Natural ventilation is carried out due to different air pressures outside and inside the house. The disorganized system assumes the flow of fresh flows through the cracks in the window and door openings and depends on the season. Organized way means a similar way of air exchange, but oxygen flows in through special devices for supplying air. Calculation of natural ventilation is required to control the rate of air exchange in the room.
Definition of natural ventilation
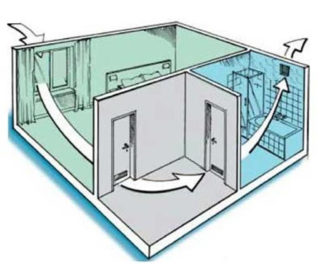
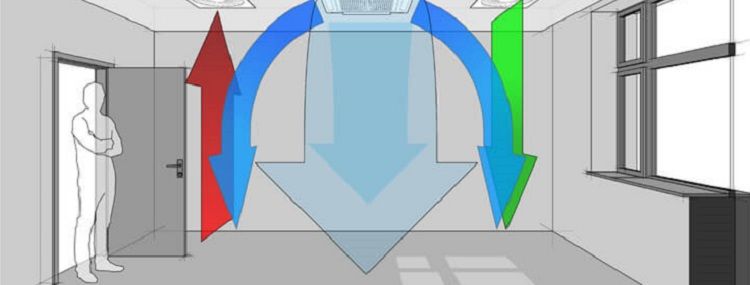
Ventilation is responsible for comfortable conditions in a private and multi-storey building. In the multi-apartment sector, ventilation risers and shafts are provided that remove exhaust air outside the building (to the roof). To normalize the microclimate requires the removal and inflow of fresh air masses.
In apartments with old wooden frames, air enters the living area through loosely closed doors. Modern requirements for interior decoration are tightening sealing measures, and metal-plastic fillings of openings with double-glazed windows are characterized by the absence of cracks. Unpleasant odors from the bathroom and kitchen are discharged through the mine, but inside the apartment there is a rarefaction area, in which the residents feel uncomfortable.
Correct organization and regulations
Natural ventilation differs in efficiency in winter and summer. The temperature difference between the outgoing and incoming masses causes an acceleration of the inflow, which is typical for cold weather. In summer, the temperature outside the window is higher than room values, the air speed in natural ventilation slows down. The operation of the air exhaust shafts becomes less efficient.
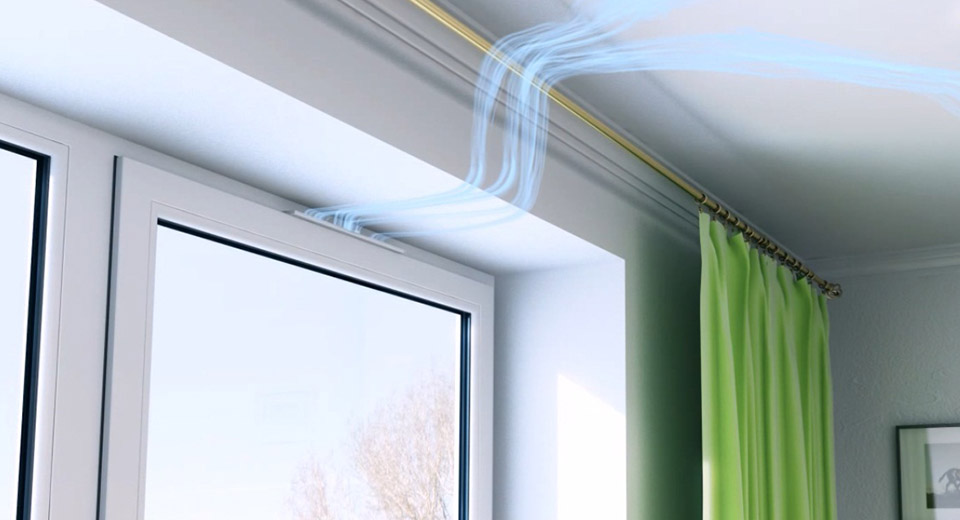
Normative acts and conditions for calculating systems are set out in the document SNiP 41.01 - 2003 "Heating, air conditioning and ventilation". Requirements for the operation of natural air ducts are also contained in SP 73.13320 - 2012 "Internal sanitary-technical systems of buildings". The organization of the inlet flow means the use of special valves in the window frames and walls of the building to optimize air exchange.
Features and application of natural ventilation

Air in unorganized air ducts is removed by traction in ducts, usually located in the bathroom, toilet and kitchen. Gravitation occurs in proportion to the temperature difference between the external and internal atmosphere and the height of the riser from the ventilation grill to the pipe head on the roof.
Through artificial channels and valves are used with insufficient draft in ventilation shafts:
- the ventilator is placed in an outer wall or frame, the device increases the air volume, but its operation also depends on the climate;
- the breather simultaneously cleans and ventilates the incoming air using one or a set of filters and membranes; it is mounted in the wall of the house;
- forced circulation refers to the installation of fans in a window or wall niche.
Windy weather plays a role. If the transom is opened in the summer, a pressure jet will push the air into the exhaust shaft. The wind load can be used to operate the deflectors, which are installed on the head and improve traction through turns.Natural ventilation remains the cheapest way of ventilation, does not require installation and maintenance costs.
Calculation and formulas

