Supply and exhaust ventilation in the garage
For the "home" of your car, your favorite "auto house", fresh air is as necessary as for our own apartment. But how to arrange proper ventilation of the garage? For this it is necessary to solve several basic questions.
Choosing a garage ventilation method
Garage ventilation is:
- Natural;
- Combined;
- Mechanical.
Natural garage ventilation is always preferred as it is the easiest DIY way to circulate air.
Combined ventilation, also called exhaust ventilation, is the removal of old air from the garage through the intake openings using a fan.
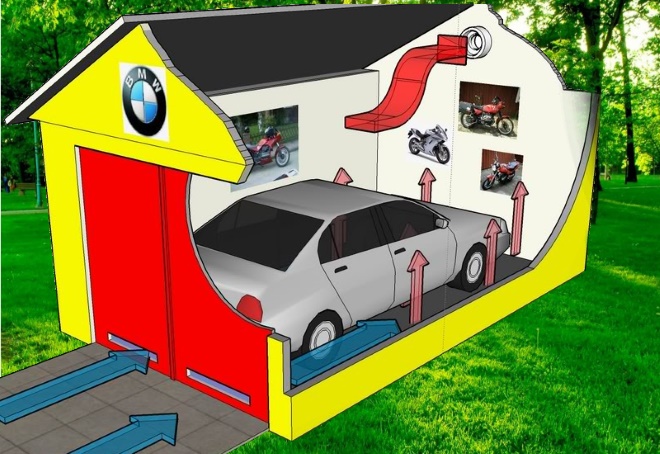
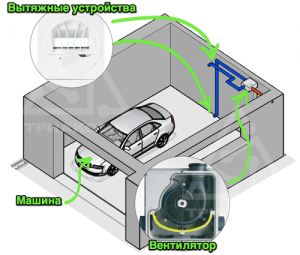
Mechanical - the most correct ventilation of the garage - creates artificial air exchange with the help of special supply units and air mass output devices through a two-channel system.
The air exchange system always depends on the owner's wallet and the architectural parameters of the garage. If it has a viewing niche or even a cellar, then in all these recesses it is necessary to provide for an air flow so that the supply ventilation device in the garage excludes spoilage of stocks for the winter.
How to draw up a diagram of exhaust and supply ventilation in a garage?
At the design stage of the garage, it is necessary to develop such a scheme in which the holes in the wall of the room, in the cellar / pit and in the basement will appear.
The height, area and number of cars in the garage are taken into account. Further, in this diagram, it will be necessary to mark the underground and surface location of the pipelines, as well as to consider all possible paths of the air vortex.
Natural ventilation of the garage, like artificial ventilation, uses a two-channel scheme. For an artificial one, sometimes one hole is enough. But still, it is advisable to do two. To calculate the diameter of the ventilation holes, you need to adhere to the following pattern: 1 m2 of the garage is equal to 15 mm of the pipe diameter.
That is, if the exhaust ventilation system in the garage is 10 m2 in area, then the pipes can be safely taken with a diameter of 150 mm.
There is another method used for the calculation: 0.3% of the total garage area is taken and equated to the area of all ventilation holes. This formula is best used for single-channel mechanical garage air exchange.