Foamed glass was known in Russia at the beginning of the last century. Manufacturing technologies were not perfect, significant costs were required, so manufacturing was not developed. Modern methods have made it possible to reduce the cost, taking into account the correction of the shortcomings of the past, therefore, foam glass insulation has become a popular material for protecting buildings from the cold.
Material description
The material is presented on the construction market in basic formx:
- blocks - light and rigid rectangular elements;
- pipes - for isolation from the cold of sewer, water supply gas collectors;
- granular insulation - mixed into the mortar for construction work in order to increase the insulating properties.
The cells of the material are hexagonal or round in shape, and their size ranges from a few fractions of a millimeter to one centimeter. The walls are obtained with a thickness of 20 - 10 microns.
- waste cullet or glass production;
- sintering rocks with a high percentage of alkalis (nepheline, trachyte, obsidian, syenite, volcanic tuff).
Gas formers carbon based promote the organization of closed pores, and carbonate - form communicating passages. The ability of the material to be saturated with water depends on this.
As foaming agents substances are used as a percentage of the glass mass:
- peat semi-coke, coke - 2 - 3%;
- marble chips or limestone - 1 - 1.5%;
- anthracite - 1.5 - 2%;
- dolomite, lamp soot - 0.2 - 0.5%.
The gasifier is selected so that the melting point is 50 - 70 ° C higher than that of the glass. Blocks are produced in gray with a greenish tint, the color depends on raw materials and impurities, it can be from creamy light to black.
Production technology

In production, complex chemical and physical processes are used, they regulate the fixation of the volume, shape, cooling and annealing of the resulting foamy mass. The production technology is regulated by GOSTs.
The processes involve large powerful ovens with the possibility of combining components and introducing chemical ingredients. Such units are connected to the compartments where foaming takes place.
Foam glass production takes place in four stages:
- cooking and preparation base glass;
- mix preparation from foaming components;
- foaming mass, annealing;
- final processing and packaging.
The main task in the production of foam glass is to reduce costs and ensure profitability. Each product manufacturer improves on a known technology.
Types of foam glass:
- Foamglas - acid-resistant non-combustible insulation;
- ETIZ - foam glass obtained by foaming liquid silicate;
- Neoporm - material with insulated honeycomb inside.
Fixing the shape is complicated by the fact that glass does not harden immediately upon cooling... Exothermic interactions appear in the melt, uneven crystallization appears, the temperature of the mass is not the same in different areas. Cooling is also impeded by the low heat conductivity of the resulting cellular blank. Eventually the annealing process takes up to 15 hours.
The production of foamed glass granulate is less complicated. The resulting material is inferior in terms of the slab variety, but is popular due to its low cost.
How to distinguish low-quality counterparts

