A thermostat with an air temperature sensor (thermostat or controller) is a device that, being built into the device, designed to create a comfortable microclimate in the room, provides control of the set temperature and maintains it in automatic mode.
Classification of thermostats

Despite the fact that the principle of operation of all thermostats equipped with temperature sensors is the same, on the market you can find a variety of models that differ in design and functional features.
- Byintended use - intended for indoor and outdoor installation.
- Byinstallation option - wall-mounted, built-in, with mounting on a DIN rail, etc.
- Byoverall dimensions - large, large, compact.
Also, thermostats with an air temperature sensor differ from each other:
- measurement limits - various modifications can measure as negative (up to -60° С) and high (up to + 1200 ° С) temperatures;
- the number of channels - single-channel and multi-channel;
- functional features - central and wireless regulation.
All thermostats, regardless of their purpose, have a similar design - they consist of a working part and a temperature sensor.
Purpose and principle of operation
Thermostats with air temperature sensors are designed to turn on and / or turn off the actuators in cases where the parameters of the thermal regime go beyond the preset values. Due to this, the stable temperature of the serviced objects is automatically maintained at the same level.
Functional purpose

Thermostats are installed in residential and industrial premises. They are used to control temperature:
- indoor air (air thermostat);
- certain items, such as gender;
- outside air (weather thermostats).
Operating principle
All thermostats, regardless of design and installation location, function according to the same principle:
- The automatic controller receives data on the ambient and / or coolant temperature from the built-in and / or remote temperature sensors.
- The controller compares the received data with preset temperature indicators and, if necessary, turns on or off the actuators of devices and heating or cooling systems.
To avoid errors in the operation of the thermostat, the remote temperature sensors must be installed away from the heating devices and radiators installed in the room.
Types of thermostats

There are several types of thermostats:
- mechanical;
- electromechanical;
- electronic.
They all have certain advantages and disadvantages.
Mechanical thermostats

A mechanical thermostat is the simplest device. Used in heating and cooling devices. Designed for indoor installation.
The main element of such a thermostat is a thermal sensor, the body of which has the form of a cylinder with flexible corrugated walls.The latter have the ability to stretch or contract. The inside of the body is filled with a special material (paraffin, gas, etc.) that can perceive changes in ambient temperature. A stem is also attached to the bellows, which acts on the control element according to a preset program when the room temperature changes. The required temperature is set manually. If the air temperature approaches the specified one, the actuators are switched off or on. In this case, the corresponding electrical circuit is broken or closed.
Advantages:
- high reliability;
- Ease of Management;
- the ability to work in freezing temperatures;
- the absence of electronic components makes thermostats immune to voltage surges and eliminates electronics malfunctions;
- long service life.
Disadvantages:
- little functionality;
- low accuracy and the presence of errors.
Mechanical thermostats are more common in heating systems. This is facilitated by low cost and simple management.
Electromechanical thermostats
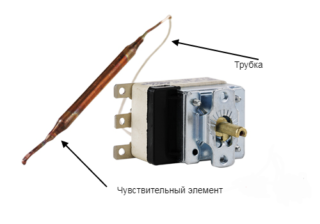
Electromechanical thermostats are widely used in various electrical household appliances. In this case, there are two modifications of such devices - with a bimetallic plate and with a capillary tube.
In a controller with a bimetallic plate, it works as follows - after heating to a predetermined temperature, the plate bends, while opening the contacts. This stops the supply of electric current to the heating elements (heating element, spiral). After the plate has cooled down, it bends back and closes the contacts of the electrical circuit. In this case, the heating elements are connected to the mains and the device heats up. Most often, such devices are equipped with electric irons and other household electrical appliances.
Capillary tube controllers use materials that expand with increasing temperature. Structurally, the temperature sensor consists of a tube with contacts, which is filled with gas. The tube is placed in a container with water, which, when heated or cooled, affects the gas in the tube. In this case, the gas closes or opens the contacts of the electrical circuit. They are installed in boilers, oil heaters, etc.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to achieve high control accuracy in electromechanical thermostats.
Electronic controllers

Electronic controllers are widely used in heating and air conditioning systems. As a rule, they consist of the following elements:
- remote thermal sensor;
- control controller;
- electronic key (contact group).
Among the many electronic controllers are:
- conventional thermostats, in which you can set the desired temperature range or its exact value;
- digital thermostats with closed or open logic.
In closed logic controllers, regulation is carried out by transmitting commands to specific devices. Temperature parameters are set in advance. It is not possible to adjust the program, but you can change the basic parameters.
Open logic controllers are able to control the heating process with high precision. Thanks to the advanced settings, you can change the algorithm of work. You can also turn on and off heating systems at a specified time. However, only specialists can reprogram these controllers, and therefore they are most often used in production.
Compared to other types of thermostats, electronic controllers have:
- a wide range of adjustments;
- high precision.
Electronic thermostats with an air temperature sensor are safe to operate, easily controlled and efficiently save energy, which makes them suitable for use in Smart Home systems.








