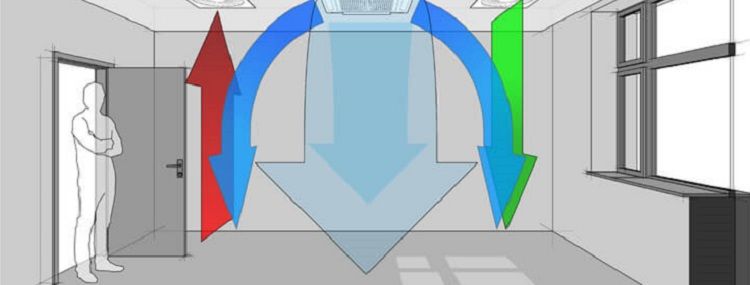
When installing pass-through exhaust systems in the kitchen, various options for masking ventilation ducts are used. Their difference is manifested in the design suitable for each specific case and in the materials selected for these purposes. When preparing for work, attention is also paid to the dimensions of the masking box for the hood in the kitchen. It is important to understand in advance the existing methods of hiding air ducts, taking into account the fact that, according to the technology of embedding in a wall cabinet, hoods are divided into classic and telescopic models. Depending on this, a ventilation duct in the kitchen is selected.
Masking hood boxes

Before hiding the exhaust pipes in the kitchen, you should familiarize yourself with the existing types of built-in hoods. The classic model is simply built over the tiles and has a fixed size, the telescopic one can expand like an antenna, increasing its original length. In modern conditions, the most in demand are classic hoods mounted directly in a wall cabinet. In this version, it is important to provide such a camouflage structure so that it does not interfere with the free outflow of air and fits well into the interiors of the kitchen space.
The peculiarity of the telescopic version is the larger size of its components, the height of which reaches 40 cm. Some users may need to hide the entire structure in hanging boxes or shelves, leaving only the control panel outside. A built-in telescopic hood works just like a conventional hood, but it will take more labor (material and time, including) to disguise it. But if the ventilation is not working, it will be almost impossible to detect it.
The instructions for installing telescopic hoods detail the required dimensions of cabinets or boxes and the free space in them. When connecting them to disguised ventilation ducts, the main thing is not to disrupt the design of the kitchen. The simplest and most convenient approach to solving the problem is to use plasterboard boxes to mask communications.
Calculation of parameters for the box
In order for the kitchen exhaust ventilation to be reliably hidden and not to spoil the interior of the room, it will be necessary to correctly calculate the parameters of the masking elements. The industry has mastered the production of products with a standard shape and size. With such data, it will be easier for the user to calculate the height, width and depth of the designed structure in relation to his kitchen.
Calculation of the optimal section

The basis for calculating the camouflage box is its internal section. This parameter determines the speed of movement of air masses through the channel at a fixed power of the exhaust unit (fan). The required section is selected after the volume of air passed through the channel has been determined. According to the current regulations and from the experience of operating similar systems for plastic boxes, the optimal speed is 3-7 meters per second.
The cross-section of the duct is taken equal to or slightly larger than the same indicator for the exhaust duct, the size of which is given in the passport for the unit.In modes of operation without overloads, the requirements of the standards allow some reduction in the standard size (section) of the used duct in comparison with the size of the outlet.
It is not recommended to install large capacity hoods in small kitchens, which allows choosing air ducts with a smaller diameter. But in this case, you will need a special adapter, which is also taken into account in the calculations.
In the general case, the cross-sectional area of the box is found by the formulaP = S * (M / N)where:
- S - cross-sectional area of the exhaust duct;
- N - the volume of air pumped through it in the limiting operating mode (at maximum load);
- M - the volume of pumped air in the normal mode.

When calculating this indicator, it is important to remember that an error in choosing the cross-section of the duct upwards leads to a significant decrease in the flow rate and an increase in friction in natural ventilation systems. This threatens with the following undesirable consequences:
- The load on the ventilation equipment increases, which ultimately leads to a sharp decrease in the service life and to additional energy costs.
- Due to the increase in resistance, the performance of the system decreases with a simultaneous drop in the volume of the pumped air masses.
- The likelihood of aerodynamic effects in the exhaust duct increases, in the presence of which the noise level of operation increases sharply.
- The pressure difference between the outside and inside of the ventilation increases, threatening the appearance of vibrations. This will require strengthening all mechanical fasteners and increasing the level of tightness.
For systems with forced ventilation, an increase in the cross-section of the duct more than the norm will not affect the modes of operation, however, it will lead to unjustified monetary costs. In addition, for the arrangement of ventilation ducts of significant dimensions, additional efforts will be required during their installation and integration into the interior of kitchen premises.
Taking into account the shape and size

