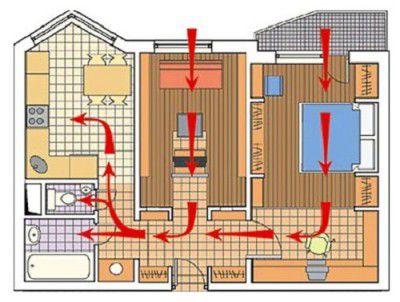
According to the regulatory documents: SNiP and safety standards for the creation of ventilation systems, the frequency of air exchange is regulated, in terms of the amount of toxic components.
Process description
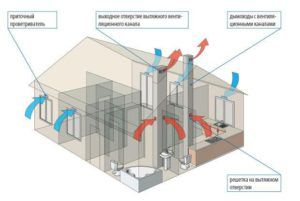
For an effective evaluation characteristic of air exchange in an industrial building, the value "kV" is used. This air exchange rate is the ratio of the total volume of air that comes "L" (m3 \ h) to the indicator of the total volume of the cleaned space in the room "Vn", (m3). The calculation is carried out for the accepted time period.
If during the design, all the calculations and the project itself are organized correctly, according to the standards, then the air exchange rate for industrial premises will range from 1 to 10 units.
In addition to calculation formulas and a theoretical basis, to determine the required indicator, experts advise conducting research on natural conditions at similar operating enterprises, where there are actual data on the release of toxic vapors, gases, etc.
To determine the multiplicity index, industry-specific documents, SNiPs, as well as sanitary standards are used.
Air circulation in industrial buildings
When building and planning buildings for future industrial needs, it is necessary to correctly calculate the ventilation paths of communication in the premises and determine the air circulation process. To do this, you need a characteristic such as the rate of air exchange, which is determined from the tabular data of the presence of toxic substances in space: oxides, acetylene oxides, etc.
When calculating the process of air circulation in the building, the amount of heat generated is taken into account so that the amount received, more than the norm, can be removed, all year round, without difficulties and obstacles.
To reduce the excess heat, aeration is used. This process has become widespread in the chemical industry, for example, in thermal production areas. In this case, the air exchange rate in the warm season reaches 40-60 points due to aeration.
With such indicators of air exchange, the organization of airways, the meteorological standards provided for by the sanitary norms are achieved.
So, directly arrangement and construction of premises, subsequently affects the estimated frequency of air exchange, for this purpose, special working openings are provided that can be opened, guaranteeing the possibility of employees receiving fresh air and removing unfavorable elements.
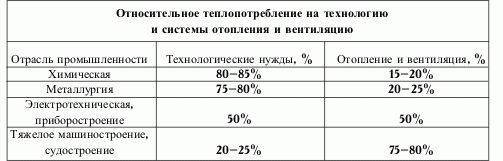
Determination of the multiplicity index
When performing production and technological calculations for the main premises, the installed large equipment is not taken into account. For example, if pumping units are installed at the main production, without specialized exhaust ventilation, then the amount of harmful gases in the atmosphere will be 6-7 times higher than those limited by official norms.
In auxiliary, additional production rooms, in addition to washing rooms, the air exchange rate is calculated based on the exchange rate indicators.
An emergency ventilation system must be provided in production, which ensures the prompt removal of a high concentration of harmful and toxic particles from industrial buildings. Such a system is relevant in case of deviation from the established norms of the production route of manufacture and in emergency situations. In order to exclude the possibility of the passage of unfavorable components through the connecting paths in the building, it is recommended to organize emergency exit paths without a compensating component of the inflow.
Multiplicity table
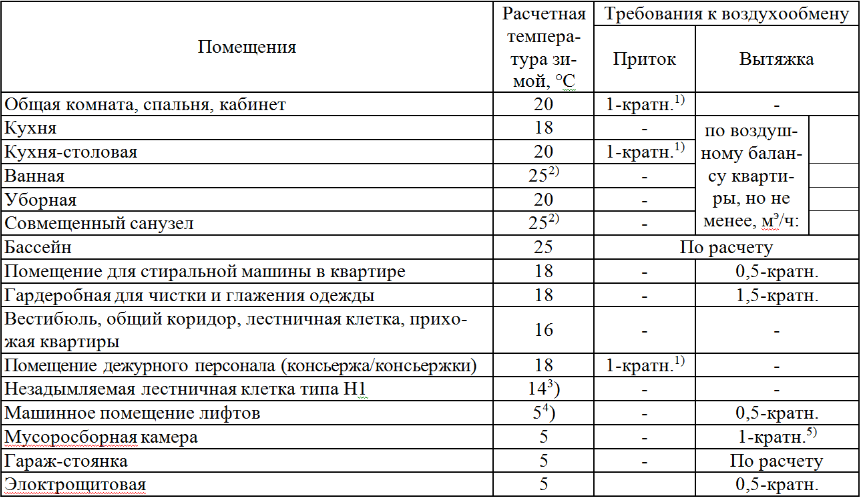
Normative documents for calculating air exchange
The air exchange rate of the hood communication system is formed on the basis of industrial safety data and regulated sanitation standards. The air exchange rate is set for a specific room on an individual basis, according to the calculated information in the project.
