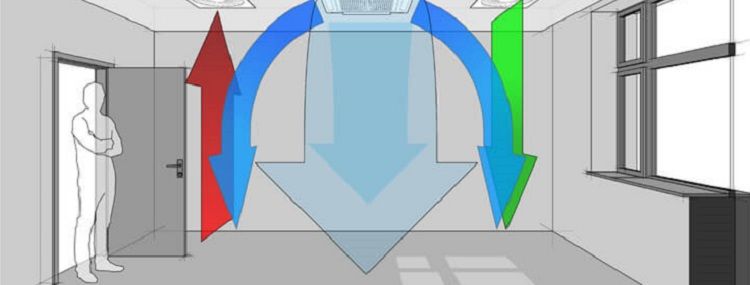
To remove polluted air from the premises, it is necessary to provide a ventilation system at the design stage. Understanding the principle of operation and the competent choice of equipment is a prerequisite for creating an effective system of any type, especially for general ventilation.
Purpose of general ventilation
General ventilation is a system that, unlike local ventilation, circulates air masses throughout the entire volume, in all rooms. It is designed in such a way that there are no “dead zones”.
It is used in such cases:
- the air in the room is heavily polluted with dust, toxins;
- high humidity;
- stuffy, constantly lacking fresh air;
- substances with a pungent or unpleasant odor are stored / used;
- high risk of mold formation;
- the level of humidity is very different at different times of the year;
- condensation constantly forms on the glass.
General ventilation allows you to solve all these problems. In case of severe air pollution, an exhaust general exchange ventilation is installed. If the air is not very polluted, but there is not enough oxygen, a general exchange supply system is installed. Supply and exhaust elements are more often used, which ensure the removal of contaminated air masses and the flow of fresh air. The system, if necessary, is supplemented with filters and heaters.
Types of systems and basic characteristics
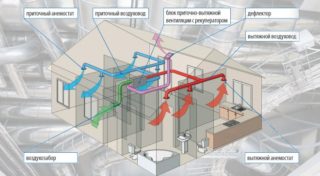
There are types of general ventilation in the direction of air movement:
- supply;
- exhaust;
- mixed.
According to the method of moving air masses, natural and forced ventilation are distinguished. In the latter, the process is carried out thanks to the operation of fans.
Supply ventilation of the general exchange type allows you to normalize the microclimate in the room, providing a constant flow of fresh air. The concentration of contaminants is reduced to a minimum level, even if it was initially very high. The exhaust is responsible for removing polluted and heated air. With the help of fans, air masses are removed outside the building. General exchange supply and exhaust ventilation is the most effective system, since it combines the properties of both supply and exhaust.
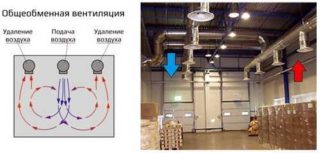
In a system of mechanical general exchange type, ventilation equipment is used for forced movement of air masses: duct, axial, roof, centrifugal fans. The use of specialized devices makes it possible to heat and clean the air, makes ventilation independent of weather conditions and wind. The main disadvantages: financial costs for electricity and repairs, noise during operation.
Natural ventilation is designed in such a way that air masses move in the desired direction due to natural draft. Advantages: low cost, since no electrical equipment is used, simple installation, no noise and, despite the absence of fans, acceptable performance. Disadvantages: air purification and heating are not provided, ventilation speed cannot be increased.
The economy of a system operating on the principle of natural draft is attractive, but in practice, any external influence significantly changes the efficiency not for the better, therefore it is preferable to install a mixed version: with forced air injection into the premises. Due to the inflow of air masses, excess pressure is created. Thanks to this, contaminants are forced out through cracks, doors, windows.
Airflow calculation

At the design stage of general ventilation, meticulous calculations are required. Any mistakes lead to disruption of the air balance and microclimate, the appearance of unpleasant odors, and dust.
In large premises, the use of automated systems is relevant. Automation maintains the required air exchange rate - the ratio of the volume of incoming air masses to the total volume of air. Setting up an automated system must be done by professionals - it is a complex process that requires maximum precision.
The sequence of calculations in the design of general ventilation:
- Determine the type of ventilation system.
- Find out the number of people constantly present in the room.
- The degree of air pollution and the nature of harmful impurities in it are taken into account. This will allow you to select the right equipment to clean the air to a safe level.
At the rate of 30 m3 / h per person, forced general ventilation is planned. If the system is of a natural type, the capacity per person is 60 m3 / h.
Exhaust general ventilation is calculated without taking into account the degree of air pollution using a simple formulaP = A * Bwhere
- A - air volume per person;
- B - the number of people in the room.

If the air is polluted, the formula is appliedP = Ain / (Ko - Kp)where
- BUTin - weight of hazardous substances in mg per hour;
- Ko - concentration of toxins in the air;
- Kp - the level of contamination of the supply air masses.
The supply capacity is calculated using a different formulaL = Ain / (U - Up)where
- L - the desired volume;
- BUTin - the weight of toxins per hour in mg;
- U - specific concentration of harmful substances in m3 / h;
- Up - toxins in the supply air masses in m3 / h.
If a general ventilation project is drawn up for a small house, it is enough to perform approximate calculations using a simple formula. More complex calculations for buildings with a large number of rooms should be done by professional designers.
Equipment and materials
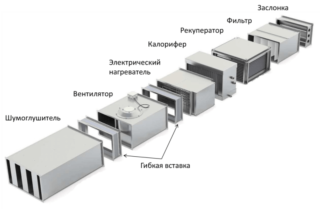
When designing supply and exhaust ventilation of the general exchange type, which is the most effective, in country houses, the hood is usually organized where moisture and intense odors are formed - in the bathroom, kitchen, toilet. Supply valves are often installed in the bedroom and living room. Supply valves should be equipped with filters and heating devices, since clean, but cold air will enter the room during the cold season. Installation of a complex general ventilation system is not complete without the following types of equipment:
- valves;
- cleaning devices;
- air coolers and heaters;
- recuperators;
- fans;
- ventilation grilles;
- air flow distributors;
- electronic monitoring and control devices;
- mufflers of noise.
Recuperators are installed in order to save money. They transfer the thermal energy of the heated air removed from the room to the incoming cold air.
General ventilation scheme
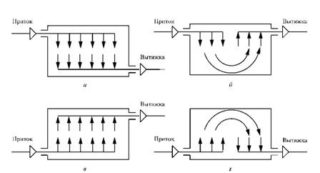
It is impossible to achieve the efficiency of general ventilation without drawing up a project and calculations. The project must take into account all the details regarding compliance with fire safety and sanitary standards.Attention is paid to the architectural features without fail, a diagram is drawn up. The more rooms in the building, the more complex the project will be.
First, it is necessary to carry out calculations regarding the volume of the supply and extract air flow. Then the types and quantities of equipment, materials, fasteners are determined. Choose a method of installation and make an estimate for each stage.
General ventilation is more efficient than local ventilation, but it is more difficult for independent design and installation, therefore, it is worth undertaking the organization of such a system with your own hands only in the case of small objects. Complex projects must be carried out by professionals, taking into account the norms of SNiP, otherwise there is a high probability of wasting money and creating an ineffective system.