Screw piles for the foundation are attractive because of the speed of installation, as well as the possibility of using them in areas with a high rise of groundwater. However, on some types of soil, such supports cannot be installed. When arranging the foundation, it is important to conduct a geological survey of the area and select products with a sufficient wall thickness that have undergone anti-corrosion treatment.
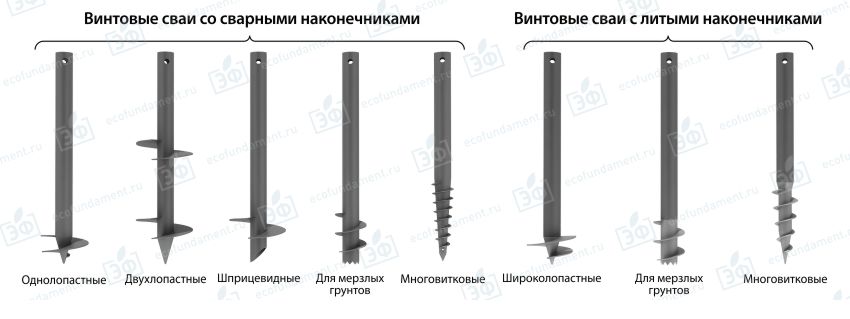
Description and varieties of screw piles
Classify screw piles can be made according to a number of parameters:
- By tip type... They are welded and cast. The second option is more expensive, but it is better suited for high-density soils (in particular, permafrost), easily passing through their structure and not deforming in the process.
- By the number of blades on the barrel (there can be from 1 to 6). Single blade products are only suitable for dense soils that cannot be called mobile or heaving. Piles with a large number of these elements can be used on different soils. But due to their greater resistance to different types of loading effects (horizontal, pulling and others), they are often used on soils with insufficient bearing capacity.
- By the dimensions of the blades. Elements are considered wide if their diameter is 1.5 times or more than the cross-section of the bar. Piles with such blades have a large support area. This makes them well suited to weak soils. Supports with narrow blades are suitable for dense and permafrost soils. A pile with a wide base cannot be installed in such soil, as this increases the risk of deformation or damage to the blades.
- The speed of work is especially attracting the attention of builders. Even when pouring concrete into the pile core no need for long waiting time for solidification, since the main load is borne by the metal body.
- Drain the sitewhere the work will be carried out, not necessary.
- Much less noisethan when working with other types of piles. When installing driving supports, not only noise is generated, but also vibration phenomena that can adversely affect the functioning of objects located near the place where work is being carried out.
- Less land work in comparison with slabs and strips made of reinforced concrete, it saves time and money (which, however, does not eliminate the cost of purchasing high-quality thick-walled piles).
- Installation of a foundation is possible on the slopes and other areas not characterized by perfect evenness. This is facilitated by the presence of blades.
- Building possibility close to existing objects due to the small displacement of the soil.
- Compatible with the installation of temporary structures. Piles can be reused, therefore, after dismantling a change house or other similar building, they can be removed from the soil and used in the installation of a similar structure or utility building.

The disadvantages are associated with the impossibility of installation on certain types of soil. Piles cannot be used:
- In localities with seismic activity higher than moderate.
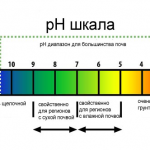
- In soils, the characteristics of which predispose to rapid metal corrosion. This includes high organic content, low pH (less than 5.5) and low electrical resistance (up to 1000 Ohm-cm). The service life of the supports in such conditions will be low. It is because of the insufficient pH that European standards do not recommend the use of piles on peat soils.
- In soils where there are hard inclusions (stones, dumps, construction debris). They can injure the tip of the pile or even its rod.
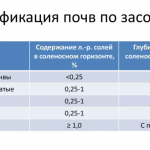
- In soils with a high content of sulfates (more than 1000 ppm). These connections destroy the unprotected concrete casting of the members.
Undesirable use piles on loose soils, not providing a stable position along the length (peaty, silty sandy and other similar soils). If this still has to be done, the supports must be deeply buried (at least 3 m).
The installation of piles into the soil, where the loose layer lies at a depth inferior to their length, should also not be allowed (for example, the installation of a three-meter structure in a place where a peat layer lies at a depth of 1.8 m).
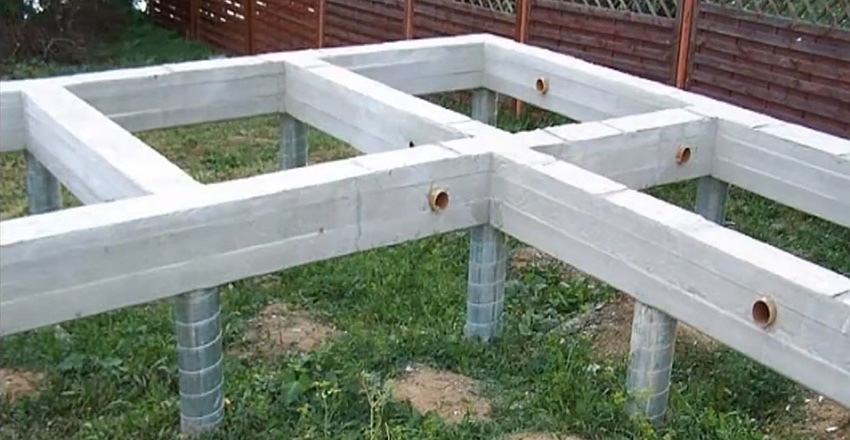
Sometimes screw piles are combined grillage (reinforced concrete tape)intended for even load distribution... The creation of such a foundation requires careful geological research and adherence to technology. One of the most common mistakes is keeping the belt on the ground.... In this case, the forces of frost heaving will act unevenly, and the grillage will bend in areas near the supports. Also, such a foundation creates difficulties when insulating the floor and laying communications. It is most suitable for areas with a strong slope of the relief and the danger of landslides.

