Ventilation ducts are made of round, rectangular cross-section, steel, plastic or metallized foil is used. At the design stage, the area of air ducts and fittings is calculated in order to guarantee the standard indicators of pressure and air speed, to ensure optimal acoustic performance.
- The need and purpose of calculating the area of air ducts
- General information for calculation
- Methods and stages of calculating the area of air ducts
- Section calculation
- Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle and the area of a circle
- Air speed calculation
- Shaped products and their calculation
- Actual duct area
- Methods for calculating fittings
- Basic calculation requirements
- Determination of pressure loss after calculating the area of the duct
The need and purpose of calculating the area of air ducts

The ventilation duct layout is an important part of the air distribution system. The calculation of the duct cross-section plays a role in determining the required material consumption in order to save money. The microclimate in the room depends on the correct calculation of the working area and configuration.
The error-free calculation of capacity and pipe diameter influences the characteristics:
- air purity;
- the frequency of air exchange;
- the risk of mold and mildew;
- temperature in the room.
As a result of calculating the ventilation indices, a structure should be obtained that passes the required volume of fresh flows to improve the internal atmosphere. At the same time, pressure losses in the line are minimized, and the microclimate meets sanitary standards for humidity, air pollution and noise level from the operation of air ducts.
General information for calculation
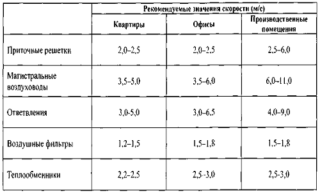
The key indicators include the cross-sectional area of the duct, which determines the speed of movement of flows. The regularity is manifested in the fact that with an increase in size, pressure decreases and vice versa. The calculation of the squaring of the ducts is carried out in several ways in order to be able to compare the results.
Indicators for the selection of pipes can be calculated according to the values:
- in accordance with the hygienic and sanitary standards given in SanPiN;
- by the number of people in the room;
- by the area and volume of the room.
The calculation is carried out for a separate room or structure as a whole. The amount of material is determined based on the configuration and dimensions of the system. For round pipes, the diameter and total length are needed, while rectangular pipes are calculated using the width, height and length of the line.
The surface area of shaped parts of air ducts is determined taking into account bends, adapters of various shapes, their width, angle of rotation and height are taken into account.
Methods and stages of calculating the area of air ducts
The size of the ventilation box depends on the volume of the discharge flow, the speed of movement and the pressure on the inner walls.
The calculation of the parameters of the ventilation line is carried out in several stages:
- the frequency of air exchange is determined in accordance with technical requirements, building and sanitary standards;
- aerodynamic selection of the pipeline section is made;
- the level of generated noise is determined (acoustic calculation);
- a layout diagram is drawn on paper with reference to the layout;
- the drawing is agreed with the customer, changes are made;
- settlement documents for power supply are drawn up;
- individual units of the air duct are drawn with detailing.
Ventilation equipment is selected only after the technical calculation of air ducts and fittings, air heaters, supply and exhaust installations, automatic devices are purchased.
Section calculation

Noise effects are reduced when the channels are widened, but in practice, an increase in the cross section is not always justified. This can be hindered by the limited height of the room, so attention is paid to the calculation of the perimeter.
The calculation of the transverse area of the air ducts is made according to the formula Sc = L 2.788 / Vwhere:
- Sc - estimated area of the box (cm2);
- L - the volume of the flow passing through the channel per hour (m3 / h);
- V - air speed in the line (m / s);
- 2,788 - unit conversion factor.
The area is obtained in square centimeters, such units are most convenient for analysis. The flow velocity in the channel is taken at the level of 3-4 m / s for residential premises. You can reduce the diameter of a round pipe by replacing it with a rectangular pipe, which has a similar cross-sectional area.
The calculation of square meters of air ducts is done for each section separately, starting from the central channel, where the speed reaches 6 - 8 m / s. The cross-section of the main duct is often larger than the diameter of the bends, and the ducts are connected with adapters.
Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle and the area of a circle
The areas of ventilation ducts are taken after calculating the required capacity. The cross-section of pipes refers to the design characteristics, which determine the optimal configuration of the duct (rectangular or round). The length of the highway is made as small as possible to save materials, but the system must provide the required frequency of exchange.
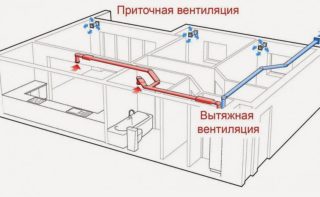
The circular cross-sectional area is calculated by the formula S = π D2 / 400, and rectangular - S = a b / 100where:
- S - area;
- π - number 3.14;
- D - diameter of the circle;
- a - the length of the rectangle;
- b - the width of the rectangle.
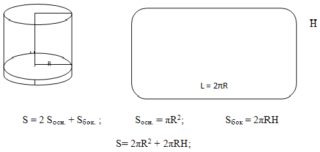
The ratios of area with diameter, length and width are summarized for convenience in a special SNiP table, where you can analyze and find out the parameters depending on the size of the section. In everyday life, boxes with a cross section of 40 x 20 or 10 x 10 cm are most common; round channels with a diameter of 20 and 10 cm are used.
Air speed calculation
The air exchange rate is found by the formula N = V / Wwhere:
- N - number of air changes (times / h);
- V - cubic capacity of fresh air per hour (m3 / h);
- W - room volume (m3).
After that, the actual flow rate (aerodynamic calculation) in the channel is calculated by the formula £ = L / 3600 Fwhere:
- £ - flow rate (m / s);
- L - rate of air exchange (m3 / h);
- F - cross-sectional area of the pipe (m2).
The speed affects the noise level, therefore, when choosing the parameters of the pipeline, this characteristic should be compared with that taken from the standard tables.
Shaped products and their calculation

