Plywood is made from veneer, gluing together sheets of different types of glue. The layers are pressed under the influence of high temperature and pressure. Depending on the impregnation, moisture-resistant types of plywood are distinguished, with increased water resistance, and environmentally friendly. Types of material differ in strength, wear resistance, durability.
Description and production of material
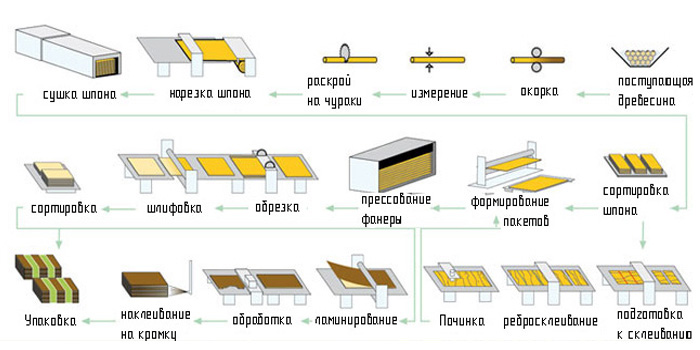
Production technology:
- preparation of trunks for peeling, debarking;
- cutting of raw materials, veneer peeling, wetting and cutting in a certain format;
- drying in gas or thermal oil chambers, sorting of sheet material;
- gluing veneered layers "on the mustache" and "rib";
- preparation and gluing of elements;
- assembly of internal and external filling;
- plywood manufacturing, cutting, grinding;
- sorting, marking of plywood, packaging.
For the connection, casein, formaldehyde, melamine compounds are used, there are bakelite varnishes, which impart high strength and resistance to water. Use adhesives based on water or alcohol. Melamine additives reduce formaldehyde emissions, so these types are allowed to be used in living rooms without harm to health.
Manufacturing methods
When gluing, the following technologies are used:
- smearing only even layers if the glue is environmentally friendly;
- impregnation of all layers if synthetic binders are used.
The preparation and composition of the glue, temperature and pressure on the line are controlled by electronic detectors, so verification is present at every stage of production.
Technologies are used for manufacturing:
- cold gluing;
- high-temperature processing under the press.
In the first case, the canvases are glued together with a knitting, placed under a press at a temperature of +24 - 28 ° С... Exposure is 6 - 10 hours, the glue hardens, the veneered panels are glued together. With the hot method, the dialed sheets with a layer of glue are placed under a press in a high-temperature mode (+70 - 80 ° C).
The coating is applied by gluing a plastic protective layer on synthetic resin or hot stamping... In the second embodiment, a corrugated or convex texture is performed along the resin layer on the surface during drying of the sheets.
Plywood classification
By the way the fibers are arranged, longitudinal or transverse plywood... In the first case, natural wood threads are directed along the long side of the slab, in the second, along the short side.
They use wood waste of soft and hard species, therefore they produce several types and brands differing:
- service life;
- strength;
- appearance;
- water resistance, heat-insulating and sound-insulating properties;
- cost and purpose.
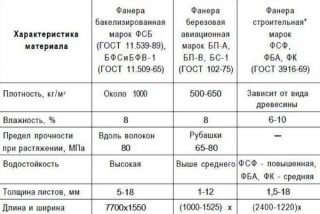
They produce moisture resistant grades and increased water resistance, which differ in the composition of the impregnating and binder component.The first varieties are used to decorate residential buildings, offices, work areas.
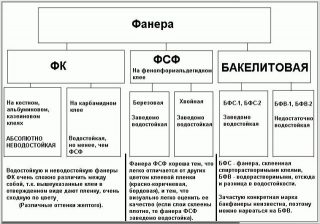
By the glue used
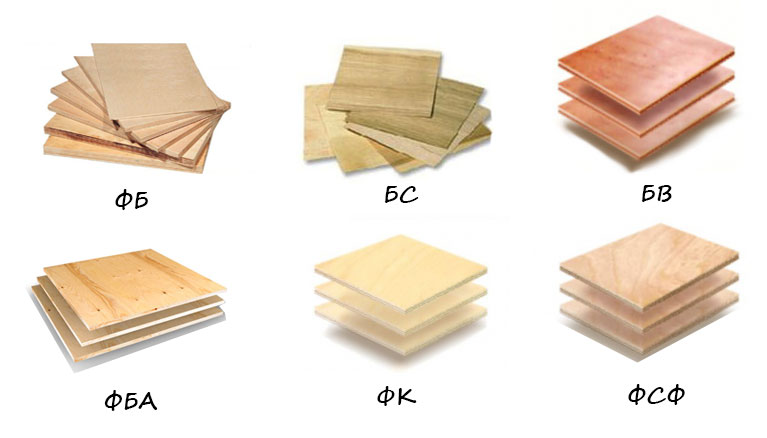
Other types of plywood:
- FC - urea resin acts as a binder. The material emits harmful substances in standardized volumes, therefore, in places where a person is constantly present, it is not used.
- FSF - glued using synthetic resins based on formaldehyde, the material is moisture-resistant and wear-resistant, but toxicity does not allow its use everywhere, for example, in the manufacture of furniture.
- FSF-TV - is an improved type of FSF, added fire resistance.
- FB - Bakelite type of plywood, the material is given high strength, moisture resistant qualities. Sheets are used in the construction of aircraft, ships, they can work under water. The material is used for decking and floors in open areas, terraces, balconies, around pools, in bathrooms.
- FBS - use bakelite varnishes for alcohol;
- FBV - for bakelite plywood, take water-soluble varnishes.
There is plywood based on melamine and melamine-formaldehyde bitumen. The harmfulness of the material is reduced due to the property of melamine to block the emission of formaldehyde.
Stamps
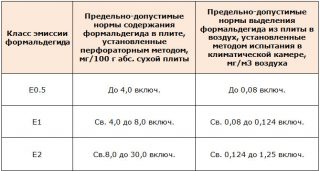
Formaldehyde emission rates depending on the plywood grade:
- FBA, FB, FK stamps belong to the emission class E1, while 1 m³ of dry mass of panels can contain no more than 8 mg of formaldehyde. In the air during a chamber study, no more than 0.124 mg per cubic meter is allowed, and the gas analysis method should reveal no more than 3.5 mg / m² · hour or not less than 5 mg for three days from the moment it leaves the conveyor.
- FSF, FOF brands belong to the emission class E2... This category includes plywood, the weight of which contains 8-30 mg of formaldehyde per 1 m³ of dry weight. The chamber study finds the volume of release of free poison into the air, and it should not exceed 0.124 mg per cubic meter. The gas analysis method also determines the emission, and it should not exceed 3.5 - 8.0 mg / m² · hour or not exceed 5 - 12 mg within three days from the date of issue of the panel.
Varieties
Distinguish plywood grades:
- Variety Elite (E)... The standard does not imply the presence of veneer defects and coating defects. Oil stains, stubborn metal particles, cracks and dents on the entire surface of the plywood board are not allowed.
- Variety I. The minimum number of defects is allowed, for example, the presence of knots in the size of a pin head, several wormholes up to 6 mm in diameter (3 pcs per square).
- Grade II... On the plane of the sheets, intergrown and separate knots with a cross section of up to 25 mm are observed, no more than 10 of them are allowed per square. Wormholes cannot exceed a diameter of 6 mm; there must be no more than 6 wormholes. for 1 m².
- Grade III. Defects of the previous grade are allowed, knots falling out are still allowed for them, and the number of healthy ones is not standardized. Such plywood is taken for hidden structures, for example, furniture walls, containers, formwork.
The lowest quality plywood is considered IV grade. It has metal blotches, greasy spots, traces of protruding glue, wormholes up to 40 mm, resin pockets. Such material, despite its poor appearance, is durable, is widely used for construction work.
Varieties of material

