Glass-magnesium sheet is a versatile building material. It is not new to the market, but it is used mainly by construction organizations. Private developers bypass products due to a lack of understanding of the benefits of using them.
Description of LSU boards and manufacturing technology
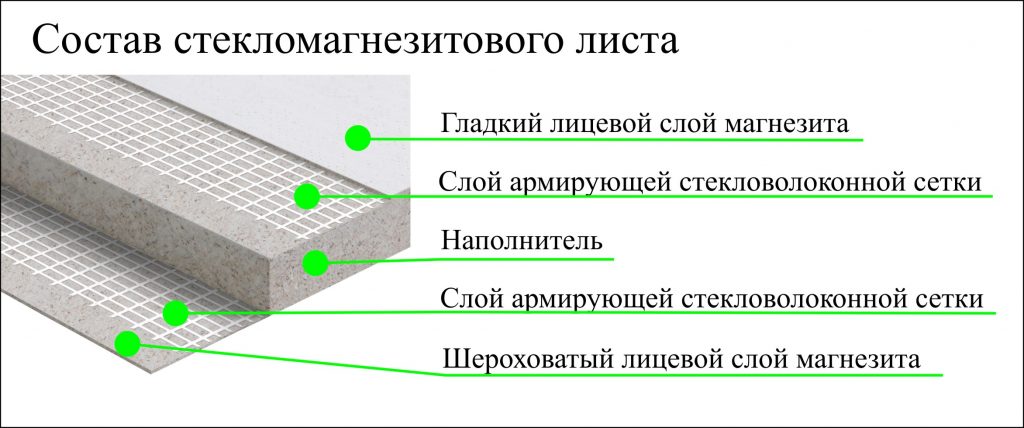
Layer order:
- front - sanded, glossy or covered with a protective material;
- fiberglass reinforcement mesh;
- filler from a mixture of perlite, magnesium oxide, wood fibers and improving additives;
- reinforcing mesh;
- the back is rough from magnesite.
Manufacturers sometimes add another outer layer of non-woven material to add extra strength. Such sheets are not sanded.
Components
Each manufacturer sets the technical characteristics of glass-magnesite sheets and quality control methods independently. For this, technical conditions are being developed.
The main raw materials are:
- calcined dolomite;
- natural magnesite;
- magnesium oxychloride;
- wood fibers.
Fiberglass mesh is used as reinforcing layers.
The technology allows the use of additional components that improve the properties of the final product.
Manufacturing steps

Manufacturing of LSU panels takes place in several stages:
- Procurement of raw materials. Laboratories check the quality of components, their safety, the proportion of impurities and their possible effect on the grade of the manufactured product.
- Dry mix preparation. The components are crushed to the required fraction and dried if necessary. The dosage affects the category of sheets, of which each plant produces three, sometimes four. Increased attention is paid to mixing, since the homogeneity of the finished slabs and, ultimately, the strength properties depend on this.
- Saline preparation magnesium chloride, which, together with settling, lasts up to 24 hours.
- Closure. Saline is poured into the mixer. With constant stirring, a dry mixture is gradually introduced until a viscous mass of the required consistency is obtained.
- Sheet forming. A substrate is formed, the "glaze" is poured for the front layer. After laying the first fiberglass mesh, distribute the bulk of the solution. Next, a second fiberglass mesh is placed and a back layer is applied. The process ends with pre-molding and cutting of blanks of the required size.
To give increased strength to the composition of products "Premium" class introduce basalt fiber.
The front coating of the glass-magnesium plate is characterized by increased strength and "gloss"... The glaze contains magnesium oxide powder, magnesium chloride solution, plasticizer-plasticizer and talc.
Facade performed in several versions:
- without finishing, for any operating conditions;
- with decorative and protective coating from acrylic for interior structures and wall decoration;
- lined with HPL-plastic and PVC-foil, can be used in buildings and structures with dry and normal humidity conditions;
- with vinyl finish for any operating conditions excluding constant contact with water.
The back side is sanded to roughness.Non-woven sheets are not sanded.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
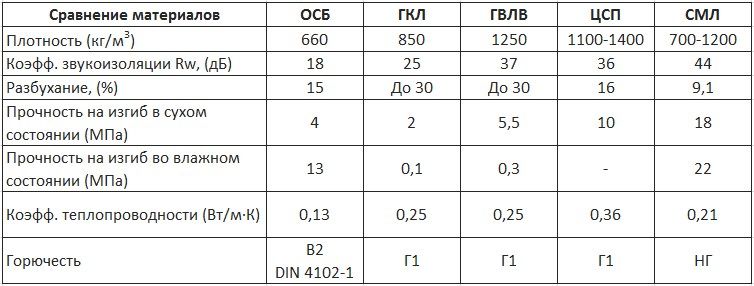
The raw materials used in the production allow to obtain better characteristics in comparison with other sheet materials - gypsum board, plywood, chipboard and fibreboard.