Scope of application
If the soil meets the requirements, and the piles have sufficient wall thickness and are galvanized, they can be used for the construction of a residential building. Subject to the construction technology, such a foundation has a chance to last more than 100 years. However, most of the piles produced in Russia are not thick enough for a residential building.
There are several areas where the use of such a foundation rationally:
- Erection light buildings: baths, gazebos, frame country houses, corrugated fences.
- Arrangement temporary dwellings... The foundation will be built quickly; large-scale earthworks will not be required.
- Construction in areas with a pronounced slope, uneven terrainlandslide probabilityI... Any areas where a lot of money would have to be spent on leveling or building a basement dug into the slope.
- Locations with high rise of groundwater.
The soil must meet the requirements for ICC FC358: it should not be rich in stony inclusions, be too soft and loose, contain a lot of sulfates or be prone to corrosive processes. This is especially true for the construction of a residential building.
Pile selection rules
Manufacturers adhering to Western standards have begun to appear in Russia.
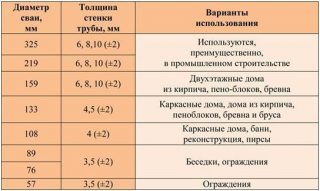
For the types of piles on the market, the following can be designated scope of application:
- with thickness 4-4.5 cm: for undemanding buildings - baths, sheds, gazebos, as well as for temporary dwellings;
- 6-6.5 cm: for light frame houses;
- 8-9 cm: for residential buildings made of any materials.

When choosing, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- Availability and quality of coverage... The greatest durability is provided by galvanizing: thick-walled piles with such protection can serve for more than a century.
- Surface smoothness: there should be no suspicion that this product is made of painted rusty pipe.
- Seam quality: it should be smooth, continuous, neat.
- Blade shape: it must correspond to the composition of the soil.
- Cleanliness inside: if the product is turned with the tip up and lightly knocked on it, rust should not fall out of it.
Life time depends on the characteristics of the pile itself and on the operating conditions. Especially the soil characteristics that predispose to corrosion reduce it.
Installation of screw piles

Do-it-yourself installation of screw piles can be done completely manual, mechanized (using devices that increase work efficiency) and using expensive equipment... The choice of the preferred option depends on the financial capabilities and on the construction conditions. Long structures (more than 3 m) are difficult to install without equipment. The distance between the elements is determined by calculation.
The technique should be used in areas with difficult terrain. Since it is expensive to purchase, it is best to rent the equipment you need. Among the common attitudes you can mention:
- electric twists - Whirlwind, Krinner, Handyman and others;
- Capstan - suitable for piles with a cross section up to 21.9 cm;
- Tornado - portable equipment powered by a 380 V mains or 5.5 kW generator and suitable for supports with a cross section of up to 15 cm);
- MGB-50P, allowing building on frozen ground.
You can also mark uncomplicated fixturesfacilitating manual screwing:
- rodthreaded into the lugs of the support;
- head from a pipe with clamps, preventing damage to the top;
- meat grinder driven by a drill with sufficient power (more than 1 kW).

How to make piles with your own hands
Instructions for creating piles looks like that:
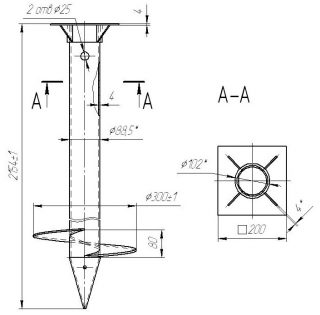
- Prepare a drawing. It indicates the diameter of the blade, the pitch of its turn, the length of the cone. The optimal pipe diameter is 9-11 cm. The length should be at least 0.3-0.5 m greater than the depth of the bearing layer.
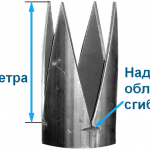
- The cone is made tetrahedral: at the end of the pipe, segments are cut, bent with a hammer and welded. The markup can be made from paper patterns.
- Blade made of carbon steel with a thickness of 5-6 mm. Its inner diameter is equal to the girth of the pipe, and the outer one is selected as follows: for a trunk with a cross section of 6 cm, it is made equal to 20 cm, for a pile of 7.5-9 cm - 25 cm, for a rod of 11 cm - 30 cm.The screw pitch is usually 20 -40% of the outer diameter. The finer and looser the soil, the more the value is made.
- Cutting out the blade blank with plasma cutting, it flex in accordance with the step with a vice.
Then the blade is welded to the rod... At the top of the support make a pair holes for the rod or create a separate head. Anti-corrosion design covered with ship paint.