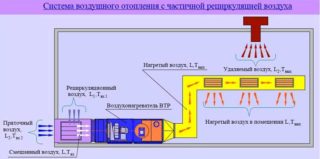
Units with air intake from the room are used with a high capacity of the ventilation system, when it changes from 2 to 15 thousand m3 / hour and is adapted for private houses with low productivity. A recirculating system supplies a mixture of indoor and cooled outdoor flow into the room. During testing, the compliance of the volume with sanitary standards is checked, the absence of toxic and harmful impurities.
The essence and purpose of recirculation

The removed air is already heated to a certain temperature, its admixture to the flow coming from the outside allows the power of the heater to be reduced. The mass is passed through a charcoal filter before being reused for cleaning. The energy efficiency is increased, it is allowed to use up to 80% of the internal air.
Purpose of the hood in recirculation mode:
- the formation and maintenance of a comfortable climate for humans and animals within the structure, as well as plants and objects of the material sphere (valuable artificial works, technological equipment);
- saving material resources that ensure the functioning of organized ventilation.
In a well-functioning recirculation system, engineering devices work sequentially, cooling or heating the streams. The operating modes differ, for example, the system operates in the presence of people or the night schedule is selected. The order of cleaning and conditioning is set separately for the weekend and working hours, set for a certain period.
Recirculation principle with ventilation
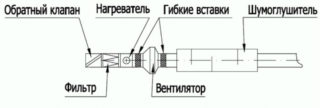
Elements included in the complex:
- two electric fans, on which the air inflow and flow rate depend;
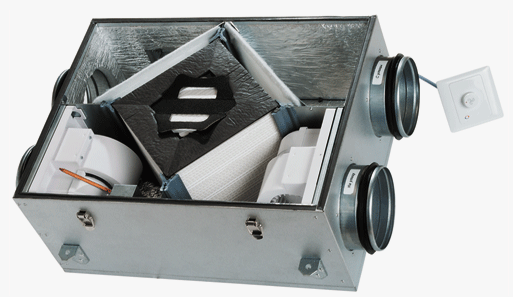
- a recirculating energy exchanger heats the street atmosphere, mixes the supply and exhaust flow;
- filters clean the jets from the external air duct, process the internal flows before supplying to the heat exchanger;
- an electric heater heats the outside air if there is not enough heat from the internal flow;
- duct valves are installed at the inlet and in front of the outlet, regulate the force of the jets or block the channel when the equipment is turned off.
Heating or cooling of the atmosphere in the room occurs quickly due to the repeated passage of the jets through the circulating heat exchanger. The recirculation mode in the hood is also used if it is necessary to stop the flow of outside air into the room (unpleasant odor, dust).
Types of ventilation with recirculation
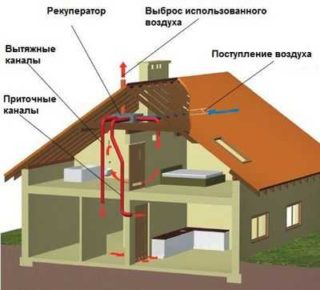
It is planned at the design stage before the start of the construction of the structure. Installation of ventilation in an already finished house is coupled with the fact that you need to build in and place channels, suspended air ducts, grilles, diffusers. In the old rooms, air exchange was partially due to the cracks in the window frames.
Modern sealed structures limit the flow of air, do not allow drafts, therefore, after the installation of metal-plastic infills, ventilation is required.The increased inflow invariably increases the heating costs; therefore, it is advisable to reuse the cleaned and heated air mass.
When calculating and installing a recirculation hood, the following regulatory rules are observed:
- the volume of the supplied street flow is at least 20% of the secondary air mass;
- after processing, the finished mixture contains no more than 30% of harmful components of the total amount at the rate.
Recirculation ventilation reduces the load on air handling units such as air conditioners, air heaters.
With heating
The system uses cold or heat from technical devices that heats up new air and mixes it with what is being removed from the room. The supply and exhaust fans and a heater are switched on. The valves are opened for the passage of the street, exhaust and recirculation flow, the work of each is set in a certain mode.
Types of heat exchangers:
- cross plate energy exchangers show efficiency at the level of 50 - 90%, condensation is allowed in them;
- regenerative rotary heat exchangers of the rotary type are distinguished by increased efficiency within 70 - 90%, due to the presence of moving elements, they are able to redistribute odors between the mixed streams;
- recuperators with an intermediate heater in their design operate with a lower efficiency (45 - 65%), the advantage is expressed in a good isolation of the energy generator.
When using the system, energy is saved for heating or air conditioning. For example, a circulating hood for a kitchen removes excess heat, if it is not required, cleans it, uses it when mixed with cold air and delivers it wherever it is needed.
Without heating
The recirculation system without heating provides fresh air and removal of the used mass from the rooms, while the renewal occurs constantly, and not in isolated episodes. At the same time, noise, the volume of dust, harmful insects that enter the openings are reduced. The ventilation outlets in the hood are positioned so that those present are not affected by drafts and harsh kitchen odors.
The purpose of a recirculated air duct without heating is only to pump fresh air in the off-season, when the heating system is operating, but the air outside is warming up. This becomes possible if the technical indicators of street flows meet sanitary standards.
The supply and exhaust fans turn on, the heater does not work. The recirculation valve coordinates the temperature of the jets entering the room. The external valve regulates the temperature readings of the outside air.
Supply and exhaust ventilation
If in such a system you open the outlet and supply air valves and close the recirculation plug, the line will work as simple ventilation. It is possible to direct the flows in a closed loop without supplying atmosphere from the street by closing the supply and outlet valves and slightly opening the recirculation valves.
Partial opening of three valves leads to the organization of the air supply with the addition of fresh atmosphere. This achieves the optimal ratio of temperature indicators and oxygen saturation. Choosing one of the schemes helps maintain comfort in hot or cold climates. The supply and exhaust system is installed in large rooms with a significant crowd of people, for example, restaurants, train stations, supermarket trading floors.
Additional schemes

