Most car enthusiasts spend a lot of time in a garage building under constant exposure to health hazards such as vehicle emissions. Therefore, it is important to provide an effective exhaust hood for the garage in the design at the design stage. Its presence will allow you to remove waste products of gasoline combustion and maintain a comfortable level of humidity in an unheated room.
The need for ventilation in the garage

The need for the arrangement of effective ventilation of the garage is explained by several reasons, the most important of which are:
- ventilation in the garage will reliably protect all structures and objects located inside the structure from the negative effects of moisture and condensation;
- The hood will allow you to remove toxic mixtures represented by exhaust gases and vapors of fuel, waste oils, solvents, etc.
The first case is especially important in winter, when the humidity in the room is noticeably higher than the established norm. It is hazardous to food stored in the pit and is the main cause of rust formation on car bodies and metal structures.
The presence of effective ventilation of working spaces, as well as an inspection pit and a cellar, is the key to creating normal conditions for storing food and maintaining a personal car.
Features of the arrangement of ventilation in the garage
The current SNiP in the section on ventilation in the garage do not allow the operation of the room without arranging a system for removing exhaust gases and harmful impurities. According to the provisions of the standards, to create comfortable conditions for storing food and the car, an inflow of fresh air and a selection of polluted air are required. The best option for these purposes is supply and exhaust ventilation.
A properly designed and well-executed hood in the garage will create conditions that meet the requirements of sanitation and SNiP. In addition, the ventilation system, albeit indirectly, will help the user to maintain their health. Not everyone is able to inhale poisonous vapors of fuels and lubricants without serious consequences for the respiratory tract.
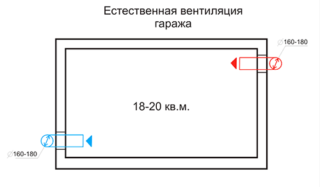
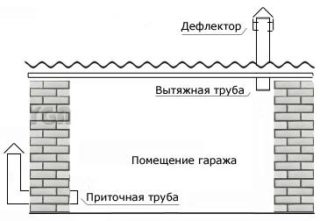
According to SNIP, in order to obtain an effective ventilation system in the garage, it will be necessary to organize the natural circulation of air masses. This can be achieved due to the always existing temperature difference between the indoor and outdoor environment. To achieve the desired effect, two ventilation holes are made in the walls of the garage building, offset in height by the maximum possible distance. One of them will be inlet, and the second will be outlet.
When arranging natural supply and exhaust ventilation in any garage building, users are guided by the following generally accepted rules:
- the inlet is located almost at the same level with the floor (10 cm above it), from the outside it rises about 30 centimeters above the ground;
- to protect from precipitation and insects, a cover with a fine mesh is made on the hole;
- the exhaust hole is arranged at the level of the ceiling;
- the upper part of the duct (the so-called "fungus") is placed directly on the roof of the building;
- the height above the roof of the garage is at least 50 centimeters.
It is important that the supply and exhaust openings are located as far apart as possible.
Calculation, device and ventilation schemes
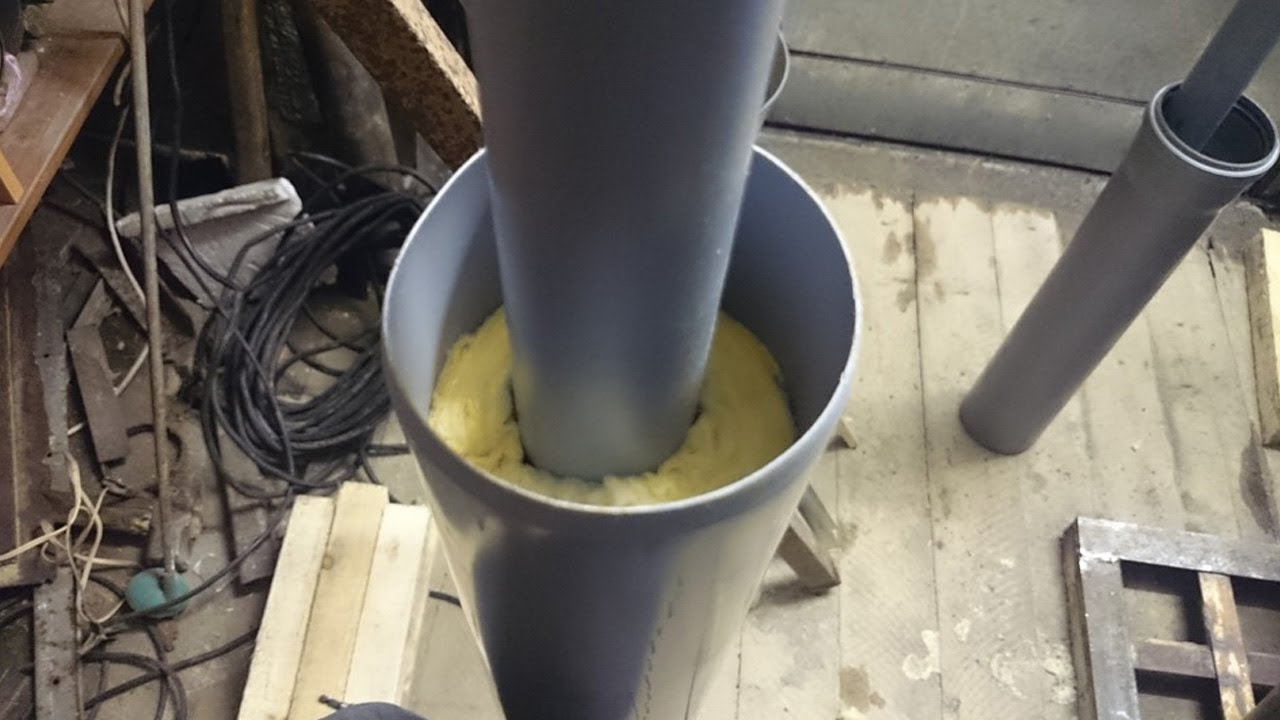
The calculation of ventilation in the garage is based on the rates of air exchange in the manned room. According to the current SNiP, this figure is at least 180 liters per hour for every 10 sq. meters of its area. In practice, it has been established that a plastic pipe with a diameter of about 15 cm is able to pass such a mass of air.
Ventilation calculation
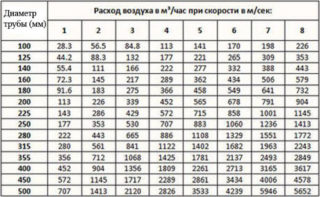
Assuming that the area of the garage is 24 sq. m. (4x6 meters), such a room will require a ventilation outlet with a diameter: (6x4) / 10x15 = 36 cm.It is possible to make an air duct with such a huge diameter, but it will look very awkward. It will look especially ridiculous in a relatively small garage building.
Another option looks much more preferable. Smaller diameter plastic pipes are used, and their total number is doubled. Then, the calculation takes into account each of these channels separately. The final result is obtained by adding them arithmetic.
When carrying out calculations, it is also taken into account that there are several types of ventilation systems:
- natural;
- forced (mechanical);
- combined.
They differ in the source of the motive force that sets the air masses in motion.
Natural ventilation
The calculation of this type of ventilation is based on the principle of natural draft created due to the temperature difference in the upper and lower points of the operated object. Due to this, a pressure gradient is created between the dense and rarefied layers of air, which leads them into intensive movement. At the same time, the air layers heated from the available heat sources rise to the upper zone, and the cold ones, on the contrary, go down.
In practice, the arrangement of an effective natural ventilation system is reduced to the following actions:
- The optimal layout of the supply and exhaust pipes is being considered, which allows to achieve maximum ventilation efficiency. To achieve the desired result, they try to spread them as far as possible from one another.
- It will be easier to achieve the movement of significant air masses if you place the inlet and outlet holes along the longitudinal diagonal of the room - at its opposite ends.
- The supply inlet is made at the bottom of one of the walls of the garage, and the hood is in the upper part of the opposite wall.
Particular attention is paid to the correct choice of the location of the supply pipe. Placing it right next to the ground is theoretically justified, but this is usually never done in practice. This is due to the fact that in winter it is immediately covered with snow, after which the flow of air stops. For this reason, the inlet hole is made at a distance of 15-20 cm from the ground.
When choosing the locations of the input and output, the wind directions prevailing for the region must be taken into account. Preference is given to the option in which the inlet is located on the leeward side.
Forced system
The disadvantage of a relatively cheap natural ventilation that does not require energy supply is its dependence on the temperature gradation and the chosen layout of the air ducts. It is possible to overcome all these difficulties by arranging forced or mechanical extraction. The advantages of this type of ventilation in the garage are:
- independence of the quality of air exchange from the configuration of the air ducts - supply and exhaust pipes can be placed next to each other along one wall;
- the possibility of distributing air flows at the discretion of the garage owner according to an arbitrarily chosen scheme;
- a device that creates a forced movement of air masses is also allowed to be placed in any convenient place;
- high efficiency of air renewal.