Plastic boxes for hiding the elements of forced ventilation, as a rule, have a rectangular or rounded shape. The second option is preferable in that for the same area, the circle has the smallest length (when compared with other sections). To minimize the resistance of the inner walls of the duct, preference is also given to the circumference. In the domestic market, plastic boxes with a diameter of 80, 100, 125 and 150 mm are widely represented with the corresponding areas of 50.3, 78.5, 122.7 and 176.7 square meters. cm.
The rectangular exhaust ducts are attractive in that they fit more easily into the interior of any kitchen. They are easily placed in niches, often found above cabinets, as well as under suspended or suspended ceilings. Boxes with standard sizes 110x55, 120x60, 204x60 mm with areas of 60.5, 72.0 and 122.4 square meters, respectively, are in great demand. see If necessary, you can always find larger items. They are represented by round boxes with a diameter of 200 mm and rectangular samples with dimensions of 220x90 mm.
Use of various materials

The hood box is made from a wide variety of materials. To mask pipes, metal blanks, modern plastics, as well as wood and plasterboard sheets (or MDV) are used. When choosing a suitable material, it should be borne in mind that the camouflage structure is used not only for decorative purposes. At the same time, it provides a significant reduction in noise from a running electric motor. In addition, the selected structures must meet the following requirements:
- pleasant aesthetic appearance;
- resistance to moisture and temperature changes;
- resistance to chemical attack and ultraviolet radiation;
- easy cleaning from dust, grease and other contaminants.
Plastic structures are lightweight and assembled very quickly. At the same time, the material itself is well processed, but it has a number of disadvantages: it tarnishes over time, it is easily subject to mechanical deformation.
Boxes made of stainless steel attract the attention of users with their durability and original design, which does not change at all over time. The disadvantages of this material include significant weight and high price.
MDV and drywall sheets are easy to install and not very expensive materials. Most consumers choose them for self-assembly of masking structures.
After pretreatment of the surfaces, wood trunks are harmoniously combined with the front panels of the kitchen set, made of wood.
The procedure for installing the box

To hide the pipe from the hood in the kitchen, you need to familiarize yourself with the specifics of the upcoming work. The peculiarities of the arrangement of masking boxes include the inconvenience of operations, the location of which is shifted to the ceiling area. It will be necessary to comply with the norms of removal from other communications established by SNiP, as well as fire safety requirements. As an example, the installation of the box body based on drywall blanks will be considered.
Installation work begins with measuring the location of the wiring of the air ducts themselves, followed by drawing up a sketch. After that, the following operations are carried out:
- Using a ruler and a building level, appropriate marks are made on the wall in the laying area.
- On the wall and ceiling surfaces, guide profiles are fixed with dowels, on which vertical sections are later fixed.
- The corrugated sleeves of the masked air duct are fixed in the openings of the hood and ventilation duct.
- According to the previously prepared profiles, the finished frame is sheathed with plasterboard sheets.
With independent work, mistakes are possible, which are most often made when laying air ducts based on corrugation or plastic. During their installation, a violation of the requirement is possible, according to which the channel cross-section must match or exceed the area of the exhaust outlet. First of all, attention is paid to this when buying a corrugated sleeve and a sample of exhaust equipment. Another common mistake is incorrect installation of the corrugated pipe, which must be fully extended after installation. In addition, they try to make the size of its bends less than the diameter of the corrugation itself, and when laying a pipeline based on plastic, the angles of the bends are made obtuse.
Restoration of the ventilation riser

Mistakes made in the independent arrangement of the drainage channel or riser in the kitchen with a ventilation duct, one way or another, have to be corrected. For the user who is familiar with the principle of operation and the structure of the air ducts, such a restoration will not cause any particular difficulties. When carrying out these works, it is important to consider the following points:
- Ventilation ducts are made only of round or square section.
- During reconstruction, additional bends are made of a corrugated pipe or by dividing the main channel using foam blocks.
- The estimate of the proposed work includes the cost of foam blocks, as well as drywall blanks, corrugations and consumable building materials.
For the restoration of the duct in the kitchen, followed by masking, gypsum-based slabs or foam blocks are optimal.