The types of building bricks are very diverse. Buildings constructed under different conditions are subject to different stresses. To choose the right brick for your home, you need to take into account its size, material of manufacture, production method.
Classification of brick products

The material is classified according to the raw material, according to the form, according to the purpose. Of greatest interest is an ordinary stone intended for the construction of walls.
By material the following varieties are distinguished.
- Earthenware - or ceramic. The raw material is a mixture of red clay, sand and water. The composition is laid in molds, dried and fired. Depending on the firing temperature - from 900 to 1200 ° C - products with different characteristics are obtained. The stone is distinguished by its strength and hardness, it is not afraid of heating and the most severe frost. Does not absorb moisture, and therefore is suitable for the construction of buildings in any corner of the earth. Clay brick retains heat.
- White silicate - consists of 90% quartz sand and 10% lime. The product is not fired, but steamed in an autoclave under a pressure of 10 atm. This material is very cheap: the production cycle lasts 5-6 hours. It has a high bearing capacity, therefore it is used for the construction of high-rise buildings. However, the material is hygroscopic, unstable to frost - withstands up to 50 freezing cycles, and weighs a lot. It cannot be used in northern latitudes.
- Concrete - hyper-pressed and vibropressed. Differs in durability, very heavy, expensive. The concrete block does not retain heat and is difficult to process. It is used to construct individual complex units in a building.
- Hyperpressed - the name speaks for itself. It is made from limestone screenings - marble, shell rock, dolomite and 10% Portland cement. The stone is pressed during molding, obtaining a brick of exact shape and size. It does not shrink, does not absorb moisture, is not afraid of the sun or frost, but it is expensive. It is very decorative: the raw materials can be painted in different colors, and the surface of the finished stone can be given an interesting texture.
- Stone with additives - the basis is lightweight concrete, into which some ingredients are added before production. This technique is used to make the material light and cheap. Since such additives are industrial or wood waste, the brick retains heat better.
Choose a stone for construction, depending on the number of storeys of the building. Silicate can be used for the construction of houses above 10 floors, and any concrete with the addition of sawdust or slag is allowed to be used only for the construction of houses not higher than 3 floors.
Varieties of bricks depending on the scope of application
Private
Regulated GOST 530-2007... It is made from different materials, but has some common characteristics. Designed for laying load-bearing and self-supporting walls, partitions and ceilings. Such a brick is not attractive, since it allows inaccurate configuration, inhomogeneity of color and structure, cracks and chips. These disadvantages do not affect the bearing capacity. The unsightly appearance of the walls is masked by finishing - siding, plaster.
Facing
Also called front or front... Its task is to give the facade a beautiful look.It is also used to protect the base material of the walls, so the brick is chosen very carefully. Facing stone, whatever it is made of, has a low porosity and high density. This ensures that its dimensions and configuration are perfectly accurate. It is also important to achieve a uniform color. Large red clay brick, intended for ordinary masonry, "amazes" with a variety of shades. The finishing clinker retains the same color in one batch.
Facing is divided into 2 types:
- Textured - imitates the specific surface of the stone, but not chips and cracks, but texture. The ragged stone finish reproduces the surface of the basalt after it has been mined. The aged "palace" imitates the irregularities and weathering of the old stone. The edges of the blocks can be smooth or rolled. Processing does not affect the packing density.
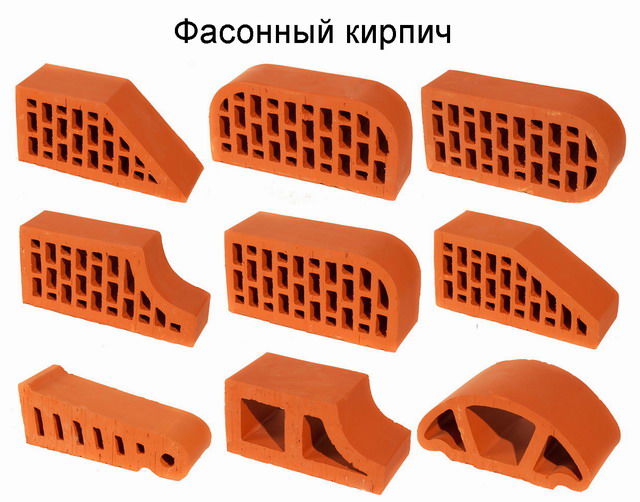
- Shaped - products of a special shape for the construction of complex architectural elements. The configuration is unusual - triangular with rounded edges, semicircular, complex with several protrusions. The material is used for the construction of arches, pillars, columns, complex framing around a window or door block.
Porosity and density provide other properties of the stone. It does not absorb moisture, and due to its low porosity it is not afraid of even the most severe frosts. During the production of cladding, the quality of the raw materials is monitored, therefore efflorescence, dark spots, small cavities do not appear on the surface of the stone.
