overlap. To prevent water seeping into the seams, they can be warmed up.
In addition to the traditional rolls RKP 350, now you can find on sale a variation RCP 350-0... Its properties are similar to the traditional version, however breaking strength he has several below... Moreover, it has strictly dusty talcum powder without abrasive stone particles. These features bring it closer to RPP 300 and similar topcoats, so it fits well for waterproofing foundations and wall structures... When arranging roofs, RCP 350-0 can be used only for the lower parts.

Installation rules
You need to lay waterproofing material in dry and warm (above + 5 ° С) weather... It is permissible to mount it at 0 ° C, but in this case the roll is preliminarily kept in a cool room for at least a day... Better post it uncoiled... If there is no time to hold the roofing material, you can unwind the roll, and then wind it up again in the opposite direction. This helps to straighten the material and remove wrinkles. It will be much easier to lay the roofing material prepared in this way.
Surface, on which the waterproofing will be mounted, must be clean... Dust, impurities, interfering fragments of old materials are removed from it. If the plane is not even enough, they will organize solid crate... It should be as dense as possible, not have gaps. Also a plane is required degrease.
Fasten the roll cover to the insulated surface in different ways. Quite acceptable mechanical method using fasteners (self-tapping screws or simple nails) and rails, but when it is implemented, it increases breakout risk in the insulating layer.
Lbetter to apply bituminous mastic... Prepare her forand 3 hours before styling rolls. The bitumen is boiled until the foam no longer forms. After that, the burner is turned off, added to the liquid kerosene and fine filler... The composition is thoroughly mixed and stored in a tightly sealed container.
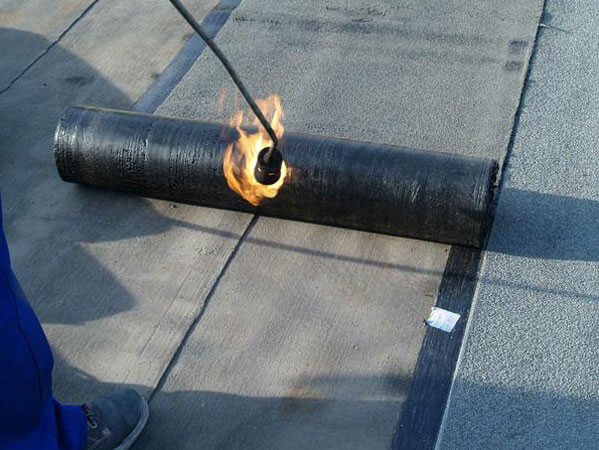
Another method is melting the bottom layer of roofing material using gas burner... In this case, it is necessary to warm up not only the rolled cloth, but also the very base on which it will be laid.
Roofing material is cut into strips the required size with a margin of 0.2-0.3 m on each side. On rooftops with very weak slope (3 degrees or less) you can lay the material across and along the slope, in other cases - only in the last way. The base is primed, and after the composition has dried, it is coated with mastic. Then make installation prepared strips of the lower layer (from lining or roofing felt) with with an overlap of 0.1-0.2 m... It is recommended to use a roller to remove wrinkles and bubbles.
It is better to lay out the fragments of the covering from the lower points of the roof up... Having covered the entire required surface, on it apply a layer of mastic and then spread next row strips of roofing material. This must be done so that it is created offset by half relative to the first layer. In general, each next row is laid so that the suture areas do not coincide with the previous ones. This will provide the underlying layers with better moisture protection.

At the end of the installation, produce insulation condition assessment and, if necessary, correct shortcomings. To design completely dry, you may need up to 3-4 days... It all depends on the humidity and temperature of the surrounding air. Special roofing material does not require leaving, but every six months it should be inspected for cracks and holes. If they appear, close up liquid bitumen.