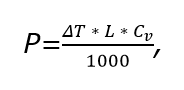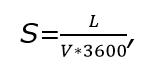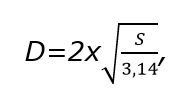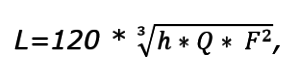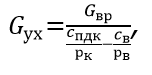Industrial technologies are usually associated with the release of dust, harmful substances, heat or moisture. Others require the creation of certain microclimatic conditions. Ventilation of industrial buildings should provide conditions for the work of employees, equipment and solving technological problems. And at the same time, comply with environmental and sanitary safety standards.
- Industrial ventilation requirements
- Types of industrial ventilation
- Industrial ventilation equipment
- Emergency ventilation of industrial buildings
- Calculation of industrial ventilation
- Calculation of air curtains
- Calculation of ventilation hoods
- Calculation of the ventilation exhaust chamber
- Onboard suction and their calculation
- Installation of industrial ventilation
- Maintenance and cleaning of industrial ventilation
Industrial ventilation requirements

Industrial ventilation systems are designed to handle large air volumes, high speeds and pressures. When calculating the ventilation system of an industrial building, it is necessary to take into account a number of mandatory requirements:
- Sanitary and hygienic. Harmful discharge is localized and removed as quickly as possible, a comfortable temperature for personnel is maintained at the workplace;
- Acoustic. The noise emitted by the equipment must comply with the accepted standards;
- Firefighters. Industrial ventilation components for premises are selected and installed strictly taking into account fire safety requirements;
- Operational. When installing industrial ventilation, the need for inspections, cleaning and repairs in the future is taken into account;
- Energy saving. The equipment should provide maximum effect with minimum energy consumption;
- Environmental. No industrial emissions should reach the environment.
Types of industrial ventilation

There are four types of industrial ventilation:
- General exchange. The entire volume of room air is involved in the process.
- Local. Serves a zone allocated from the general area.
- Local. Pulls emissions directly from where they originate.
- Combined. Used if one type is not effective enough. Example: a car spray booth, in which a local blowout is installed directly from the painting site and a general exchange system in the room. This combination prevents the spread of paint mist and solvent vapors.
A number of technological processes require special types of ventilation systems:
- technological;
- anti-smoke;
- emergency.

The listed systems can operate on natural or forced draft.
With natural draft, ventilation of an industrial enterprise is provided by gravity and wind, while forced by a variety of mechanisms, mainly fans.
The quality and intensity of natural industrial ventilation depends on weather conditions, as well as the presence of slots and special openings in the vertical fences of the building.
To induce traction, deflectors are often used, and air exchange is activated due to aeration.
With a forced system, air masses move along specially equipped air ducts due to the work of mechanisms. Such ventilation of an industrial premises can be exhaust, supply or supply and exhaust.
The installation height of the supply air devices is 1.5 - 2.0 meters from the floor level, and the exhaust devices as high as possible to the ceiling.
If it is necessary to remove large volumes of air, supply and exhaust industrial ventilation is installed.
The content of harmful components in the air removed by local systems is higher than in the air removed by supply and exhaust industrial ventilation. Therefore, as a ventilation of industrial buildings, local systems are more efficient.
Industrial ventilation equipment

General ventilation performs the function of purifying the air by diluting the polluted air with clean air. It works according to the inflow-blowout scheme and allows you to filter the exhaust air.
Air is supplied and removed by ejectors or fans through air ducts. To collect dust, dust and gas receivers or filters are equipped. The air is heated by air heaters and cooled by spraying moisture. It is fed into the workshop through the supply nozzles.
Local ventilation of an industrial enterprise creates the necessary microclimate in one or several separate areas.
The following settings are used:
- air shower;
- air curtains and air-thermal curtains;
- air oases;
- zone ventilation;
- fume hoods;
- protective and dustproof casings;
- onboard suction;
- exhaust umbrellas;
- suction panels;
- ventilation installations.
Emergency ventilation of industrial buildings
Emergency ventilation is used in industrial buildings and premises in case of emergency emissions of hazardous or explosive substances.
Emergency ventilation is started remotely. The equipment used is backup and main communications of general industrial ventilation, as well as local suction units that operate only in emergency mode.
The height of the emergency exhaust equipment placement depends on the specific weight of possible emissions. Supply emergency systems are not provided.
Calculation of industrial ventilation

