The vast majority of private houses, summer cottages, baths and garages are equipped with autonomous heating. Boilers operating on gas, solid and liquid fuels are used to heat the heat carriers. During its combustion, in addition to heat, toxic volatile substances are released, which need to be removed to a height that is safe for people and buildings. During this process, a rather unpleasant phenomenon occurs in all respects - condensation in the chimney. By itself, the water in the pipe does not bode well. The main damage to the structure is soot and soot, which, when mixed with the liquid, forms active and aggressive compounds that form a hard and oily coating.
Definition of condensate

Moisture is present in hydrocarbons, wood and coal. When heated, it evaporates and, together with the smoke, leaves the furnace. Upon contact with the pipe walls, the steam cools down, turns into a liquid state and is retained on the walls in the form of water droplets. Condensation forms in the chimney when its temperature is below the dew point, which for combustion products of various fuels is 45-60 degrees.
Condensate is water that forms in different volumes in the outlet channel under the influence of low temperature. The process begins with fogging of the material, then droplets form, partly flowing down, and partly absorbing solid particles and toxic gases. The result of such a phenomenon is always negative - the formation of build-ups consisting of a dense and flammable substance.
Chimney design requirements
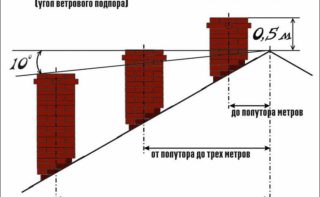
Requirements for the construction of household chimneys for solid fuel and gas boilers are set out in SNiP 41-01-2003:
- the total height of the pipe from the furnace to the upper cut of the pipe is more than 5 m;
- chimney elevation above the roof - at least 100 cm;
- elevation above the ridge - 50 cm;
- the length of the horizontal section is no more than 100 cm;
- number of corners per channel - up to 2;
- compensation of horizontal sections - the same increase in height.
By design, the chimney can be central, extending vertically from the room through the floor slabs, and wall-mounted, when the chimney is brought out directly from the boiler or at a slight elevation from the branch pipe.
Consequences of condensation

The formation of steam and water droplets on the inner walls of the flue gas pipe is a problem that cannot be ignored.
If condensate runs through the chimney pipe, this can provoke such dangerous consequences:
- In winter, there is a gradual freezing and thickening of the ice layer. First, the thrust decreases, then the channel is completely closed.
- The substance accumulating in pipes is flammable and explosive. Condensation in the chimney of a wood-burning stove can cause an explosion and fire.
- When water and combustion products combine, sulfuric and hydrochloric acids are formed. They attack ferrous metal and stainless steel.
- Condensation flowing down in a sandwich chimney of a direct-flow type can extinguish the fire and cause malfunction of the parts of the heating device.
- If the drain pipe is made of bricks, moisture, absorbing into its walls, leads to cracks during freezing, thinning of the walls and a quick collapse of the structure.
It is easier to prevent a problem than to eliminate it if you know the prerequisites for its occurrence.
Reasons for the appearance

Steam is contained in combustion products of all types of fuel. On contact with a cold surface, it becomes saturated and turns into water.
The reasons for the occurrence of condensation in the branch ducts are as follows:
- Excessive height of the sandwich pipe, when the head practically does not heat up.
- Lack of thermal insulation in the chimney of a gas boiler.
- Using raw firewood in a solid fuel boiler.
- Low exhaust gas temperature. This is typical for modern double-circuit boilers.
- Incorrectly planned canal shape, when there are many knees and horizontal sections along its length. The thrust decreases, the temperature drops.
- Roughness of the walls. They slow down the speed of the exhaust gases, which leads to cooling of the pipe and the formation of droplets.
- Lack of access to the required amount of fresh air to the blower - a defect in the furnace or an incorrectly planned ventilation system.
If a problem of condensation formation is detected, it must be dealt with by all available methods, without putting it on the back burner.
Remedies

It is difficult, but possible, to prevent condensation without compromising the efficiency of the furnace. The following options are used:
- Maintaining the installation scheme. Sometimes it is advisable to spend money on expensive materials for the chimney and its laying in a direct way through the ceilings. Subsequently, this will affect the economical operation of the heating system.
- Warming. The best solution is to use rock wool and an outer, top-sealed sleeve.
- Use of fuel containing a minimum percentage of moisture. These are natural gas and factory briquettes.
- Preliminary drying of fuel. It can be simply stored in a warm and dry room, or pre-laid on hot surfaces.
- Chimney cleaning. The smoother its inner surface and the wider the clearance, the better the draft and the higher the temperature of the gases. This means less condensation and deposits. There are chemical, thermal and mechanical cleaning methods.
- Using a steam trap. This is a vessel that is installed in the lower part of the vertical channel, below the outlet of the branch pipe or the horizontal outlet. The container is equipped with an access for draining the liquid.
It is not difficult to drain condensate from the chimney for a gas boiler and a solid fuel analog if you do the necessary measures constantly and systematically.
Prevention of condensation

To eliminate the appearance of moisture in the pipe from the boiler, several simple rules should be followed:
- Competently design and correctly assemble the branch structure.
- Use high quality materials and modern technologies during construction.
- Use well-dried and proven fuel from reliable suppliers.
- Timely diagnose and clean the pipe from soot.
- Install a nozzle at the end of the chimney that increases the draft and eliminates the dew point - a deflector.
All this will simplify and secure the process of boiler operation, extend the service life of the heating system.