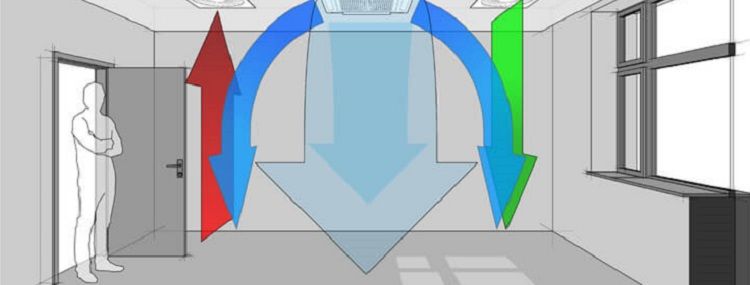
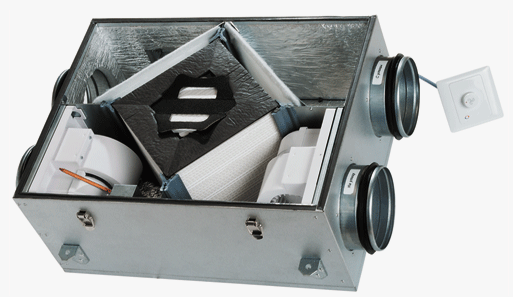
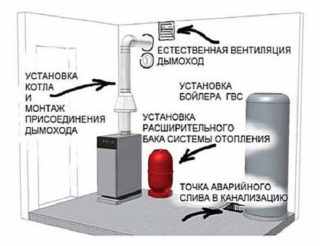
The room for the gas boiler must be supplied with fresh air in accordance with state regulations and SNiP. The requirements for ventilation in a private house are met by consumers so that the accumulation of by-products does not cause a fire and explosion. Inhalation of the substance harms the human body, therefore supply and exhaust ventilation ducts must be provided at the design stage of the heating system.
- The need for ventilation in a private house
- Types of systems
- Natural and mechanical
- Exhaust, supply and combined
- Channel or channelless
- Principle of operation
- Requirements for ventilation in a private house with a wall-mounted gas boiler
- Ventilation system device
- Ventilation installation
- Organization of outflow and inflow of air
The need for ventilation in a private house

Wall-mounted units of various capacities are used, which have a compact and efficient open or closed type firebox. The equipment placement is subject to less stringent conditions than for floor types, therefore they are placed in a boiler room, kitchen, bathroom or utility rooms.
The owners sometimes doubt the need for an exhaust hood in the boiler room, considering it sufficient to open the transom. Keeping the window open constantly is inconvenient in winter, and periodic ventilation does not completely solve the problem of air exchange. A forced air supply is organized, in addition to the natural inflow. In the absence of normal ventilation, the performance of the wall-mounted boiler decreases, and a normal air flow ensures the combustion of fuel without residues, therefore, the efficiency indicator increases.
The system performs the functions:
- supplies oxygen in the volume that is needed for gas combustion;
- the hood removes smoke and carbon monoxide;
- removes accidental gas emissions that cause poisoning of pets and humans.
The lack of fresh air reduces heat transfer and ensures incomplete combustion. Insufficient intake leads to the deposition of soot on the walls of the chimney, which reduces the working clearance and reduces the traction performance. The system protects against negative consequences if it is designed in accordance with the requirements of sanitary and technical standards.
Types of systems
Air exchange parameters depend on the power of the boiler and its operating features. The efficiency of the ventilation duct is influenced by the area of the room and the frequency of use of heating equipment. The functionality of the hood is determined by the number of door and window openings and the local climate.
Ventilation systems differ:
- according to the principle of obtaining traction, there are natural and forced;
- at the rate of air supply - supply, exhaust, combined;
- the structure can be canalized or without canals.
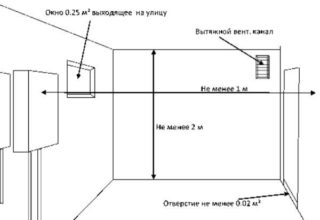
Air is supplied from the street, from an adjacent room along aisles in the wall or through openings and structural slots at the bottom of the door leaf. For each 1 kilowatt of boiler power, at least 8 cm2 of air from the street should be provided, and at least 30 cm2 should come from the next room, based on a similar indicator.
Natural and mechanical
Easy movement is ensured by the difference in air pressure inside and outside the building. Natural exchange of air masses occurs through the cracks in windows, doors and when the canvases and sashes are opened.Air exchange refers to an organized type if hinged or internal channels are arranged for movement, the flow in which is regulated.
The natural scheme works with low equipment power and subject to the requirements for the exhaust hood for a gas boiler in a private house. The system does not differ in productivity, it is suitable for houses with an area of 50 - 70 m2. Correctly calculated ventilation renews the entire volume of air in the boiler room, while the outlet and inlet are located on opposite walls. The door, opposite to which the boiler is placed, can be considered as the flow inlet. Windows in this arrangement can be on any walls.
If it is impossible to ensure the natural flow of air, they resort to a mechanical scheme. In this case, the pressure difference is generated by electrical appliances. Effective feeding is combined with dust removal, increased humidity and temperature.
Equipment used:
- fans;
- mufflers;
- electric motors;
- traps of impurities.
Forced systems move the flows in the required volume, their efficiency does not depend on the climate. The equipment changes the air parameters, which cannot be done with a natural pattern. If the room is completely sealed from drafts, during the simultaneous operation of the hood with a column, a convector and a boiler, the draft may overturn, and carbon monoxide will be drawn into the room.
Exhaust, supply and combined