In SNiP, TB and specialized norms of each specific branch of industry and industrial design and construction, different information is given on the frequency of air exchange (hourly). All values are given depending on the type of industrial premises:
- additional auxiliary premises;
- working shop areas.
So, in the corresponding SNiP, the characteristics of the numerical values (calculated) for auxiliary premises of the production type are regulated.
Also, the values of the air exchange rate are entered in SNiP P-92-76, for secondary buildings.
With the constant formation of toxic gases in the space of the industrial zone and an increase in the degree, the maximum specified value is taken as the rate of multiplicity, for each type of unfavorable industrial hazardous emissions.
So, having available the value of the total volume of the room (m3) and the rate of air exchange rate, using simple mathematical formulas, you can calculate the required volume of incoming air for a certain zone, per hour.
L = n * S * H,Where:
L - required productivity m3 / h;
n - the frequency of air exchange;
S - area of the room, m2;
H - room height, m.
Air exchange rates in industrial premises

For buildings of an industrial type, a general exchange ventilation system is provided, the calculation of the needs of which is based on the conditions of a specific production and the availability of a certain amount:
- heat;
- liquid or condensate;
- harmful particles.
If there is equipment with gas or vapor emissions in the room, the amount of required air exchange is calculated taking into account the emissions:
- from this equipment;
- laid communications;
- provided fittings.
All the necessary indicators are included in the technical documentation of the room, otherwise the data is taken from the actual parameters. This calculation is regulated by VSN21-77 and the corresponding SNiP.
If, in the calculations, the air exchange rate exceeds tenfold, it is necessary to make an adjustment to one of the construction sections of the documents. So, in order to lower the level of industrial harmful and toxic particles, it is necessary to provide additional measures around the perimeter of the entire room.
Sanitary standards for the design of industrial enterprises
According to the rules of SNiP, any unfavorable elements, such as moisture and heat, emitted in the industrial premises are taken from the calculations of the technological part of the design documentation.
If such data are absent in the technological design standards, the amount of industrial hazardous substances emitted in the room may be taken based on the natural collected research facts.Also, the desired value is indicated in the passport papers of the acquired specialized equipment.
Emissions of toxic substances into space occur through concentrated and dispersed devices of the general ventilation system.
The calculation of the emitted substances must provide for their quantity not exceeding:
- Maximum value for cities and towns.
- Indicators of the maximum amount in the air that penetrates into residential buildings through the windows according to the principle of natural ventilation (30% of the established limit for the concentration of harmful, toxic substances in the working area).
Determination of the coefficient of dispersion into the working space of toxic elements that are in the system at the time of release are included in the ventilation design of the enterprise. So, according to standards, in industrial premises, subject to the volume of air per subject - 20 m3 the process of supplying the outside air must be taken into account. So in total, it should be up to 30 m3\ h for each subject on the premises. If, however, there are more than 20 m per person3, the amount of air supplied from outside must be at least 20 m3\ h for each subject.
For a work area in which the air volume is more than 40 m3, subject to the location of ventilation windows and transoms and in the absence of toxic elements, the standards provide for a working (active) natural ventilation system.
When creating a project for a working area for industrial production purposes, in which there is no natural ventilation, while supplying outside air to them only through the means of existing mechanical ventilation, the total amount of air must be at least 60 m3/ h per subject. The indicator may vary within the tabular data, but at the same time be at least one multiple air exchange flow per hour.
If the calculated air ratio is less than the tabulated one, and at the same time recirculation is used, the volume of the external flow may be less than 60 m3/ h for one subject, but not less than 15-20% of the total air exchange flow in the system.