On the basis of sanitary and hygienic and building codes, each object, both residential and industrial, must be provided with a ventilation system. The created microclimate affects the performance and health of people. To ensure comfortable living conditions, special standards have been developed that determine the composition of the air.
- The importance of air exchange
- Rules for determining the speed of air in the duct
- Noise level
- Vibration level
- Air exchange rate
- Algorithm and formulas for calculating air speed
- Calculation of air flow
- Cross-section design
- Material and cross-sectional shape of air ducts
- The right choice of ventilation pipes
- Recommended speed rates
The importance of air exchange
The task of any ventilation is to provide an optimal microclimate, humidity level and air temperature in the room. These indicators affect the comfort of a person during the work process and rest.
Poor ventilation leads to the proliferation of bacteria that cause respiratory tract infections. Food starts to deteriorate quickly. An increased level of humidity provokes the appearance of mold and mildew on walls and furniture.
Fresh air can enter the room in a natural way, but it is possible to achieve compliance with all sanitary and hygienic indicators only with the operation of a high-quality ventilation system. It should be calculated for each room separately, taking into account the composition and volume of air, design features.
For small private houses and apartments, it is enough to equip mines with natural circulation of air flows. But for industrial premises, large houses, additional equipment is required in the form of fans that provide forced circulation.
When planning a building for an enterprise or a public institution, the following factors must be taken into account:
- high-quality ventilation should be in every room;
- it is necessary that the composition of the air meets all approved standards;
- the enterprise requires the installation of additional equipment that will regulate the air speed in the duct;
- for the kitchen and bedroom it is necessary to install different types of ventilation.
In order for the air exchange system to meet all the requirements, it is necessary to calculate the air speed in the duct. This will help you choose the right device.
Rules for determining the speed of air in the duct
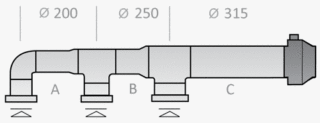
The air flow rate in ventilation is directly related to the level of vibration and noise in the system. These metrics need to be considered when calculating behavior. The movement of the air mass creates noise, the intensity of which depends on the number of pipe bends. Resistance also plays an important role: the higher it is, the lower the speed of movement of air masses will be.
Noise level
Exceeding the listed parameters is possible only in exceptional cases, when additional equipment needs to be connected to the system.
Vibration level

Vibration is generated during operation of any ventilation device. Its performance depends on the material from which the duct is made.
The maximum vibration depends on several factors:
- the quality of the gaskets that are designed to reduce vibration levels;
- pipe material;
- duct size;
- air flow rate.
General indicators cannot be higher than those established by sanitary standards.
Air exchange rate
Purification of air masses occurs due to air exchange, it is divided into forced and natural. In the second case, it is achieved by opening windows, vents, in the first through the installation of fans and air conditioners.
For an optimal microclimate, air changes should occur at least once an hour. The number of such cycles is called the air exchange rate. It must be determined in order to establish the speed of air movement in the ventilation duct.
The frequency ratio is calculated according to the formula N = V / WwhereN - frequency rate per hour; V - the volume of air that fills a cubic meter of the room per hour; W - the volume of the room in cubic meters.
Algorithm and formulas for calculating air speed

The calculation of the air flow can be done independently, taking into account the conditions and technical parameters. To calculate, you need to know the volume of the room and the rate of multiplicity. For example, for a room of 20 square meters the minimum value is 6. Using the formula gives 120 m³. This is the volume that must move through the channels within an hour.
The duct speed is also calculated based on the parameters of the section diameter. For this, the formula is used S = πr² = π / 4 * D²where
- S - cross-sectional area;
- r - radius;
- π - constant 3.14;
- D - diameter.
Once you have a known cross-sectional area and air flow rate, you can calculate its speed. For this, the formula is used V = L / 3600 * S, where:
- V - speed m / s;
- L - consumption m³ / h;
- S - cross-sectional area.
The parameters of noise and vibration depend on the speed in the section of the duct. If they exceed the permissible standards, you need to reduce the speed by increasing the section. To do this, you can install pipes from a different material or make the curved channel straight.
Calculation of air flow
It is important to correctly calculate the area of sections of any shape, both round and rectangular. If the size is not suitable, it will be impossible to ensure the correct air balance. A too large air line will take up a lot of space. This will reduce the area in the room and cause discomfort to the residents. With the wrong calculation and selection of a very small channel size, strong drafts will be observed. This is due to the strong increase in air flow pressure.
Cross-section design