The air handling unit is mounted in the fresh air supply duct. Electric fans provide a constant combustion flow, which is important for open chamber boilers that use the surrounding atmosphere. To clean the outside air, a filter is installed in this channel. A monoblock circuit with a common body, where the required elements are assembled, works effectively.
Exhaust ventilation uses the power of a vane device, which is placed in the extraction channel. In this case, air is sucked in through an organized supply passage. The exhaust system reduces the carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere of the boiler room not only with a hinged boiler, but also with a floor-standing boiler, or in a boiler room with a solid fuel unit.
The combined smoke extraction and oxygen supply system is one of the best solutions. Compressors and condensers are used, fans are installed in the inlet and outlet pipes. Two streams interact in the system, which differ in purpose and chemical composition. The combined model for air exchange can use any number of rooms in the building.
The first stage provides for the intake of air from the outside and the exhaust of the exhaust smoke, while the incoming and outgoing flow is cleaned. Factory-made supply valves are equipped with a mesh, grate, hatch. The exit hatch is not done next to the heating unit, because cold air in winter can reduce the efficiency of the boiler.
In the kitchen, the exhaust pipe is led out into the ventilation shaft in a standard way and goes through the attic to the roof. Combined systems also include a coaxial chimney, in which smoke is removed in one pipe and oxygen is supplied.
Channel or channelless

