The use of open heating systems in private buildings is dangerous because in certain situations it can lead to a fire. The smoke evacuation pipe included in them heats up so much that fire is possible on contact with combustible substances. The most important elements of its protection include a ceiling-through-passage chimney unit (PPU), which provides a safe discharge of exhaust gases and is mounted in accordance with the safety requirements.
Tasks of the chimney duct ceiling

PPU is designed to organize the passage of the smoke exhaust pipe through the ceiling in the house. It is manufactured in a modular design with a round or square shape with a hole in the middle. Its main task is to protect wooden parts from overheating and fire, possible during the operation of the heating system.
Pass-through units for the chimney in assembled form go on the free sale, but if you wish, you can assemble them yourself. When choosing a ready-to-use product, you will need to consider the following factors:
- size (diameter) of the smoke exhaust duct;
- the location of the oven;
- features of ceiling slabs.
Basalt wool with a protective foil screen that can withstand high temperatures is used for thermal insulation of the passage.
Types of devices and requirements for them
But the domestic market presents many samples of passage ducts for the chimney. They differ in their shape, they are square and round. Passage nodes of the first type are made single and double. Models of the second type are made in the form of a double square box with a pipe hole in the middle.
A more complex structure is characteristic of structures with a rounded shape. Outwardly, they are a cylinder mounted on a flat square base. If it is present, there are no problems with assembling the assembly in the right place.
Safety requirements

When installing PPU, the safety requirement is mandatory, according to which the channel passing near easily flammable structures should not heat up above 50 ° C. These conditions are described in more detail in SNiP 41-01-2003. Direct pipe laying without the use of a transitional protective structure is a gross violation of the requirements of current standards.
It is also necessary to arrange the passage of the chimney through the ceiling if the pipe does not have direct contact with the wooden structures of the building. The operating temperatures of its outer walls reach values sufficient for charring and subsequent smoldering of adjacent areas to begin. This makes it necessary to protect the elements of the passage by means of insulation class NG.
When purchasing a finished product, it is advisable to study the attached instructions for its installation and documentation regarding compliance with safety requirements.
DIY preparation and installation

Installation of a PPU chimney in a bathhouse or in another wooden structure begins with preparatory measures. This takes into account the type of design chosen, the characteristic size of the chimney and the class of material from which it is assembled (brick, sandwich or steel).Before starting work, you will need to prepare the following tool and consumables:
- electric jigsaw;
- hammer and electric drill;
- marking tool;
- brackets and blanks for a double box or other base;
- hardware (screws, screws, etc.).
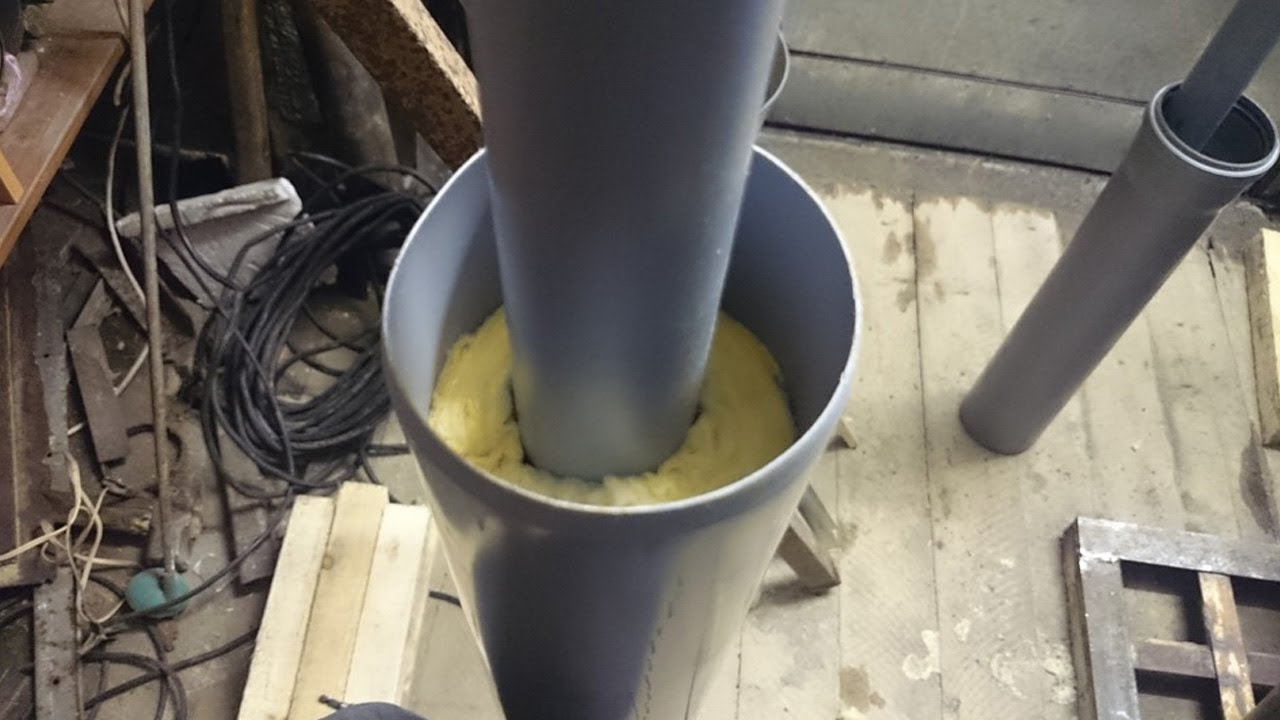
During the preparatory procedures regarding the arrangement of the passageway, a zone is marked on the ceiling intended for the installation of PPU. When the rafters are located close, experts recommend making an intermediate wooden box with walls sheathed with minerite. If it is not required, proceed to the following operations:
- A ceiling hole is made according to the size of the passage structure.
- It is lined with a heat insulator of the same class as that of the unit itself. It is allowed to use any other insulation material with similar or better characteristics.
- For greater reliability, steel strips are attached over the thermal insulation.
- The purchased passage assembly is inserted into the finished hole. It is allowed to put it on the pipe and mount it together with it.
- Having placed the structure on the prepared place, you should fix the PPU panel with self-tapping screws, the holes for which are drilled in advance.
After that, it remains to fill the formed gaps with heat-resistant insulating material. Sometimes the wooden surfaces of the floors are covered with protective compounds (fire retardants), which reduce the likelihood of fire.
A heat-resistant protective coating will not be able to protect such structures from accidental fire, their service life is limited to one year.
Brick chimney passage