Requirements for the design and calculation of industrial ventilation depend on the nature of the production. The standards are developed for each type of production and are indicated in specialized reference books.
The air exchange rate is one of the first indicators required for calculating industrial ventilation of general exchange type. With its help, the performance of the equipment is determined by multiplicity:
P = n * h * s,
Where n - the required frequency of air exchange,s - the area of the room,h - the height of the room.
The power of the heater must be determined when calculating the ventilation system of an industrial building:
here T - air temperature difference at the inlet and outlet (from the reference book),L - system performance,Cv- volumetric heat capacity of air.
The cross-sectional area of the ducts is calculated as follows:
here L - equipment performance,V - the speed of air movement in the system.
Now the diameter of the duct can be calculated:
S - cross-sectional area of the duct.
The calculations also take into account:
- types of air pollution;
- simultaneous operation of machines;
- radius of harmful emissions;
- air consumption.
For the design of general ventilation of an industrial building, general indicators are sometimes sufficient. But local and local systems require elaboration of every element in every workplace.
Calculation of air curtains
When calculating air-thermal curtains, the following indicators are determined:
- mass air flow;
- the area of the air opening covered by the curtain;
- curtain air temperature;
- relative heat loss of the curtain;
- width of the slotted curtain outlet;
- air speed;
- heat output of the curtain.
Calculation of ventilation hoods
The main indicator of the fume cupboard, determined when calculating the ventilation system of an industrial building, is the amount of exhaust air.It depends on the toxicity and temperature of the discharge and is calculated using the formula for reactions with heat absorption (endothermic):
L = u * F * 3600
Where u - permissible air speed, the value is taken from the reference book.
The air consumption in the fume cupboard during exothermic reactions (with heat release) depends on the cupboard configuration and the heat generated:
Where h - opening height,Q - heat generated, W,F - the area of the opening.
Calculation of the ventilation exhaust chamber
It is necessary to calculate how much harmful substances are released into the air and how much must go to ensure the safety of workers. The calculation of this element of industrial ventilation is carried out for each hazardous component separately:
here Gvr - the volume of harmful substances released in the chamber,Spdk and St- the concentration and maximum permissible concentration of this substance at the location of people,PB and Pk - the density of air at the workplace and in general in the chamber.
The maximum permissible concentration of hazardous substances in the chamber is the maximum amount that does not cause occupational diseases for people.
Onboard suction and their calculation
You can calculate these elements of industrial ventilation manually using the formulas from the textbook of V.N.Bogoslovsky or take ready-made figures from the AZ-782 reference book.
Installation of industrial ventilation

The installation of industrial ventilation differs in materials and scale of work, as well as high requirements for components and assembly quality. Therefore, many companies take over the entire process from cutting industrial ventilation fittings to commissioning. This is the only way to guarantee a truly first-class result.
When installing ventilation of an industrial facility, at least 70% of the area of the air ducts must fall on straight sections. This avoids performance losses.
When installing industrial ventilation, usually use metal air ducts of rectangular or round cross-section. Air ducts and fittings for industrial ventilation, cut from 1 mm thick sheet steel, will not melt at an air flow temperature of up to 80 degrees and high humidity.
All work on the installation of industrial ventilation is regulated in SNiP 3.05.01-85. Here there is information about the quality of the material, the maximum permissible heating temperatures, the method of rolling (sheet metal), and more.
If the planned type of industrial ventilation will transport gas mixtures, air ducts with a wall thickness of at least 1.5 mm made of metal or metal-plastic are installed.
Requirements for the placement of air diffusers:
- The supply air streams do not intersect with the local suction flares.
- It is not allowed to mount air distributors above technological lines or equipment.
- Supply air ducts should not interfere with the main production.
- Air distributors are installed above aisles and places of work so that there is a minimum distance from the area where people are located to the distributor.
- The type of air diffusers is selected in accordance with the specifics of the production technology.
Maintenance and cleaning of industrial ventilation

Specialists carry out periodic diagnostics, testing, repair, adjustment, replacement of filters of various types and control of air indicators in the ventilation system of an industrial enterprise. Sophisticated ventilation equipment is a source of increased danger, since untimely cleaning of the ventilation chamber from dust can lead to a fire at an industrial enterprise, and dirt in the air ducts can be a source of infection with pathogenic microbes for hundreds of people.
The frequency of maintenance and cleaning of industrial ventilation depends primarily on the intensity of use. So, at a furniture assembly factory, cleaning and inspections are carried out once every 6 months. Whereas in food processing plants, the supply and exhaust ventilation is cleaned and disinfected every month.
The organization of service, diagnostics and cleaning of ventilation of an industrial enterprise is the responsibility of the management. After all, the health and ability to work of employees, the operation of equipment and the state of the environment often depend on the cleanliness of the air in the workshops.
Cleaning and maintenance of industrial ventilation are allowed only to companies that have a special license, certificates and approvals.
And here is what the ventilation cleaning process is like in a large plant: