What is home ventilation? How to make it right? And is there a fundamental difference between the ventilation of aerated concrete and log houses? We will deal with these issues, and at the same time we will debunk several common myths about how to design ventilation in your home.
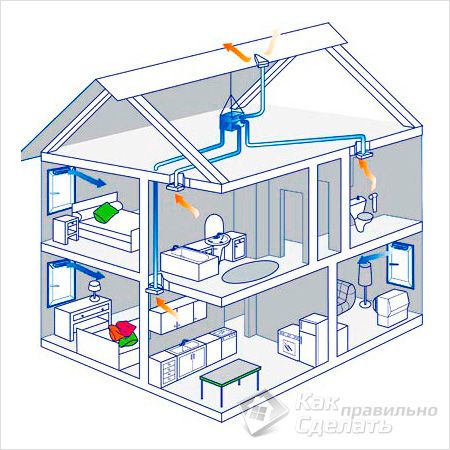
Panel house ventilation
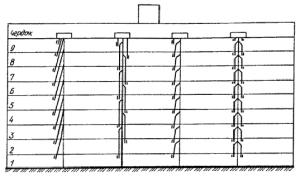
The ventilation system of panel houses is a set of concrete structures assembled together like a children's construction set. The ventilation of all panel houses belongs to the uncontrolled natural type and is based solely on the use of natural phenomena. Air removal occurs due to the difference in temperature and pressure in the ventilation shaft and above the roof of the house. In the apartments, a vacuum is formed, which is replenished by the supply air.
According to the ventilation plan of the house, the exhaust ducts are bred in such a way that air flows do not flow from one apartment to another. It is correct to bring a satellite channel to each bathroom and kitchen at home, which flows into the ventilation shaft on the next floor. To prevent back draft in the ventilation of the last floors of Stalinist houses, air ducts emit gases into the atmosphere, bypassing the common riser.
The air inflow into the apartments is planned through the slightly open vents, door and window cracks. The ventilation of panel houses is not designed for modern construction technologies that provide complete isolation of apartments from the outside world. Therefore, without modernization, the ventilation of multi-storey buildings is inactive.
DIY ventilation modernization
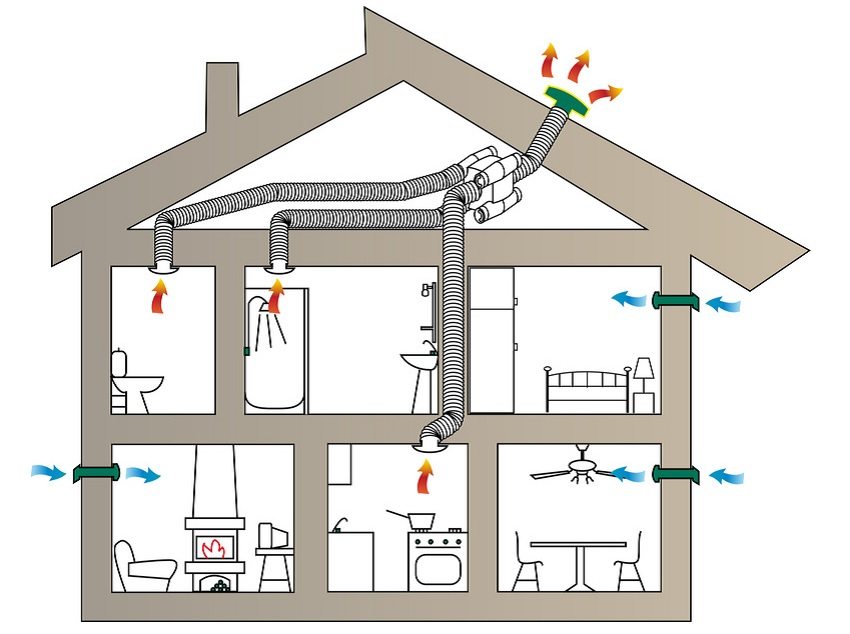
Dampness, crying windows and stuffiness make residents think about how to properly ventilate the house. Most often, attempts to make ventilation in the house with your own hands begin with the installation of an exhaust fan and a kitchen hood. Before doing it yourself, understand the principles of ventilation in the house:
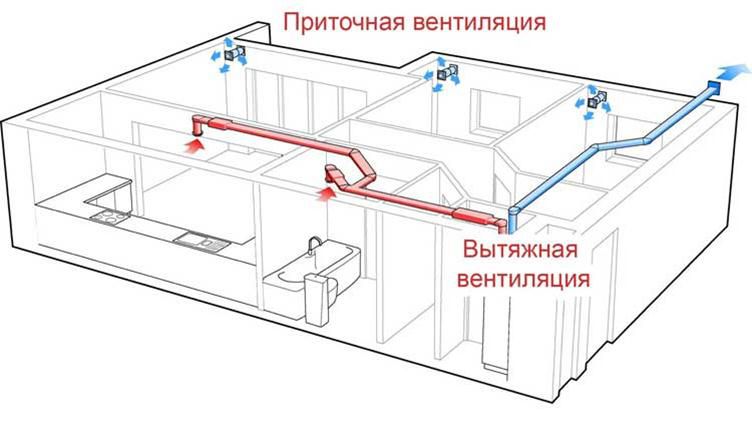
- The house ventilation plan includes an extract and a supply.
- Free passage of air flows inside the apartment.
- Clean air is supplied to bedrooms and living rooms, exhaust air is removed from the toilet, bathroom, kitchen.

This is a minimum of conditions for proper ventilation in the house. Correctly installed ventilation in the house, in addition to the hood, also provides air supply. For this, a variety of supply devices have been developed:
- wall and window valves;
- compact supply units;
- ventilators.
Any of the listed devices will cope with the ventilation of an apartment in a multi-storey building, providing more or less comfort. Valves they serve outside air without heating, only by filtering it. And here supply units and compact ventilators warm the inflow without disturbing the temperature regime of the apartment.
