Polyurethane foam from an aerosol can is considered a convenient material for filling construction joints. Winter and summer polyurethane foam behave differently at subzero temperatures, so builders choose an insulator depending on the conditions of application and operation. In the cold, the street seal expands in a given mode, unlike the summer seal, which does not foam, does not gain volume.
Features and characteristics of winter polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam sealant is divided into types:
- by composition - two and one-component;
- by operating temperature - winter, all-season;
- by method of use - pistol, household;
- by combustion category - fireproof, self-extinguishing, combustible (B1, B2, B3, respectively).
In cold weather, the winter-type insulator does not change the volume of the outlet from the cylinder. The amount of the mixture and its foaming remain within the normal range. The mass is not affected by humidity, wind, adhesion to surfaces does not decrease.
When filling openings in a house, winter foam for windows works effectively, which adheres well to slopes made of stone, brick, concrete, wood. Do not apply the material to oily, icy surfaces.
Scope of application
Scope of frost-resistant foam:
- sealing joints in vertical wall structures from the outside;
- filling the gaps between the panels of the frame house;
- sealing joints during the installation of floor slabs, parapets, ridge;
- gluing plate foam, polystyrene foam for insulation of walls, floors, ceilings;
- sound insulation of voids and gaps;
- waterproofing gaps between door, window frames and wall ends;
- installation of external piece slopes, ebb tides in window openings.
Frost-resistant foam is needed when organizing the exit of the chimney, ventilation ducts from the walls to the street, if work is carried out in winter. The material is used for repairs on the facade, roof, basement, unheated rooms.
Difference from summer
The difference manifests itself when the polyurethane foam is applied and its further use. Summer foam in the frost when exiting the tube "falls" not capable of increasing volume... If it is applied at positive temperatures in winter, it will expand, but when the indicators drop to minus, it will collapse. This will manifest itself as a crunch when pressed, the appearance of cracks, dips.
The composition of winter foam is different, the chemical components are selected so that the substance expands under frost conditions and subsequently gets a stable form. Polymerization (setting of winter foam) slows down, but the process ends after a certain time. At the same time, the number of closed cells in which the gas is enclosed remains minimal.
Quality foam for winter use does not have any subsequent expansion or shrinkage after curing. In this state, the mass cannot freeze, crack and collapse.
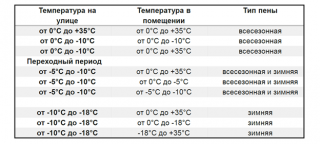
What temperature can it withstand
Recommended application temperature of polyurethane foam:
- Some brands work well at -10 °, other manufacturers indicate the application limit at -18 ° C, and even -20 ° C.
- With the correct application technology, the frozen foam retains its quality characteristics when the temperature drops to -35 ° C.
- The insulator cylinder must have a positive temperature (+ 5 ° C) during the application.

Terms of use
The builders follow the technology of work to ensure the correct functioning of the valves of the can, uniform polymerization inside.
The exhaust valve sticks due to the following reasons:
- heterogeneous heating of the contents inside, when part of the mass remains thickened;
- rapid and too strong heating of the aerosol container, while the accelerated transformation of the prepolymer causes the appearance of clots;
- the cylinder is stored upside down - the mass thickened in the cold clogs the valve.
In the latter case, the cylinder is placed with the valve upwards, expelled by pressing some gas.
It is impossible to use an unheated balloon - this will cause excessive consumption of foam, reduce the quality of the suture filling. Optimally - keep the container at a temperature of + 15 ° - + 20 ° C for 24 hours.
Work at subzero temperatures
Procedure:
- the aerosol container is shaken for 30 seconds;
- the mixture is placed in the seam so that it takes up 1/3 or 1/2 of the space (options for a pistol and a cylinder with a tube);
- after application, the foam is moisturized, preventing the appearance of frost or ice.
The frozen mass is covered from ultraviolet radiation with a finishing material, for example, plaster, putty, sealant, paint. You can cut off the excess only after 1 - 1.5 days, after complete drying.
How long does it take to dry

First crust on the surface of the mixture is formed after 20 - 40 minutes, and the time until complete solidification can take up to a day or even more.
The polymerization period depends on the indicators:
- frosty air temperature;
- humidity of the atmosphere;
- composition of the material.
If the insulator is oversaturated with unbound gas filler, a large number of open links inside are obtained. Expansion is rapid, but shape stabilization is delayed. The lack of active surface components leads to the integration of cells into large cavities.
The manufacturer coordinates the polymerization and expansion processes by introducing different volumes of blowing agent.The component breaks open closed bubbles and large cavities so that gas escapes and solidifies uniformly.
Storage of polyurethane foam
Rules for the maintenance of foam cylinders:
- it is better to organize the temperature at the storage place at the level of + 5 ° С;
- long storage at minus indicators reduces consumer characteristics;
- two-component formulations are stored longer, since the reagents are in different sections of the cylinder or containers (depending on the type of release).

Popular manufacturers
Russian manufacturers are actively involved in the manufacture of a popular product:
- Proflex - Tula enterprise, has been operating for over 15 years, produces household and professional foam aerosols.
- LLC "Vlad PromPen" - a well-known manufacturer of the Master brand. The company's products are distinguished by an optimal ratio of quality and value.
- Premium (LLC "De Lux")... The products are characterized by high performance properties, effective expansion, excellent adhesion thanks to innovative technologies.
- "Premium product". The company has been operating since 2014, a highly specialized production, aimed only at the production of foam.
- Kudo (JSC "Elf Filling") - the company has developed the Home and Proff lines, the products are distinguished by a good yield, solidification rate, resistance to moisture, combustion.
Foreign manufacturers and brands: Soudal, Penosil, Dr. Scenk.
What to consider when choosing
Consider properties:
- the size of the primary and subsequent increase in cubic capacity;
- the density of the material, which is less for household options than in cylinders for a pistol;
- viscosity indicates the fluidity of the mass, its adhesion to the seam surface;
- shrinkage (expressed as a percentage of the volume of the stabilized form to the original volume).