- Sheets without a decorative coating do not burn (category NG), but with a coating are classified as category G1 (slightly flammable). The material is completely resistant and does not deteriorate at temperatures up to 800 ° C. When exposed to fire, there is no release of toxic substances and smoke.
- Resistance to shock loads is due to the double-layer reinforcement of the fiberglass mesh.
- The composition does not contain materials that are sources of radioactive radiation. Manufacturing technology does not provide for the use of asbestos and formaldehyde.
- The properties of heat and sound insulation are due to the porous structure and the content of up to 35% wood fibers. LSU saves energy on heating and eliminates additional sound insulation of internal partitions and external walls.
- LSU sheet does not deform and does not swell even in direct contact with water. The property allows the use of products for the installation of building structures in bathrooms, toilets, swimming pools and other places with high humidity.
- Sheets are painted in various colors or decorative coatings are used, which excludes additional finishing. The joints are closed with decorative strips or moldings.
- To create arches, it is permissible to use LSU 6 mm thick, which excludes the combination of materials and various finishing technologies. During transportation, sheets are rarely damaged.
- Different front and back. When leveling the walls for plastering, the sheets are applied to the wall (inside the partition) with the glossy side. The roughness ensures the adhesion of all types of plaster.
- The density of the product is 900–1250 kg / m³, which roughly corresponds to the mass of gypsum board with a significantly higher strength.
- The frost resistance of LSU corresponds to F50, after 50 cycles the strength decreases by 3-5%.
- Installation does not require special tools and specific skills of the builder.
Solid wooden walls are not upholstered by LSU. The difference in the coefficients of thermal expansion leads to the fact that the sheets warp. In order to exclude breakage and destruction of the material, it is necessary to strictly observe the installation technology, which provides for the arrangement of the battens from galvanized steel profiles.
Areas of use
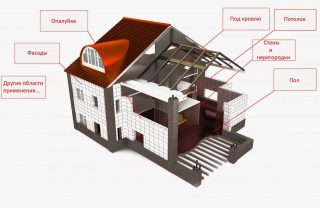
Magnesite glass sheets are used for interior and external works... The main directions of use in open space:
- decoration, thermal and sound insulation of buildings and structures;
- production of billboards;
- refractory layers of pipelines and steel structures;
- registration of water transport and yachts;
- production of permanent formwork, including for strip and pile foundations;
- construction of fireplace walls - internal fire-resistant and external decorative;
- production of walls of freezers and industrial refrigerators.

- base for the topcoat of the roof;
- sheathing of prefabricated frame buildings;
- walls and partitions of attics, verandas;
- heated and unheated warehouses and storages, basements and garages.
- production of partitions in damp rooms or in places where sound insulation is needed;
- leveling the walls before plastering and painting;
- decorative finishing of walls and ceilings with painted or decorated products;
- filing of ceilings, production of rounded arches;
- laying a sub-floor for finishing with tiles, laminate, parquet;
The cost of LSU is comparable to drywall, but in terms of its characteristics, glass magnesite has many advantages, especially when used in humid rooms.
Specifications
Each manufacturer manufactures products according to its own specifications, but in general characteristics are about the same:
- density - 900-1250 kg / m³;
- geometrical dimensions - length 2000–4000 mm, width 600–1250 mm, thickness from 6 to 16 mm.
- dry heat conductivity - 0.14 W / (m2 * oK);
- frost resistance brand - F50;
- water absorption - no more than 5% by weight;
- biostability class - 4;
- sound insulation coefficient - not less than 44 dB.
Installation rules
Conditions, features and typical solutions for the installation of LSU are contained in Typical technological map.
Transportation and storage
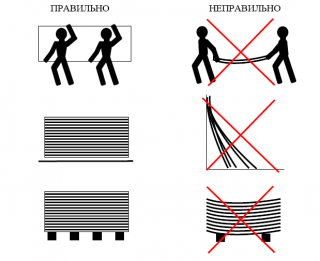
Unloading is carried out mechanically or manually. Sheets carried in an upright position, 2 piecesavoiding jerks, bends, undulating movements.
Store the material on a flat floor, in stacks up to 3.5 meters, providing protection from precipitation and direct sunlight.
Cut open
- The sheet is laid on a flat surface with the glossy side up. It is best to cut on a large table or specially made stand.
- A metal ruler, corner or strip is pressed along the marking line, they will serve as guides.