Before starting work, order diagnostics of general exchange exhaust ventilation in a Stalinist house. If the mine is blocked by neighbors or littered with debris, an exhaust fan will not help.
Ventilation in a log and log house
The walls of log houses "breathe", so you can save on the installation of expensive ventilation systems.This can be heard in many construction companies involved in the construction of log and squared houses. Many buyers who do not know how to properly ventilate the house believe.

The myth of the "breath" of wood is associated with the ability of this material to absorb moisture. Indeed, untreated wood is able to somewhat regulate the humidity in the room. The amount of adsorbed moisture is sufficient for wood to rot. Therefore, devoid of any ventilation, a wooden house will become completely unfit for habitation in 5 years.
We are talking about untreated wood. Modern building technologies widely use various types of sealants and impregnations, which protect the material from decomposition. The ends of the logs are especially intensively processed. By the way, it is the ends that let the air through, giving some hope for the ventilation of the log house.
The latest technologies for the construction of log and log houses completely exclude the presence of cracks due to poor caulking of the walls. They are simply no longer caulked and the tow is used to a limited extent. Another way is excluded for ventilation of a one-story house.
Up to a third of the air is filtered through the fibers of the timber per day - also an attempt to mislead buyers. A wooden beam, sandwiched with glue, is generally not able to let air through. Therefore, the owner will have to deal with the ventilation of the log house.
Solution to the problem
A small log house with an area of up to 150 square meters can be equipped with combined ventilation with your own hands:
- forced draft + natural inflow;
- forced supply + natural draft.
In the first case, ventilation ducts can be taken out through the wall to the street, equipped with a fan and a check valve. If the winters in the area are severe, the check valve will have to be additionally heated to avoid icing. Fresh air enters the house through supply devices (wall or window).
In the second case, the exhaust ducts are led up, without turns and bends, through the roof and end with ventilation fungi 50 cm above the ridge. The inflow is provided by mechanical supply units.
With an area of more than 200 sq. meters, it is recommended to install ventilation supply and exhaust equipment with automatic control and recuperation in the house.
House ventilation from SIP panels
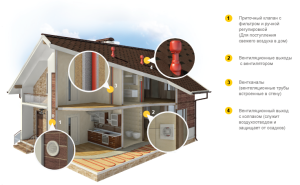
It is not for nothing that houses made of SIP panels are called "thermoses" for their high thermal insulation. Energy efficiency is achieved due to the absence of cracks, cold bridges and the special qualities of the SIP panels themselves. There is no need to talk about any natural ventilation in such houses. All air exchange is forced. But even here there are more or less costly options for ventilation of a house from SIP panels.
The most inexpensive solution is as follows: exhaust ducts are conducted only into the kitchen and bathrooms. These are two separate channels, they are not combined so that the smell from the toilet does not penetrate into the kitchen and vice versa. Thus, the house will have 2-3 air ducts (depending on the number of bathrooms). Before passing the roof, the ducts are combined together so as not to punch holes in the roof in several places.
With a high-quality exhaust hood, the inflow can be organized by micro-ventilation through windows or supply valves. This method slightly reduces the energy efficiency of the building. Therefore, in such houses, ventilation air supply units with heated air are used, which are difficult to assemble with your own hands.
The second option for low-cost ventilation of a house from SIP panels is the installation of breathers. Breathers are compact air handling units for one room. The breather delivers about 100 cubic meters of air to the house per hour. If there are 3-4 people living, at least two units should be correctly installed for ventilation of the house.
Each breather has two exits to the street: for air intake and exhaust.The air is heated by a recuperator or heater. Installation of breathers will cost 2-4 times less than a full-fledged supply and exhaust ventilation. But what is the plan of ventilation at home without hoods from the toilet and kitchen.
The most expensive and effective option for ventilation of a house made of SIP panels is an air handling unit, which serves all the premises of the house. Such ventilation scares off many owners of ready-made houses by the need to lay air ducts. Therefore, it is advisable to design it as early as possible.
Ventilation in a brick house

When creating a ventilation plan for a brick house, special attention must be paid to the location of the ventilation shafts for natural ventilation. Brick ventilation ducts in private houses can be carried out:
- parallel to chimneys;
- install with separate risers.
In any case, the exhaust shafts are led out through the roof. The draft is formed due to the difference in air pressure in the house and above the roof, carrying vapors and gases outside the home. This type of ventilation in a brick house is most effective during the cold season.
Channels are most often placed inside masonry walls:
- with a wall thickness of 0.38 m - in one row;
- with a thickness of 0.64 m - in two rows.
For ventilation of a two- or one-story house, it is most convenient to make channels with a square section of 14x14 cm. The brick is placed on the mortar for laying the walls, but you can also make a clay-sand mixture.
Prepare solid fired brick, buoys, test ball, and template in advance. As inventory buoys, plank boxes with a section of 14x14 cm, up to 10 bricks long are used. The template is a board 2.5 x 0.14 x 0.025 m, holes are cut out in it, with the shape and location corresponding to the future air ducts.
During laying, it is necessary to check the vertical with a plumb line. At the end of the work, the walls are mopped. The laying is done vertically. Distance to corners and doorways from 38 cm. Thermal insulation must be installed between the exhaust shaft and the chimney.
Important points when building home ventilation with your own hands:
- Install the template with its end to the inside of the cross wall. Mark the location of the holes with chalk and check the template from time to time during work;
- The walls of the channels are made 1 brick thick;
- The solution is cut and the channels are stacked end-to-end;
- Next to the ventilation ducts, the laying is ligated in one row;
- To make the shaft stronger, you can lay bricks across the channel, but it will be more difficult to clean such a channel;
- Branch channels are laid out of bricks hewn at the desired angle (more than 60 degrees to the horizon). The diameter of the main and branch ducts must match;
- The ligation of the wall and the shaft is done with three-quarters and halves of bricks;
- The buoys, which are repositioned from time to time, simultaneously help maintain the shape of the canal and keep it clear;
- When mopping, the walls are moistened and thoroughly rubbed.
Channel deviation from the vertical impairs traction. In this case, there is only one outlet - an exhaust fan.
Ventilation in aerated concrete house

In houses made of aerated concrete, ventilation is laid from plastic, galvanized or asbestos-cement pipes. A special duct runs into each room. It is possible to combine exhaust ducts from the toilet and bath, as well as from the kitchen and sauna. This is done at the level of the attic, here all the exhaust pipes are insulated, insulation is also laid between them. The place of passage of the exhaust ducts through the roof is sealed with silicone or a special passage element is installed.
For natural ventilation of a house made of aerated concrete, pipes with a cross-sectional area of 15 square cm are suitable; for forced ventilation, you can take pipes a little thinner. A hole of the required size is cut in the blocks of aerated concrete. A pipe with a diameter of 12.5 cm is hidden in a wall opening with a width of about 13 cm and is fixed with mortar.In the first block of aerated concrete, you need to fit a branch, to which the ventilation ducts are attached. When passing floor panels or partitions, the holes must be coated with waterproofing.
If the wall opening is thinner, the channel is made of flat slate cut into strips. The strips are installed in the prepared opening, burst and plaster.
You can make pipes for ventilation in the house with your own hands from wave slate. Two slate half-waves are sawn off and connected together with a wire. Such a pipe is installed on a brick base, plastered from the inside.
No ventilation ducts are laid in external load-bearing walls! A separate mine is equipped for them, this is a convenient way to make ventilation in a finished house.
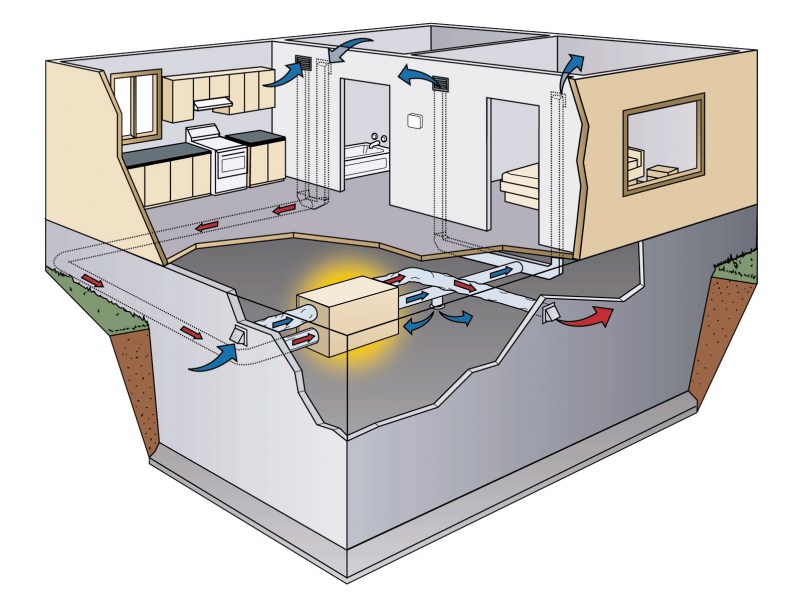
Foundation ventilation

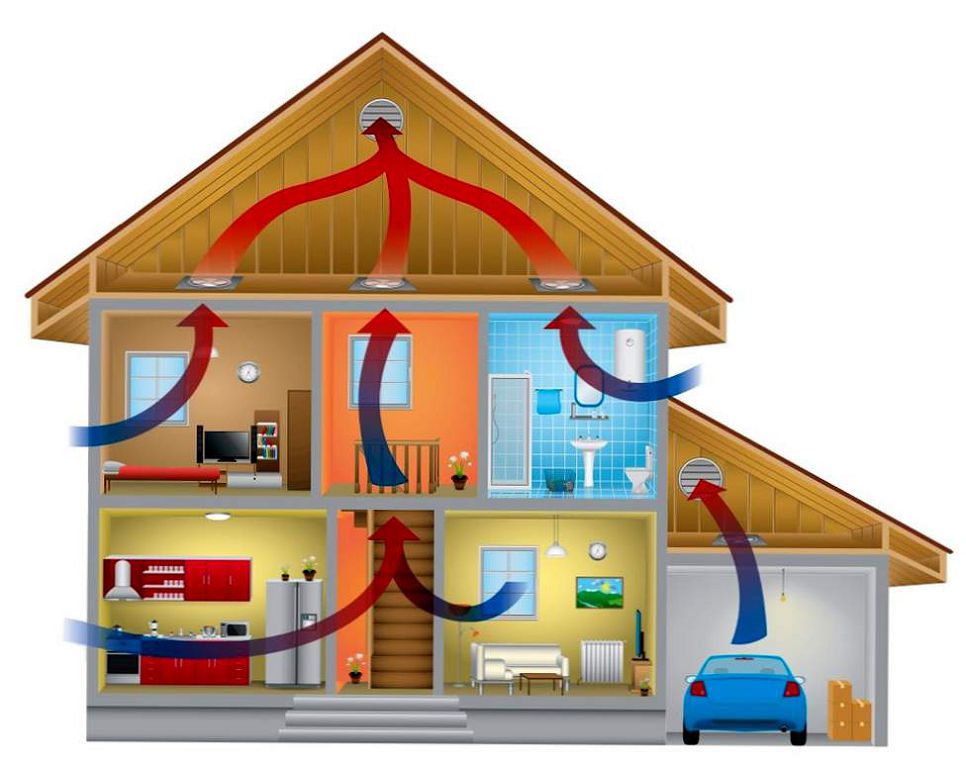
Taking care of proper ventilation at home, it is important not to forget about the safety of the enclosing structures: roofs, ceilings, foundations. The ventilation of a private house should be designed in a comprehensive manner, including auxiliary buildings and sewerage.
It is advisable to plan ventilation of the foundation of the house during the construction of the foundation itself. When a floor slab has been installed on the first floor, it may not be possible to reach the required areas.
House foundation ventilation is a system of holes (air vents) located in the basement. The total area of the vents and their placement depends on the size and location of the house.
Rules for arranging ventilation of the foundation of the house:
- The area of one vent should be from 0.25 sq.m. You can make several adjacent holes of a smaller area or one larger. The total area of the holes should be 0.25 square meters for every 100 square meters of the house area.
- The vents are evenly distributed, otherwise areas of stagnant air will form.
- From a blind corner to the nearest air outlet, the distance is up to 1 meter.
- On each side of the foundation, 2 air vents are made.
If the cottage is located on a hill or plain and is well blown by the winds, for high-quality ventilation of the foundation of the house, it is enough to equip 2 air vents with a diameter of 0.15 m on each side.
If the vents are covered with nets or decorative grilles, the net opening area is reduced. Therefore, it is advisable to make one additional vent on each side of the house.
In winter, the ventilation in the foundation of the house is closed, some air vents are periodically opened for ventilation. Then the floor in the house will retain its temperature, but excess moisture will not accumulate in the subfloor.
Ventilation in the foundation of the house can be done after its construction. The holes are made with a suitable sized carbide drill bit. If the plinth reinforcement is cut during drilling, the foundation will weaken in this place.
Features of ventilation of two-story houses
Often, the ventilation system of two-story houses is designed only for servicing the first floor. And this is a big mistake, because heat and moisture rise from below to the second floor, in summer the second (especially attic) floors are heated more by the sun. Therefore, they need ventilation.
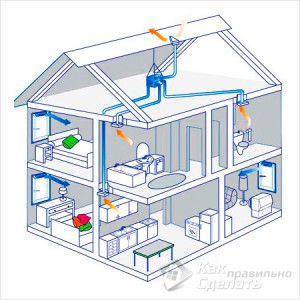
Due to the height of the house in two-story buildings, natural ventilation can be very effective. But unlike the ventilation of one-story houses, it can bring unpleasant surprises. For example, reverse thrust on the second floor, too strong thrust or no thrust at all.
When trying to make ventilation in the house with your own hands, you should know:
- separate exhaust ducts must be removed from the premises of each floor;
- you cannot combine the channels of the bathrooms of the first and second floors;
- when calculating the ventilation of a two-story house, the air exchange is first determined by the total area. After that, the resulting figure is "scattered" over the floors, taking into account the premises located there. This algorithm is quite complicated and requires knowledge. Therefore, as you understand, it is quite difficult to design ventilation in your home;
- during the calculations, the number of interior doors, partitions, and the construction of the staircase are taken into account.