The size of the curly elements in the line is determined using an online calculator or using special tables in the collections. Products are complex in shape, you need to have special knowledge to calculate.
Shaped links include the following elements:
- round, oval, square and rectangular bends are placed to turn the pipeline at an angle;
- transitions are used for joining boxes of different sections, differ in complex geometry of the section;
- nipples and couplings connect straight sections of the duct;
- tees are used for branching the channel;
- plugs interrupt the flow of flow;
- crosses serve to separate or combine adjacent streams;
- ducks are placed to move the pipeline axis to a different position vertically or horizontally.
The air speed, its volume, the tightness of the system and the cost of electricity depend on the parameters of the fittings.
Actual duct area
In addition to the calculated one, it is imperative to calculate the actual area of the already installed channel. There are special calculation formulas for each section. The dimensions of the diameter, width and length are not taken by the selection method from the normative documents; for a correct determination, it is necessary to measure the distances, perimeter and lengths on site. The formulas for calculating the actual cross-sectional area of a rectangular shape are used in the same way as those used for the calculated indicator. For the area of the circular duct, you also need to measure the diameter.
The oval cross-sectional area is calculated by the formula S = π A B / 400where:
- π - number 3.14;
- A - diameter along the major axis of the oval;
- B - diameter along the minor axis of the oval.
The actual performance of the duct is compared with the specification and compliance is determined.
Methods for calculating fittings
An error in the selection of sections of the figured parts can lead to incorrect circulation of the air flow, even with an error-free design. Many manufacturers give nomograms in an explanatory note to the project. These are graphical calculations of a function in several variables, presented in the normative literature.
Engineering assistance for calculating air ducts says that there is a way to apply a ruler, with the help of which functional dependencies are worked out without using formulas. The cross-sectional area of the duct fittings is taken from the monograms, which is able to balance the noise level in the system.
Follow these steps to size the pipe for a branch or turn:
- find on the monogram the point of intersection of the air flow moved in an hour and the line of optimal speed for a given section;
- not far from this point, find the value of a suitable diameter.
With the help of the nomogram, the calculation of the area of the fittings of the air ducts is facilitated, the decrease in the pressure in the system at a set flow rate is specified.
Basic calculation requirements
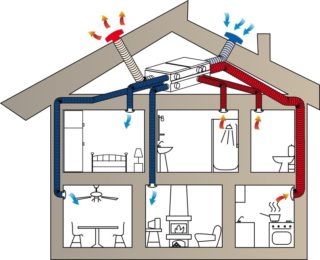
The location of the ventilation pipeline is determined at the stage of drawing up the project, while the sites for the installation of engineering equipment are being prepared, the number of bends, transitions, tees and crosses is laid.
The calculation of the air ducts must guarantee the conditions:
- the required temperature regime is provided in the building with the transfer of heat to the required premises;
- the air speed in the channels does not reduce the level of human comfort;
- harmful chemical particles and suspended impurities are present in the atmosphere in a volume that is allowed by sanitary standards.
In some areas, constant pressure must be maintained and outside air must not be allowed to enter. For proper functioning, the resistance of the inner surface of the duct is analyzed.
Determination of pressure loss after calculating the area of the duct
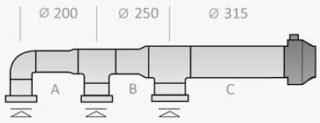
The pressure loss is calculated after calculating the area of the pipelines, the air exchange rate and the resistance of the utilities. This indicator affects the selection of the fan in terms of power.
The formula is used P = R L + E V Y / 2where:
- P - pressure loss (Pa);
- R - specific indicator of friction pressure when air interacts with the inner walls (Pa / m);
- L - the length of the calculated section (m);
- E - the numerical index of the head losses in the area in total;
- V - flow rate at the desired location (m / s);
- Y - the density of the atmosphere (kg / m3).
The pressure loss is determined using a reference guide. The coefficient E has a direct dependence on the parameters of the area where the calculation is made.
Using an automatic online calculator improves the accuracy of the calculation compared to the manual method.