The channelless type effectively functions in boiler rooms of a small area. Such a system is installed when placing a wall-mounted gas boiler in an apartment, garage, warehouse. The monoblock is placed on the roof, above the installation area of the unit, placed in the wall, displayed through a window or under a door.
Air is supplied:
- outside;
- from the underground;
- from under the ceiling space.
The channelless system requires little electricity (if combined with ventilation), is easy to install and is inexpensive. Ventilation without channels is natural, mechanical, exhaust and supply.
Duct ventilation of the boiler room is complex, but it works more efficiently. Models are selected according to their capacity, depending on the parameters of the boiler and the conditions of use. Air ducts are round, square, rectangular, of different sizes and diameters. Communications are located hidden in the walls, behind protruding structures, or hanging boxes and pipes are used at a height.
Principle of operation
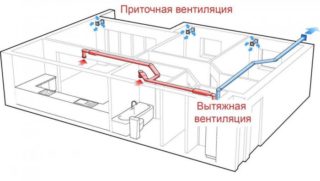
The equipment is an installation of exhaust or supply ventilation for processing air flows and supplying it to the boiler room. The device is a component of the heating system and is often connected to a central pipe. The air is supplied directly from the street or through the air duct. A complex system consists of metal boxes or pipes, between which functional devices are mounted. The outer elements are weatherproof.
Working elements of the system:
- A fan with a two-phase electric motor supplies air to the boiler room or to a common air duct.
- Filters purify the air, coarse types or method of electrostatic precipitation are used. Coarse elements are placed in front of thin filters, protect them from breakage and are easy to replace.
- Heating or cooling devices change the temperature of the incoming stream. Heat pumps, electric heaters or evaporators are used.
Balancing devices, shock absorption and noise isolation in the system eliminate vibration and reduce sound during operation. Oscillations are isolated and damped by obstacles, and the fan is placed on spring supports.
Requirements for ventilation in a private house with a wall-mounted gas boiler
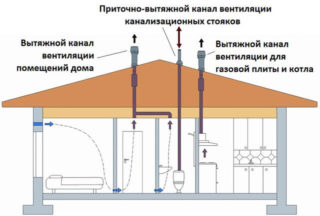
The rules for choosing and installing ventilation systems are contained in SNiP 2.04.05 - 1991. Attention is paid to air exchange, which must occur at least 3 times per hour. For a natural inflow, a window must be made in the window opening, and there should be a gap of about 2 cm under the door, or holes are drilled at the bottom of the canvas.
Requirements for ventilation in a gas boiler room:
- smoke extraction and fresh air supply are carried out through isolated channels so that oxygen does not come into contact with combustion products;
- the area of the window for supplying outside air should not be less than 1/30 of the floor area of the boiler room;
- wall-mounted boiler is mounted next to the outlet of the smoke channel and ventilation shaft;
- if a coaxial pipe system is installed, an outlet is made and a technical one is made for repairing and cleaning the chimney.
In a private house, ventilation in the boiler room should always be with open hatches so that air exchange takes place constantly. Before starting heating, gas workers check the laying of sewerage, water supply, heating and the compliance of these systems with the norm. The gas outlet must be insulated, the ceiling height should not be lower than 2.2 m.
Ventilation system device

For a heating unit with a closed firebox, a coaxial chimney is optimal, which contains two insulated channels in one pipe. The inner pipe is used to remove the combustion products, and oxygen enters the outer chamber.
When installing ventilation, follow the rules:
- no more than two types of gas equipment are connected to the chimney;
- the ventilation shaft is tightly insulated;
- the supply and discharge system is made of materials that do not burn;
- the cleansing channel is made 25 cm below the main one;
- from the horizontal smoke exhaust pipe to the ceiling must be at least 20 cm;
- the hood outlet is insulated from the cold by heat-resistant materials.
For a wall-mounted boiler with an open firebox, separate air supply and smoke exhaust pipes are arranged, with the holes provided opposite each other. The system is equipped with a check valve to prevent the rod from overturning.
Ventilation installation
The ventilation shaft holes are closed with metal or plastic gratings, decorative elements are fastened with dowels. A blade or axial fan is mounted in the hole using self-tapping screws. Before tiling on the walls, the supply wires are wired so as not to lay them along the finish. If the fan runs periodically, a switch is placed to start it, a special time timer can be used.
For the passage of the pipe, a hole is made in the wall with a slight slope (condensation drainage) to the outside of the wall. Brick is drilled with a drill, and concrete is broken with a hammer drill or hammer. The air duct is inserted and insulated with a heat-resistant material (mineral wool or foam for installation work). A ventilation grill is installed on the outside.
Organization of outflow and inflow of air

The pipe diameter is determined by the boiler output. For a 30 kW boiler, a size of not more than 20 cm is provided. Too high or low hole location leads to a slowdown in air exchange. If the chimney outlet is located below the ridge of the roof, a cold stream will enter through the outlet, and the combustion products will not be removed.
The chimney can be equipped with:
- horizontally;
- with rise and bend;
- vertically into the ceiling with a bend;
- vertically directly through the roof.
A yellow flame of the burner and a large volume of soot indicate an insufficient oxygen level, therefore a fan must be used for the supply system.