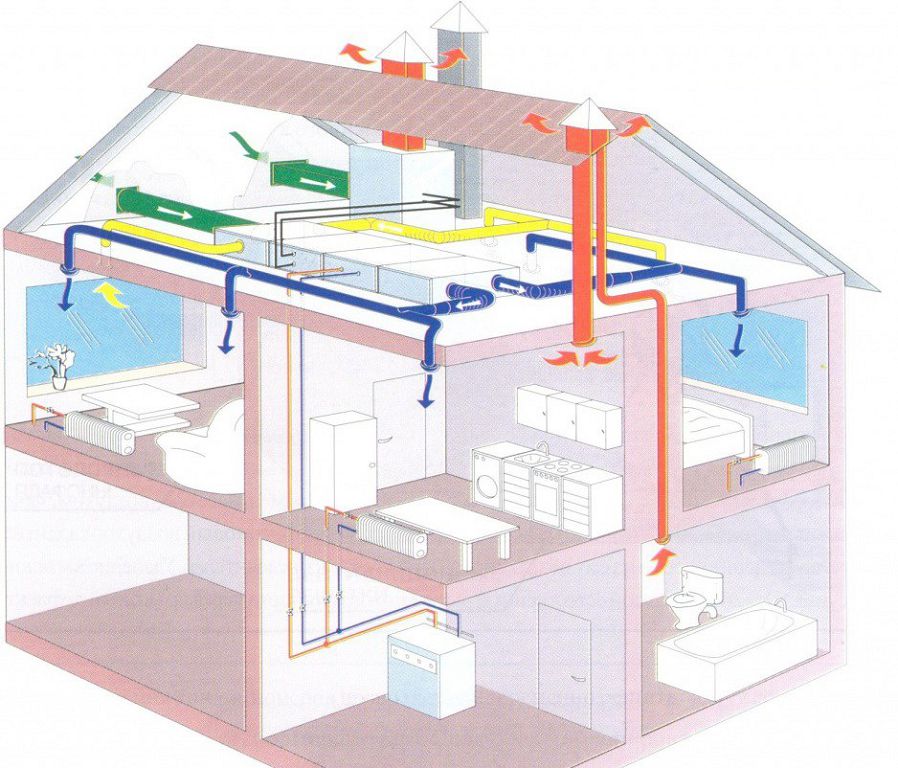
Passive house ventilation
Passive houses do not require heating! They are heated by the heat emitted by residents and household appliances, so each kilocalorie of heat must be stored and used rationally. Equipment that is successfully used for ventilation of brick houses is unacceptable here. Cold air currents must not be allowed inside, as well as the loss of precious heat.
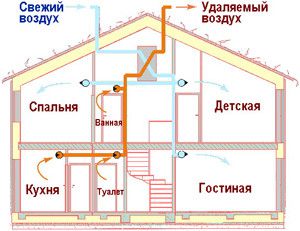
Therefore, ideally sealed passive houses are equipped with special supply and exhaust ventilation units with heat recovery. Energy efficient counterflow heat exchangers and fans with EC motors have been developed for passive houses. Such equipment returns up to 95% of the heat from the exhaust air and allows you to spend an average of 5 kilowatt / hour on heating per 1 sq. square meter of the house per year. One of the most important requirements for the ventilation of a passive house is the very quiet operation of the equipment.
Ground heat exchangers (heat pumps) are a good addition to the energy efficient ventilation of a passive house. Devices receive heat directly from earth or water. The air that has passed through the underground heat exchanger, even in winter, has a temperature of at least 17 degrees. In summer, the hot outside air is cooled in the same way. Therefore, in passive houses there is always a comfortable temperature.
Learn more about what an energy efficient home is and how to build one in the video:




Here you write that ventilation of a passive house is beneficial and makes an ideal climate. Why, then, isn't everyone using it?
Because this ventilation system must be designed even before the construction of the house, taking into account all premises and building materials.
As a rule, it is almost impossible to make such a system in an existing house.