Despite the fact that a brick is a good heat insulator, in the manufacture of chimneys, the rules for the design of passages through easily flammable materials and structures are observed. The distance from the edge of the hole to the pipe is made at least 25 cm. For this, in the masonry scheme, the stove-makers provide for a separate row, which increases its thickness in the area of the wiring through the ceiling. If for some reason it was not in this place, the regulations allow you to cut a hole in the ceiling that is 10 centimeters larger than the structure itself. Then you can proceed to the design of the penetration through the prepared place. To do this, you need to do the following operations:
- seal the edges of the overlap with the selected heat-resistant material;
- cover it with several strips of metal or minerite;
- sew up the passage from the side of the room with steel sheet blanks;
- fill the existing voids on the side of the next floor or attic with the same heat-resistant compound;
- close the PPU cut from the side of the next floor or attic with a steel sheet of a suitable size.
After completing these operations, the brick pipe will be well insulated from the floor elements.
For reliability, it is recommended to use insulating materials with a melting point of about 800-1000 ° C.
Roof entry clearance

When passing the chimney through the roof, the following tasks are solved:
- limiting the contact of a steel or brick channel with elements of the roofing structure;
- ensuring the tightness of the passage, excluding the ingress of moisture into the attic;
- reliable fixation of the outlet structure.
For this, a box of rafters and several transverse beams is arranged directly in the passage area. Its shape and composition depend on the specific wiring conditions (chimney material and dimensions).
Sandwich pipe passage arrangement

Many users prefer sandwich chimney designs for the following reasons:
- only with their help it is possible to reduce the temperature of the outer circuit to 200 degrees;
- their use avoids the accumulation of condensate;
- the heating of pipes going from the furnace towards the sandwich channel decreases;
- the service life of the entire structure as a whole increases;
- simplifies the installation of a system containing no more than 3 elbows.
At the initial stage, a simple protective module with a length of no more than one meter is installed on a bath or home stove at the passageway (it is allowed to use a heat exchanger instead). Further operations are carried out in the following sequence:
- An adapter is mounted up the sandwich pipe, which matches the heat exchanger with a double-walled PPU structure. When choosing a place of junction, one should remember the requirements of SNiP, according to which the joining of pipes in the interfloor and attic ceilings is strictly prohibited.
- The chimney is led through the ceiling by means of a ready-to-use PPU assembly.
- At the end of this stage of the chimney assembly, the gap between the walls of the structure and the pipe is filled with basalt wool with a protective screen.
When preparing the filling, it is allowed to use other heat-resistant materials, not only based on basalt rocks. It is not recommended to make horizontal sections when laying, as they impair traction in the structure. If this fails, their total length should not exceed one meter. Traction is also affected by the number of knees in the system, which should preferably be reduced to 2.
Since most materials expand when heated strongly, the structure should not be too rigidly fixed at the point of passage.