Thanks to the advantages of the forced option, the complete ventilation of garage spaces takes much less time. At the same time, the considered systems have some disadvantages:
- for the operation of a mechanical air blower, it will be necessary to lay a stationary power line;
- in the absence of electricity, the air exchange system will not work;
- in the presence of garage electrical wiring, the requirements for electrical and fire safety increase many times over;
- Like other mechanical devices, the fans used in the system need maintenance and periodic repairs.
Given all these difficulties, before deciding on the use of forced ventilation, the user will have to calculate all the upcoming costs.
Combined option

In some cases, for garage buildings, the option of combined ventilation is more suitable, almost completely repeating the case with natural air exchange. Its difference from the latter is that a powerful fan is additionally installed in the exhaust duct. A feature of this scheme is the possibility of using the built-in device even in the absence of electricity, since its blades will rotate due to the natural movement of air masses.
With the fan plugged in, the performance of the entire system increases dramatically. The choice of the type and power of the ventilation device depends on the size, location and construction of the garage, as well as on the internal layout of its spaces.
Temporary ventilation in metal or capital garages is organized through the use of a powerful ventilation device installed in a convenient place. When using this method of ventilating the room, the most important thing is to securely fix the fan on a solid and rigid base.
Air exchange in the inspection pit

Any major garage has an inspection pit and a small basement in which food is stored, if necessary. Their presence will require additional efforts from the contractor aimed at arranging ventilation in the basement of the garage, which allows removing extraneous odors and moisture from it. It will be even more difficult to organize a hood in the inspection pit, since it is small in size.
There are two ways to implement stable air exchange in this part of the garage space:
- by arranging the hood, which is part of the general ventilation system;
- by making our own exhaust structure.
The least costly solution is considered to be autonomous cellar ventilation in the garage, made as an addition to the overall system.
Before arranging ventilation in the inspection pit, first of all, a general scheme is prepared for the entire garage complex. It must indicate the holes in its walls, foundation, as well as in the basement part, which are necessary for the further placement of air ducts.
If the groundwater at the location of the garage is too close, in addition to ventilation issues, it will be necessary to provide for the arrangement of good waterproofing of the bottom and walls of the pit.