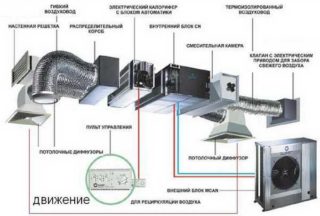
A system of movement of air masses with the use of a channel air conditioner is used. A fan coil unit is an indoor complex unit of an air conditioner, functioning as an active battery. It has a condensate drain, an energy exchanger, a filter device and a fan.In summer, the heat exchanger is supplied with cold water (10 - 12 ° С), in winter, hot liquid is supplied from the mains (up to 60 ° С). The fan coil unit is equipped with a control unit and automatic temperature control devices.
The damper circuit works as exhaust and supply ventilation or mixes the incoming and outgoing flows. The system is used in private buildings, for example, as a recirculation hood for the kitchen. The temperature values of the outside atmosphere change, but the comfort value remains constant. The volume of the mixed materials is regulated by overlapping gates and flaps in automatic or manual mode.
The movement of air masses inside the room using a ceiling fan excludes stagnation of the masses in one part of the hall, but does not apply to a full-fledged recirculation scheme. These systems without fan coil are used in large rooms, halls, foyers, lobbies.
Where the use of recirculation is prohibited

Secondary use of the removed air is not allowed if it comes from rooms with pathogens, fungi, microbes, the concentration of which exceeds the permissible standards. Do not use streams from workshops or industrial facilities with a pungent odor.
A recirculating hood is not installed in such situations:
- a significant mass of hazardous components of 1 and 2 hazard categories is released;
- harmful substances rise into the air upon contact with the heating elements of heat exchangers, but the system does not provide filters in front of the heaters;
- premises belong to class A and B (this does not include thermal and air curtains at the entrance);
- explosive air compounds of their vapors and gases appear;
- around the equipment of rooms of class B1 - B4, D and D, a hazardous zone arises (air is not taken within a radius of 5 meters from the machines).
The air is discharged outside if there are laboratory benches in the room, and work with harmful components is being carried out or the premises are airlocks.
Advantages and disadvantages of the system
The advantage is that it is possible to simultaneously create the required modes in the whole building using automatic control. Air duct routing is done using standard ventilation elements. The work is coordinated by remote controls that regulate the degree of heating or cooling.
The disadvantages include full recirculation without the use of outside air. The air is not renewed by mixing, therefore, the mode can only be set for a short period. The air of not all rooms can be used for mixing, therefore, in hazardous conditions, it is necessary to provide for another update of the microclimate.