Clinker
- one and a half - with a standard length of 24-25 cm, its width is no more than 11.5 cm, and its height is 7.1 cm;
- single less in height - 6.5 cm;
- euro - the width is reduced to 8.5 cm, such material is lighter;
- half is 6 cm wide and 6.5 cm high.
A clinker laid in a standard way, even a euro, looks like an ordinary brick in appearance. In fact, it forms a thin wall - a cladding. In this case, the strength does not provide the bearing capacity of the facade wall, but the protective qualities of the finish.
Chamotny
Yellow brick is an example of a refractory product. The description indicates that the material is brittle with high heat resistance, therefore if, for example, a large furnace is folded, fireclay blocks are taken only for finishing the furnace, and the body is built of clay.
Types of bricks depending on the nature of the filling
Another important parameter when choosing a building material is filling... There are 3 types.
- Corpulent - the product does not include voids. Solid brick is always denser, and, therefore, withstands a higher load-bearing capacity. However, the rest of its qualities - hygroscopicity, thermal conductivity, cost, are determined by the material of manufacture.
- Hollow - contains voids. They look different: it can be 2 large round holes, as in a concrete block, several through round holes. The voids are filled with air, and this improves the ability of the stone to retain heat. In addition, such a brick is lighter: it is easier to lay, and the walls from it load the foundation less. Hollow bricks can be ordinary and facing.
- Porized - the brick is riddled with many thin cracks. Porous stone is classified as heat-insulating. The total pore volume here can reach 75%. Most often, a brick is taken for thermal insulation of load-bearing walls. However, buildings up to 3 or 5 stories high can be constructed from higher density porous blocks. This option refers to structural and thermal insulation materials. Buildings made of it in mid-latitude do not need insulation.
If the volume of voids is below 22%, GOST considers such a brick as solid.Moreover, its weight is lower, which is beneficial.
Product shape
According to the form, the following options are distinguished.
- Private rectangular - may have different sizes and different aspect ratios. It is used for masonry of main walls, partitions, ceilings and foundations. This configuration allows you to lay bricks in a different way: on a poke, on a bed, using a spoon method. In this way, walls of different thicknesses can be built.
- Special shaped - not only the finishing stone has a specific shape, but also the base one. It is not so difficult, however, triangular, rounded stones, cut at different angles, are required quite often.
The dimensions and proportions of an ordinary stone are regulated by GOST. The configuration of special products is often carried out according to technical specifications. There are a number of standard fittings available from most manufacturers. Complex elements with individual proportions are made to order.
Brick sizes, domestic and European standard
Brick shape and dimensions are determined construction features... It is more convenient to put large blocks. However, their weight will be too heavy. In addition, a complex arched passage cannot be made of large stone. Small bricks weigh less, allow you to lay out columns and arches. However, the construction of them is a more laborious process.
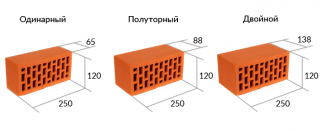
- single - 250 * 120 * 65 mm;
- one and a half - 250 * 120 * 88 mm;
- double - 250 * 120 * 138 mm.
Special products are also produced, the dimensions of which can deviate very far.
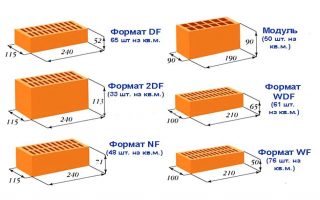
- DF - 240 * 115 * 52 mm;
- 2DF - 249 * 115 * 113mm;
- NF - 240 * 115 * 71 mm;
- RF - 240 * 115 * 61mm;
- WDF - 210 * 100 * 65 mm;
- WF - 210 * 100 * 50 mm.
Dimensions of special elements - with projections, beveled or rounded edges, are designated differently.
What to consider when choosing a brick
- The nature of the building - a one-storey farm building or a building with a height of 10 floors. For different buildings, a stone with an appropriate bearing capacity is required.
- Weather - if the level of precipitation in the region is high, you need to choose a stone with minimal hygroscopicity. If this is not possible, then additional finishing must be included in the estimate to protect the walls from moisture.
- Separately evaluated frost resistance, since it is not always combined with moisture resistance. For construction in northern latitudes, frost-resistant material is required.
- Appointment - ordinary brick is needed for laying the wall, facing brick for finishing. They do not replace each other.
- Decorativeness - this parameter is important when choosing a facing material. It is necessary to determine the color, texture, and configuration of the stone.
- Quality - to evaluate, you need to inspect at least a couple of dozen samples from 1 batch. If they differ too much from each other in color and texture, it is better to refuse to purchase. It is worth evaluating the parameters inherent in each type of stone. So, ceramics, when struck, emits a sonorous sound. If the sound is dull, the stone is poorly burnt and will crack over time.
The sample should be viewed outdoors and not indoors, as artificial lighting changes shades and prevents some imperfections from being seen.