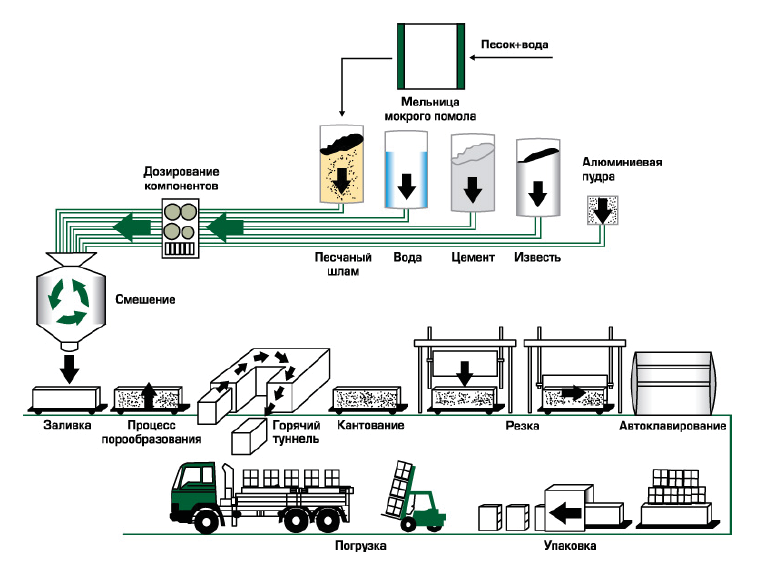
Traditional wall masonry involves placing bricks on top of a cement mortar. In this case, some space remains between the stones, filled with cement. Such a seam, even with the complete safety of the solution, plays the role of a cold bridge. One of the tasks of modern construction technology is to minimize the size of the seam. For this, silicate tongue-and-groove blocks are used.
Silicate tongue-and-groove plate
The tongue-and-groove plate has a specific shape. On the end sides of the product, protrusions are formed - ridges, and indentations - grooves. In size, they exactly match each other. When joining, the crest of the next element enters the groove of the previous one, which provides precise and tight fit... Silicate GWPs are assembled using assembly glue. The seam thickness is no more than 2 mm and the joint does not turn into a cold bridge.
The second feature of the material is related to its manufacture. The raw material for the production of silicate blocks is a mixture of quartz sand, water and lime. Make a brick by autoclave method - blocks are pre-processed under a pressure of 12 atm. at temperatures up to + 200 ° Сso that the material gains maximum strength. Therefore, in terms of bearing capacity, GWP slabs are in no way inferior to conventional blocks.
The autoclave manufacturing method provides another important advantage - dimensional accuracy... Silicate blocks rarely include chips and irregularities, so when laying, there is no need for a thick layer of mortar for leveling. The same quality guarantees the exact joining of the tongue and groove.
Like ordinary sand-lime bricks, blocks cannot be used to build a foundation.
Description and specifications
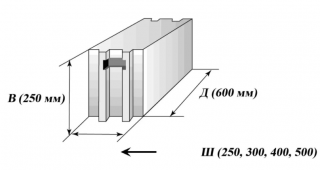
- Tongue silicate block wall - has an approximately cubic shape. With a width and height of 250 and 248 mm, they have a thickness of 250, 288, 139 and 88 mm. As a rule, they have several grooves and grooves at the ends, sometimes of different depths. This provides a very tight fit, but requires high qualifications from the builder.
- Partition an ordinary slab with a length and width of 498 and 250 mm has a thickness of 115 mm. The material is used to remove interior partitions, where the bearing load is lower. Models are also available, even thinner - 80, 70 mm thick. The advantage of this solution is the thinness of the partition, it takes up a minimum of space, but at the same time it is durable and does not conduct sound.
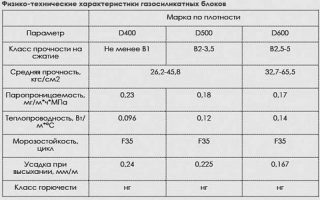
- density - varies depending on the voidness from 1220 to 1879 kg / cu. m;
- strength - corresponds to the M 150 brand;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity - on average 0.045 W / (m * C). However, this characteristic also depends on the porosity of the material;
- noise insulation index (air) - from 468 to 52 dB;
- water absorption - from 5% for waterproof ones, up to 26–32% for ordinary ones;
- fire resistance - REI240 if the wall thickness is 25 cm.
The wall tongue-and-groove block allows the erection of 5-storey buildings without a frame-monolithic system.
Block classification
Silicate blocks are classified according to several parameters. With a rectangular slab groove and ridge shape can be different:
- rectangular - standard version, suitable for most construction work;
- trapezoidal - more difficult to install, but provides a tighter joint and greater wall strength.

The main disadvantage of silicate bricks is the high water absorption. According to this parameter, 2 types are distinguished:
- Standard - with water absorption up to 32%. Suitable for the construction of premises in which the humidity will not exceed 60%.
- Hydrophobized - moisture resistant. Hydrophobic additives are added to the raw materials during manufacture, while the water absorption is reduced to 5%. The material is more expensive, but can be used to build swimming pools, for example. The blocks are colored turquoise or green.
There are also shungite slabs... Coal is added to the feedstock for them. The block is black and highly durable.
- Corpulent - monolithic options. They are distinguished by their high strength: the slab suspended at 2 points can withstand a load of 200 kg. It is used for the construction of load-bearing walls in private cottages.
- Hollow - include longitudinal circular cavities. Such blocks are lighter - the difference in weight is 25%. The bearing load is only slightly less, so they are also used for solid walls. But because of the voids, console furniture or equipment can be attached to them only with butterfly dowels. Hollow ones are often taken for the construction of interior partitions, since they constitute a smaller load on the foundation.

Comparison of solid and hollow blocks
The technical characteristics of the slab with and without voids are slightly different. This determines the purpose of the material.
Monolithic blocks correspond in strength to the M150 grade. Hollow cores withstand less stress, however both options can be used to construct load-bearing walls... In this matter, the thickness of the stone is more important. If it is 70 mm, then it is intended for an interior partition. The thickness of the block for the wall is greater - from 115 mm.
Solid blocks are heavier. Weight standard averages 20.5 kg, and hollow - 15.6. It is easier to build from a block with voids.
Soundproofing void above. The perforated block baffle reduces the noise level by up to 42 dB.
It also matters water absorption... However, this quality does not depend on voidness, but on the presence of hydrophobic additives.
Installation technology
- Laying begins in warm dry weather at an air temperature of at least + 10 ° С. The surface of the foundation is waterproofed before work: covered with roofing material, coated with mastic.
- First row blocks put for cement-sand mortar... This allows you to level the slightest unevenness in the foundation. For the first row, the lower ridge is cut off from the slabs.
- The solution is applied to both sides and put the slab from the corner first.The following blocks are joined by sliding the ridge into the groove. Excess solution is immediately removed. Once installed, each block is leveled and tapped with a rubber mallet to secure it in place.
- Next row put on glue. It is applied to the top and to the ends of the slab. Each next row is laid out offset so that the vertical seams do not line up.
- The partition is erected in the same way. To improve sound insulation, an elastic gasket is placed between the wall and the partition - felt or cork.
The wall or partition does not require additional processing. Immediately after the glue dries, you can wallpaper or cover it.