Types of foam glass are cellular products obtained also by foaming, but only of dissolving glass... Production takes place at a temperature not higher than + 200 ° C, in which a foam former is added to the water glass. As a result, moisture is removed from the mixture and the solution becomes viscous, then it is cooled according to the technology.
You can distinguish such a heater by its characteristics:
- dissolving glass insulator absorbs moisture;
- material collapses from the action of aggressive atmospheric factors.
Low-quality insulation is sold in different sizes, while the dimensions of real slabs always match up to a millimeter... In the structure of the branded material, the cells are always located separately from one another and do not touch.
Manufacturers use different technologies, therefore different vapor permeability index... Such information is indicated in the documents, and if not, it is better not to purchase products.
The technology for the production of foam glass plates is complex, so the material cannot be sold at a low cost. If the price of a product is understated, then a low-quality analogue is being sold.
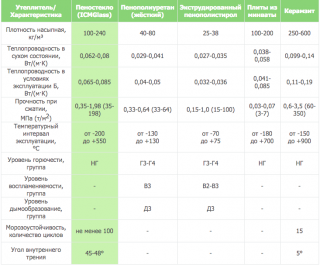
Specifications
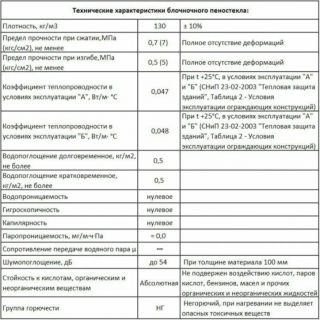
An important indicator is the property of foam glass resist ignition. According to fire categories, foam glass is classified as a material that does not burn. (group NG)... According to the results of tests in critical conditions, a temporary limit of fire resistance was revealed - the ability to contain heat from a fire lasts for an hour... This quality has led to the use of the material in buildings with an increased risk of fire.
Foam glass characteristics and features:
- the material does not collapse, does not change properties when working in the temperature range -255 - + 230 ° С;
- temperature melting is + 1000 ° C, after that the foam glass melts, but does not burn;
- slabs contain 80% air, density — 130 - 600 kg / m³;
- compressive strength - 0.5 - 4.0 MPa;
- bending strength - 0.4 - 0.6 MPa;
- thermal conductivity foam glass - 0.06 W / m K, the indicator is more effective than the values of the tree;
- water absorption is 0,1 – 5 % from the total volume of the panel;
- vapor permeability — 0.005 mg / (m h Pa);
- sound absorption - up to 56 dB.
- 20 x 550 x 450 mm, slab area - 0.248 m², volume - 0.003 m³;
- 40 х 550 х 450 mm, panel square - 0.248 m², volume - 0.01 m³;
- 60 x 550 x 450 mm, respectively - 0.248 m2 and 0.015 m³;
- 80 x 550 x 450 mm - 0.248 m² and 0.02 m³;
- 80 x 300 x 380 mm —0.114 m² and 0.0091 m³;
- 80 x 250 x 380 mm - 0.095 m² and 0.0076 m³;
- 100 x 550 x 450 mm - 0.248 m² and 0.027 m³;
- 120 x 550 x 450 mm - 0.248 m² and 0.03 m³.
Foam glass in the form of an insulating shell for pipes is produced with a length of 50 - 100 cm, the thickness is agreed with the customer, usually -20 - 40 mm. The inner diameter is in the range of 22 - 325 mm, the outer one differs taking into account the wall thickness.
Comparison with other heaters
Compared to many organic and inorganic thermal insulation types shrinkage of the material is at zero, therefore, this characteristic distinguishes it favorably. Resistance to heating in case of fire material outperforms glass wool, mineral wool boards, polystyrene, polyurethane foam... The fire resistance limit of foam glass is slightly lower than that of brick.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity foamed glass approaches the values of stone wool, but higher than thermal insulation with polyurethane foam and autoclaved foam concrete. For the insulation of pipelines, foam glass is out of competition, since the temperature indicator at which the properties are preserved is higher than that of all heaters.
Applications
Foam glass is used in the construction of buildings and structures in the industries:
- agricultural;
- energy;
- chemical and oil refining;
- mechanical engineering;
- food;
- pharmaceutical.
In private housing construction the material is used to insulate the walls of the house, used on the roof, in the basement. Due to its moisture resistance, foam glass is suitable for insulating vertical surfaces of subfloors, foundations, plinths from moisture and cold. Plates insulate the floor in living quarters, soundproof walls and partitions.

Building insulation instructions
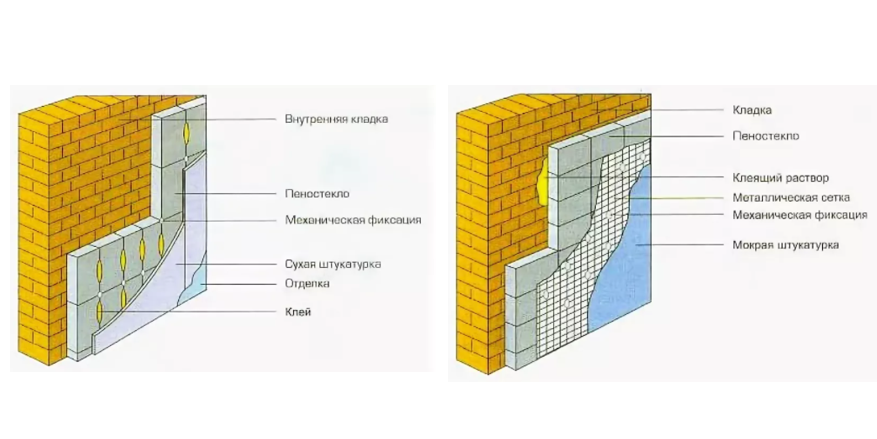
The technology for installing blocks or slabs is simple, within the power of site owners. The panels are fixed to the wall with adhesive, after hardening, the surface is decorated with finishing materials. Glue take two-component, the parts of which are connected before work. For outdoor installation use frost-resistant glue.
On the tree fix special dowelsto create a gap for air exchange between the wall and the foam glass layer. Before gluing, the surface is cleaned of dust and primed.
Before starting the installation a plank is placed at the level of the base to obtain even rows, the installation is carried out from the bottom up, the vertical seams of the subsequent rows are shifted to obtain a dressing.
Further finishing:
- for plaster, putty put a reinforcing mesh on top;
- under the tiles, tiles, each panel of foamed glass is screwed with 3 - 4 dowels, a frame made of slats or a profile is installed on top;
- under the lining, siding, plastic panels, a lathing frame is also provided.
To insulate the floor from the cold take granular or slab insulation. Be sure to provide waterproofing, a cement-sand screed is performed on the top.