There are operating conditions under which plywood cannot be used. Despite the moisture-resistant impregnation, the sheets have wooden particles in the structure, which are sensitive to moisture. Therefore, the classification of plywood in this regard depends on the degree of resistance to dampness and the action of direct streams of water.
Low water resistance material not used in bathrooms, kitchens, where there is a direct effect of moisture and steam. Under the influence of temperature, plywood with increased environmental friendliness does not produce toxic fumes, but swells and deforms when exposed to abundant drops. The water resistance of the material can be increased by treating it with paint or varnish after installation.
The division is also based on the difference in the number of layers, distinguish plywood:
- multilayer;
- five-layer;
- three-layer.

By surface treatment method

Plywood with rough sides has a rough surface. It costs less, but they use the material only for various rough work. You can grind the sheets yourself, but the price of such work will be unreasonably high, unprofitable in artisanal conditions.
Plywood is divided by the degree of processing:
- unpolished material (NSh);
- sheets sanded on one of the sides (Ш1);
- slabs sanded on both sides (Ш2).
There is a variety with a facing film layer on the surface, which is glued on one or two sides. The material is paper impregnated with synthetic bitumen. Resistance to moisture, aggressive action of other factors increases.
Film faced plywood made from high quality birch veneer. The material is used for front cladding, the panels are distinguished by increased mechanical strength, abrasion resistance. Microbes, bugs do not live on the surface, mold does not develop. Acrylic moisture-resistant paint is applied to the ends.
By wood species
Coniferous lightweight veneer, mainly pine wood is used. Coniferous plywood is distinguished by resistance to rotting and mold development. The structure contains natural resins that provide moisture resistance and strength. The material is placed in living quarters on floors, walls, partitions, used as a base for metal tiles during roofing work.
Combined types of veneered boards are made from different woods. More often, birch veneer is placed outside, and the inner layers are made with conifers or alternate with deciduous ones. Due to the combination, the cost is reduced, therefore the scope of application is expanded.
By appointment
In construction, the material is used for cladding internal surfaces. Moisture-resistant plywood is used as an external cladding if the wall is hidden under a canopy. The external finish must be impregnated with protective agents and painted. When erecting concrete structures, plywood is used in the form of removable and non-removable formwork.
Others plywood applications:
- in shipbuilding for the device holds, bridges, decks, other critical planes (bakelized view);
- in transport for installation as a sub-floor of cars, trams, wagons, cladding of internal walls, ceilings;
- in aircraft construction bakelite plywood is used to make wear-resistant coatings, tank walls, parts.
Simple brands are used in furniture production. The front walls are made of laminated grades, and the back walls, the bottom of the boxes are made of lower grades.
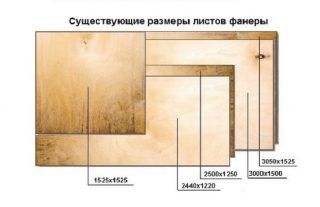
Dimensions and thickness
Release sheets of standard sizes:
- 3.0 x 1.5 m;
- 3.0 x 1.525 m;
- 2.44 x 1.22 m (most used);
- 1.525 x 1.525 m.
Size standards are spelled out in GOST 39.16.1 - 1996. Deviations are allowed for processed panels of 0.5 - 0.7 mm with a thickness of 12 mm. Unsanded should have a thickness deviation of 1 mm. Material weighs 350 - 520 kg / m³, depending on the density, the number of layers.