To calculate the speed at which air will pass through the pipe, you need to determine the cross-sectional area. The following formula is used for the calculation S = L / 3600 * V, Where:
- S - cross-sectional area;
- L - air consumption in cubic meters per hour;
- V - speed in meters per second.
For round ducts, it is necessary to determine the diameter using the formula: D = 1000 * √ (4 * S / π).
If the duct is rectangular, and not round, instead of the diameter, you need to determine its length and width. When installing such a duct, an approximate cross-section is taken into account. It is calculated by the formula: a * b = S, (a - length, b - width).
There are approved standards according to which the ratio of width and length should not exceed 1: 3. It is also recommended to use in the work tables with typical dimensions that are offered by manufacturers of air ducts.
Round ducts have an advantage. They are characterized by a lower level of resistance, therefore, during operation of the ventilation system, the level of noise and vibration will be minimized.
Material and cross-sectional shape of air ducts
Round air ducts are most often used in large factories. This is due to the fact that their installation requires many square meters of floor space. For residential buildings, rectangular sections are most suitable; they are also used in clinics, kindergartens.
Steel is the most commonly used pipe for making pipes.For a round section, it should be elastic and firm, for rectangular sections, it should be softer. Pipes can be made of textile and polymeric materials.
The right choice of ventilation pipes

Before designing a ventilation system, all indicators of speed, noise and vibration must be taken into account. It is necessary to make calculations taking into account the area of the room in order to ensure high-quality air exchange. The material of manufacture also plays an important role in the selection.
The most versatile are the galvanized steel air ducts. They can be operated at high temperatures and pressures. They can be used for all climatic zones.
In industry, the most commonly used air ducts are made of black steel. They are heat and fire resistant, but highly corrosive.
An aluminum corrugated duct has a high degree of flexibility, strength and elasticity. The material is resistant to high temperatures. But this duct has a drawback. Due to the high aerodynamic resistance, there is a lot of noise during operation.
Plastic air ducts are distinguished by their high strength, long service life and ease of installation. They are popular for their low cost and light weight. The downside is the low resistance to high temperatures.
In residential buildings, polyisocyanurate pipes are often installed. They are characterized by high fire safety properties, long service life, ease of installation.
Recommended speed rates

When drawing up a project for any building, it is necessary to calculate the ventilation distribution for each site separately. If we are talking about the construction of an industrial building, the calculation should affect all shops, for residential buildings, schemes are drawn up for each apartment, for a private house, floor blocks should be drawn up.
Before starting the installation of the ventilation system, it must be known what the routes and dimensions of the mains will be, and the geometry of the ventilation ducts must be worked out. All this is necessary in order to select the optimal pipe size.
It is very difficult to make calculations of the movement of air masses in residential and industrial buildings. Therefore, it is recommended to entrust this to specialists.
When designing and commissioning any object, the orientation goes to the recommended speed in the duct, which is approved by SNiP. Based on the standards, the indoor air speed should not exceed 0.3 m / s. Temporary exceptions are possible due to technical work. For example, when carrying out repairs or installing construction equipment, the parameters may be higher, but by a maximum of 30%.
For large industrial premises, more often than one ventilation system is designed, but two. This is true for warehouses, hangars, large garages. In this case, the load will be divided in half, therefore, the air speed must be selected in such a way as to ensure 50% of the total volume of air mass movement.
It is recommended to install supply valves and cut-off valves in the air ducts, so that in the event of a fire, the speed of movement of air masses can be reduced to a minimum. This will help prevent smoke from spreading to all adjacent rooms.