- Several cutting movements are applied with a knife until the reinforcing mesh is cut.
- The sheet is shifted so that the notch line matches the edge of the surface.
- Break the sheet with a downward movement.
- The second reinforcing mesh is cut through.
- Separate parts of LSU.
To cut through holes in a round shape, use a cutter or crown for rosettes. The figured cut is performed with an electric jigsaw.
Installation features
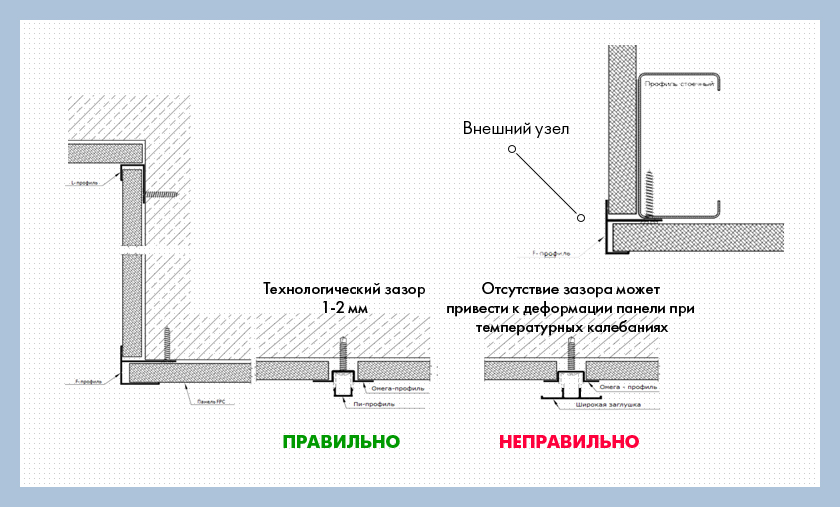
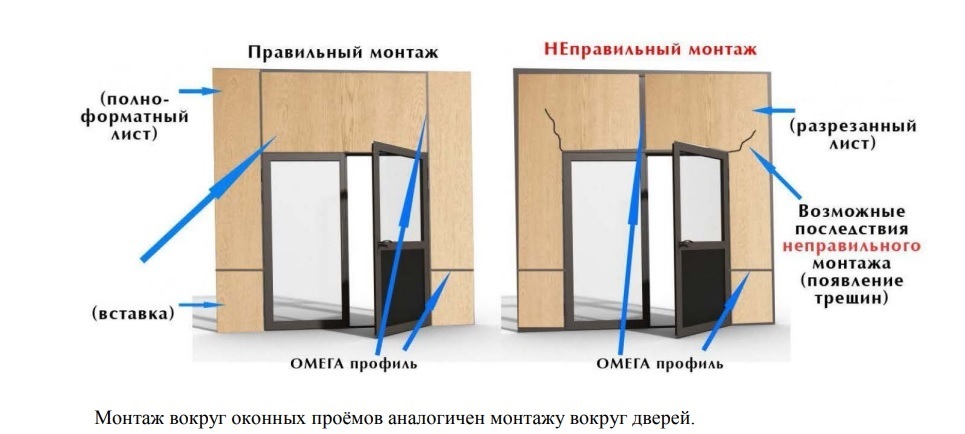
Installation of LSU when facing walls, ceilings, manufacturing partitions inside the house is carried out on a metal profile... When used for the frame of a wooden beam between the sheathing sheets, leave thermal gap a few mm... The same gap is chosen when using outdoor material, regardless of the type of frame.
Before installation the panels are thoroughly dried in room. Temperature and humidity should be brought to normal conditions and during operation, sharp fluctuations in microclimate parameters should not be allowed.
Before grouting, plastering, tiling, wallpapering or painting LSU is primed with deep penetration compounds.
To cover the seams, putties on an acrylic or gypsum base are used.
Considering the weight of the sheets and the typical size of the width of 1120 mm, choose between the vertical posts step 400 mm for sheets with a thickness of 6-8 mm and 600 mm for thicker products.
The sheets are fastened to the frame with self-tapping screws. TN 25 in 250 mm steps. The distance from the edge of the sheet is at least 10 mm.For premium class LSU with a particularly durable face in the sheet pre-drilled through hole 2.1 mm... If, when screwing in, the screw cap cannot be recessed, a preliminary countersink of the plate should be carried out to the required depth.
Both sides of LSU are workers, the choice of the method of attaching the product to the frame depends on the further finishing. The smooth side holds wallpaper and paints well. It is better to lay the tile side on a rough surface.
When used externally, the joints are not putty... The sheets themselves must be treated with water-repellent compounds and painted with facade paints.