The creation of an optimally working air duct system is impossible without aerodynamic calculations. These data allow you to select the diameter of the section, the power of pipes and fans, the number of branches, materials. Modern requirements are regulated by the set of rules of SP 60.13330.2012, as well as in GOST and SanPiN. The calculation is performed according to a strictly defined algorithm using well-known formulas. To accurately determine all the criteria, you can use the help of specialists or calculate the parameters yourself.
Types of air ducts

Modern air ducts can be classified according to several parameters: installation method, material of manufacture, sectional shape.
For installation, external and built-in channels are distinguished. The first ones are installed over the walls and are visible to the eye. Internal ones are mounted in the walls and structures of the house.
The pipe material may vary. These are various metals (copper, steel, aluminum) and plastic. Metal products are distinguished by their strength and reliability, but their installation is more difficult. Plastic devices are easier to install, but they are not used at high temperatures.
The section can be rectangular and round. Rectangular pipes are versatile, but eddies can be created at the corners. Round models do not have this disadvantage.
Step-by-step aerodynamic calculation of air ducts
The work includes several stages, at each of which a local problem is solved. Based on the data obtained, various parameters of the air ducts are calculated.
The main tasks of the ventilation system equipment:
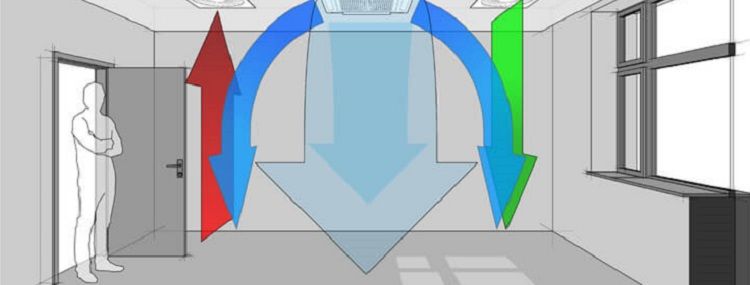
- Fresh air intake from the street and its transfer inside the premises. An additional function is heating air masses in winter and cooling in summer.
- Air purification from dirt, dust and lint.
- Decrease in sound pressure.
- Uniform distribution of fresh air throughout the apartment.
- Removal of exhaust air and its discharge to the street.
The ventilation system is characterized by the following parameters:
- Working body. In this case, it is air. It is characterized by density, dynamic viscosity, kinetic viscosity. These values depend on the temperature of the working fluid.
- Working fluid speed.
- Local aerodynamic resistance of air ducts.
- Pressure loss.

Algorithm for carrying out aerodynamic calculations:
- Development of an axonometric diagram of the distribution of air masses through the channels. On its basis, the best calculation method is selected, taking into account the peculiarities of ventilation.
- Carrying out aerodynamic calculations along the main and additional lines.
- Selection of the geometric shape and cross-section of pipes. Determination of technical characteristics of fans and heaters. Determination of the possibility of installing fire extinguishing sensors, automatic control of ventilation power.
These are the main stages of calculations.
All received data can be collected in a table, and then select materials to create a channel.
Calculations

The main purpose of the aerodynamic calculation is to determine the resistance to air circulation in each part of the system.
There are direct and inverse problems of aerodynamic calculation.Direct deals with the design of ventilation systems and consists in determining the cross-sectional area of each section of the system. The inverse problem is solved by determining the air flow rate in a given area.
For the calculation, it is necessary to determine the frequency of air exchange. This is a quantitative characteristic of the system's operation, which shows how many times the air in the room has been refreshed per hour. The indicator depends on the characteristics of the room, its purpose.
The creation of a system diagram in axonometric projection is done on a scale of M 1: 100. It is necessary to apply air ducts, filters, noise mufflers, valves and other ventilation components to the diagram. Based on the data obtained, the length of the branch, the flow rate at each section, is determined, and the resistance of the duct is calculated.
After that, the optimal pipe laying line is selected. This is the longest chain of consecutive sections.
If there are several lines in the circuit, the main one is the one in which the flow is higher.
Basic formulas for calculating
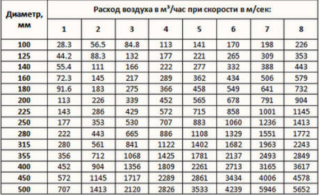
The duct cross-section can be round or square. It is calculated by the formula F = Q / vwhere under Q the air flow rate is indicated, and v - recommended air speed (reference value).
The diameter of the section is determined from the area Dif the pipes are round, or the height and width BUT and IN for rectangular. The values are rounded to the nearest larger standard and get BUTst and INst.
For rectangular ducts, the equivalent diameter is calculated using the formula DL = (2Ast*INst) / (BUTst + Bst).
The value of the Reynolds similarity criterion is calculated as Re = 64100 * Dst * vfactic... The coefficient of friction depends on this indicator, which is determined by the formulaλtr = 0.3164 ⁄ Re-0.25 at Re≤60000, λtr = 0.1266 ⁄ Re-0.167 at Re> 60,000.
Local resistance coefficientλm is selected from the reference book and then substituted into the formula for the pressure loss in the calculated area Р = ((λtr* L) / Dst + λm) * 0.6 * v2 fact. L - the length of the calculated section.
When all the losses are summed up, the total losses of the main line and the ventilation system are obtained. Based on these values, a fan is selected with a margin of 10%. From its characteristics, the efficiency is considered nand then the power N = (Qvent* Pvent) / (3600 * 1000 * n)... Here Qvent, Pvent - air flow and pressure generated by the fan.
The calculation of the pressure loss in the duct can be performed using the formulaDP = x * r * v2/2where r - air density, v - movement speed, x - coefficient of local resistance.
Possible mistakes

The calculation of the ventilation system is lengthy and consists of several stages, at each of which mistakes can be made. The most common problems are:
- Rounding of the cross-section of gas pipelines downward. Then there may be excessive noise or the impossibility of passing the required number of air flows per unit of time.
- Incorrect calculation of the length of the duct section. Leads to incorrect choice of equipment and an error in calculating the speed of movement.
The whole project requires careful and competent calculation of aerodynamics. If it is impossible to calculate the system yourself, you can use an online calculator or seek help from specialists.