Ventilation system calculations are about determining the optimal conditions in which air is supplied and removed most efficiently.
The calculation of room ventilation includes sections:
- determination of the flow rate;
- calculation of air volume;
- calculation of the parameters of the inlet or channel.
When calculating, the frequency of air exchange is taken into account according to the standards, hygienic and sanitary standards, and the area of the room are taken into account. There are technical calculations that calculate the microclimate renewal, heat removal, changes in humidity, degree of pollution.
Air speed calculation

The parameter is defined as the speed of the flow at each point, while the value does not depend on the direction. In some rooms, there is uneven air movement, which leads to a loss of body heat. The average airspeed value is taken and chosen between lower and higher cooling efficiency.
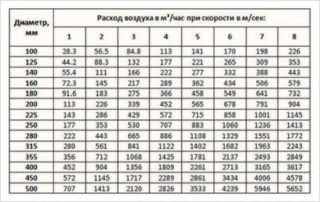
The calculation of the ventilation system in terms of air speed is based on the exchange rate and is found by the formula B = M / 3600 Swhere:
- B - speed of moving masses (m / s);
- M - air consumption rate (m3 / h);
- S - cross-sectional area of the duct (m2).
The flow rate is determined at the rate of 60 m3 / hour per person if he is continuously in the room and 20 m3 / hour if his stay is considered temporary. Such standards are spelled out in the sanitary and hygienic rules.
Air volume calculation
The multiplicity index can be calculated by the formula N = V / Ywhere:
- N - the frequency of air replacement (times / h);
- V - the amount of air that replenishes the room per hour (m3 / h);
- Y - the volume of the required room (m3).
The indicator is given in special tables so as not to calculate it for rooms of the same area and functionality.
Recommended frequency:
- living quarters - 3 m3 / h for 1 square of area;
- kitchen - 6 - 8 m3 / h;
- bath, shower, laundry - 7 - 9 m3 / h;
- wardrobe, storage room - 1 - 1.5 m3 / h;
- garage, cellar - 4 - 8 m3 / h.
If the multiplicity is below the norm, fresh streams will not flow, and the microclimate will not be renewed, harmful microorganisms and gases will accumulate in it. With an increase in air exchange more than it should be, the atmosphere is dried, cooled, which leads to diseases of the respiratory system.
Calculation of the channel diameter
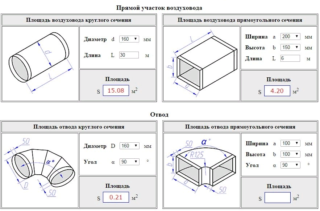
After determining the volume and flow rate, the cross-section of the outlet channel is calculated.
The diameter of the ventilation channel of a non-residential premises is calculated by the formula, which is the inverse of the calculation of the speed S = B / 3600 Mwhere:
- S - Area, m2);
- B - flow rate (m / s);
- M - consumption (m3 / h).
The result is used to calculate the diameter D = 1000 √ (4 S / π)where:
- D - obtained diameter (m);
- S - calculated cross-sectional area (m2);
- π - mathematical number (3.14).
The result of the diameter is compared with the parameters of the finished product and a product close in size is selected. Determining duct dimensions, flow rates and air exchange rates are complex calculations, therefore, it is easiest to calculate ventilation by contacting specialist engineers.
Purpose of calculation
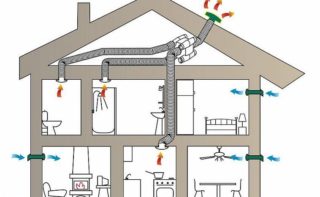
Correctly selected size of ventilation shafts, risers and ducts allows equalizing the incoming and outgoing air volumes.As a result, the risk of respiratory diseases decreases, comfort, sleep improves, and efficiency increases.
If, when calculating, the volume of the inflow mass is greater than that of the removed mass, it is recommended to take the value according to the maximum index. An online calculator is offered on the Internet to obtain results, you only need to substitute individual values.
Correct duct equipment
Galvanized boxes can be round, square and rectangular. Pipes are often installed to organize the supply flow in industrial and public premises. For installation, clamps are used that are attached to the ceiling with studs. Rectangular boxes are suspended from rigid cross-beams, where the height is adjusted with a control nut. Rubber gaskets are required.
Flexible air ducts up to 5 m long are laid without intermediate supports, longer pipelines are fixed with hangers, clamps on studs to avoid deflection. Despite the flexibility, there are certain radii for such highways, beyond which it is not recommended to turn the route.